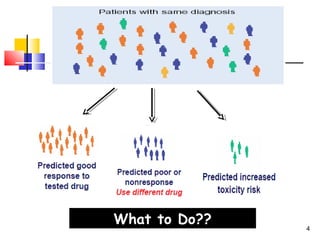
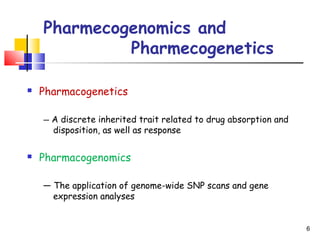
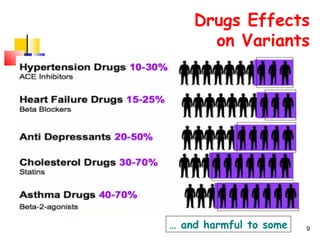
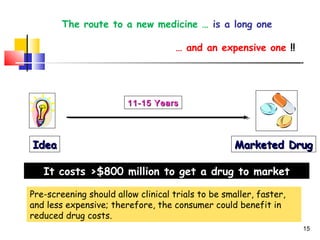
This document discusses personalized medicine and pharmacogenomics. It begins by noting that current drug treatment is only effective for 60% of patients, with 40% experiencing poor effects or no effect at all. It then introduces pharmacogenomics as the application of genomics to understand how genes influence individual responses to drugs. The document outlines several ways that pharmacogenomic research could improve drug development and clinical practice, such as identifying genetic variants that influence drug metabolism and toxicity. It envisions that in the future, pharmacogenomic testing may allow for "made-to-order" drugs tailored to a patient's genetic profile. However, it also notes some bioethical challenges will need to be addressed for personalized medicine to be realized.