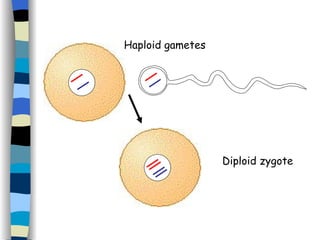
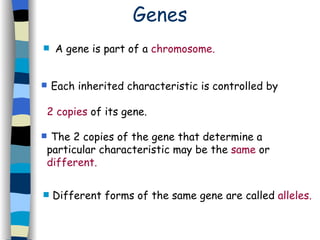
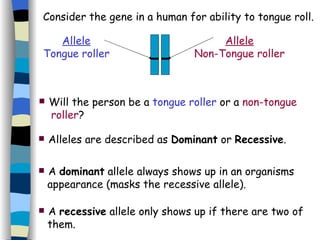
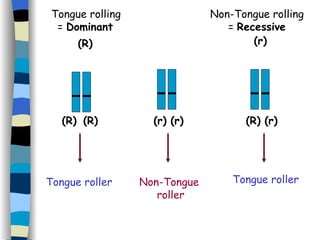
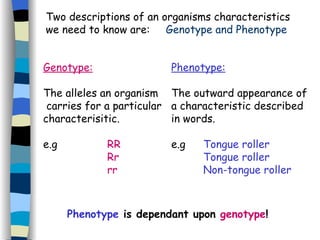
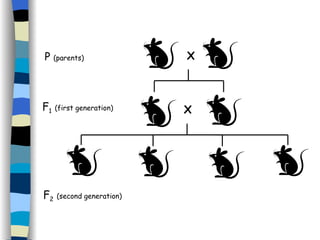
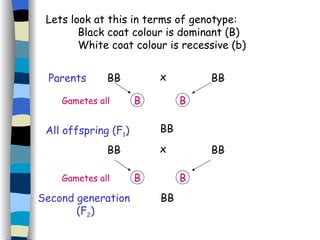
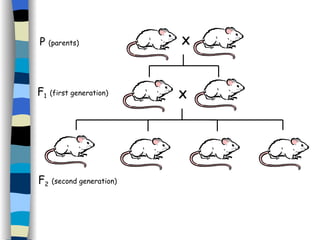
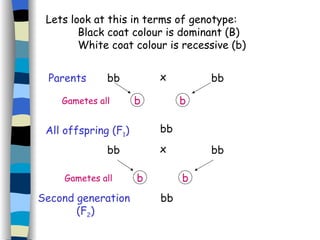
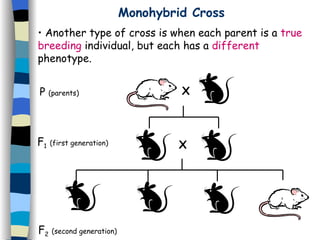
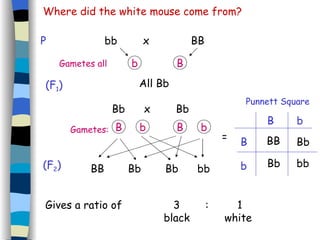
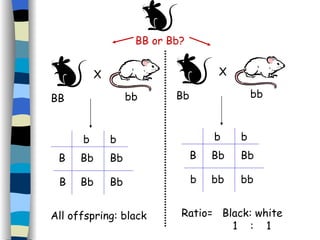
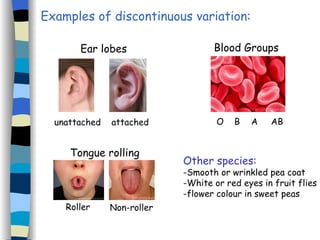
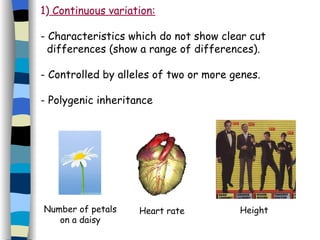
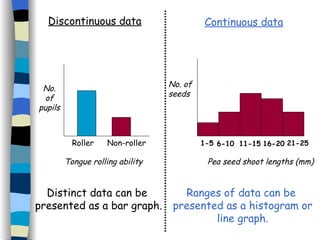
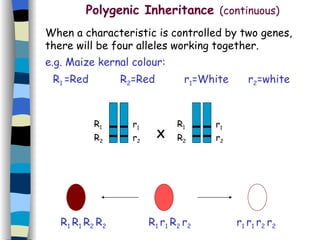
The document discusses genetic inheritance, including dominant and recessive alleles, genotypes and phenotypes, homozygous and heterozygous organisms, monohybrid crosses through generations F1 and F2, codominance and polygenic inheritance. It provides examples of inheritance patterns and uses Punnett squares to determine expected ratios of offspring genotypes and phenotypes from genetic crosses.