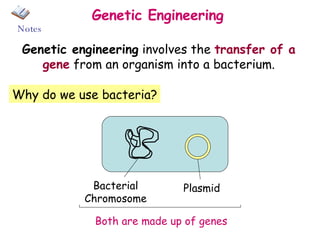
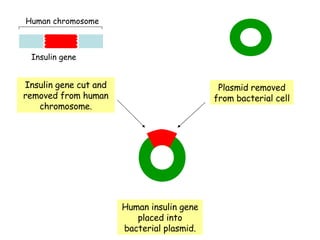
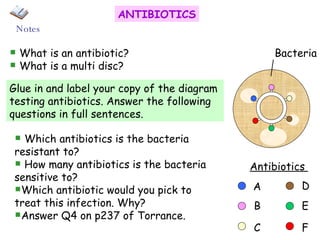
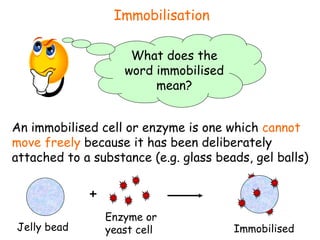
The document discusses using genetic engineering to produce human insulin in bacteria. It describes how the human insulin gene is inserted into a bacterial plasmid, which is then placed into bacterial cells. The bacterial cells grow and multiply, producing more plasmids and insulin. The human insulin is then collected and purified from the bacterial cells.