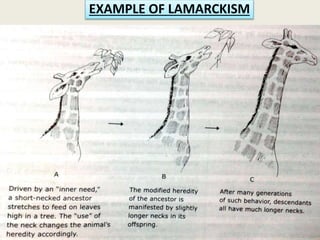
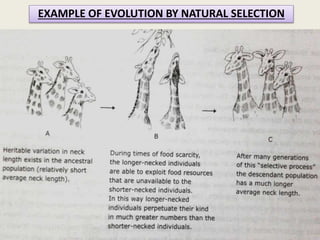
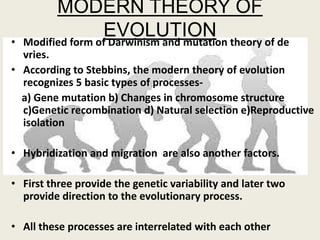
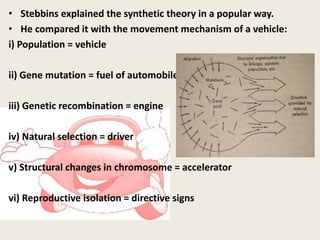
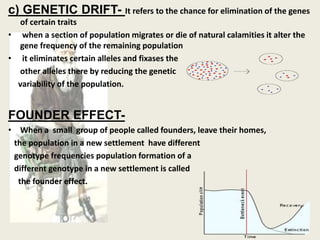
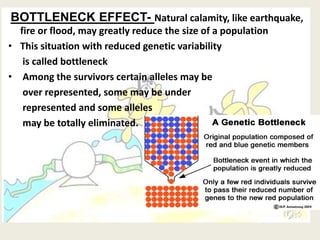
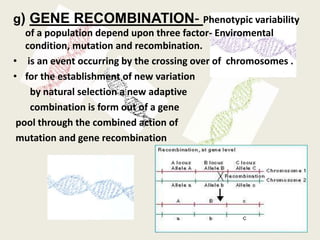
The document presents a comprehensive overview of the modern concept of evolution, discussing various historical theories including Lamarckism, Darwinism, and the mutation theory proposed by De Vries. It outlines key mechanisms of evolution such as natural selection, genetic variation, and reproductive isolation, along with the contributions of notable scientists to this field. The modern synthesis combines these ideas to illustrate how genetic mutations and natural selection interact to drive evolutionary change.