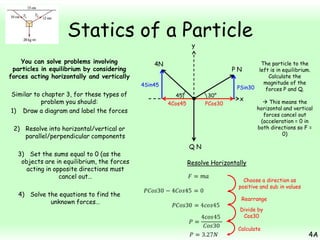
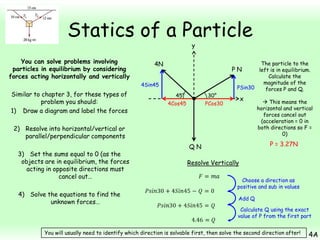
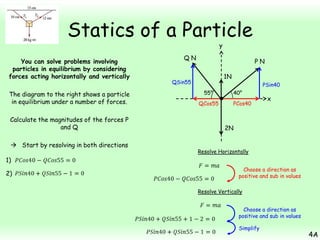
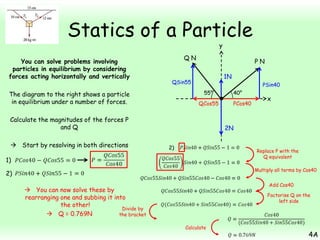
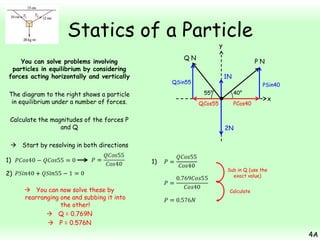
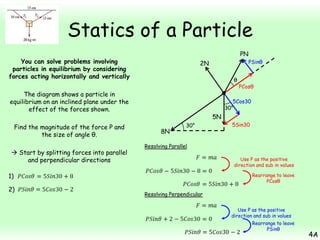
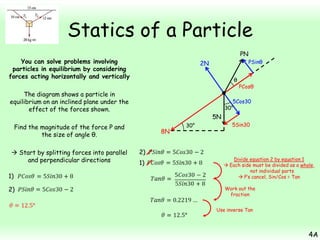
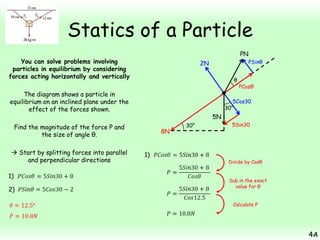
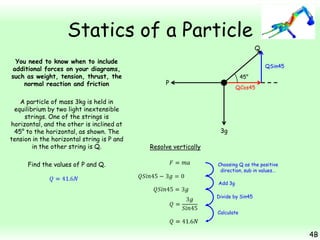
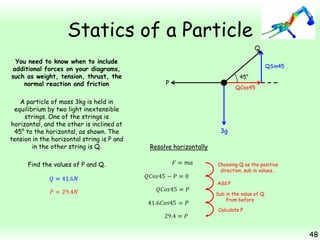
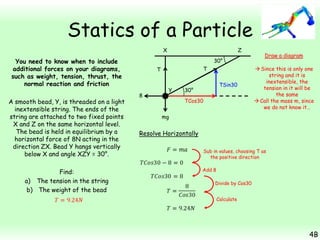
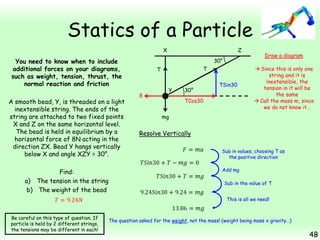
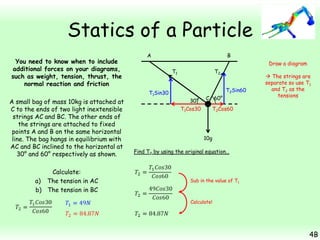
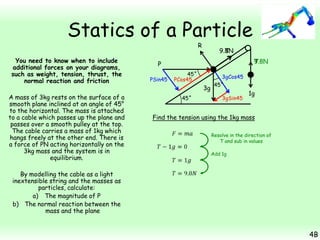
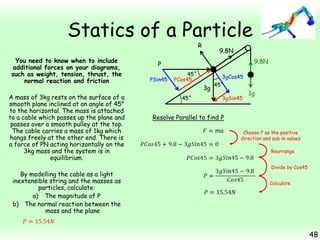
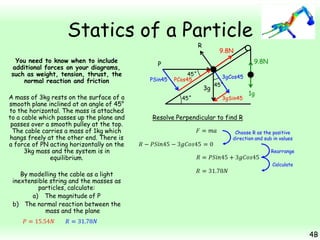
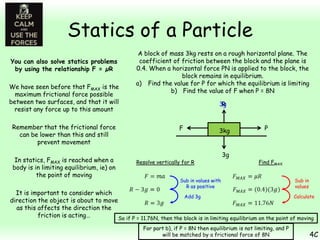
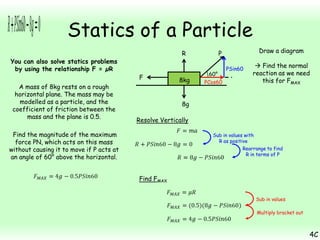
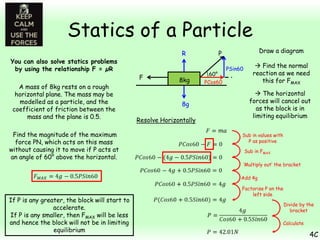
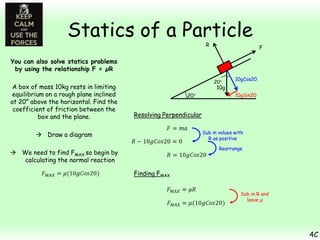
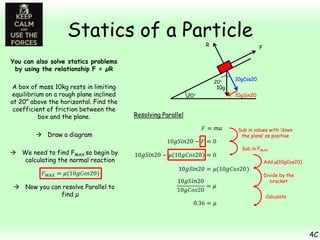
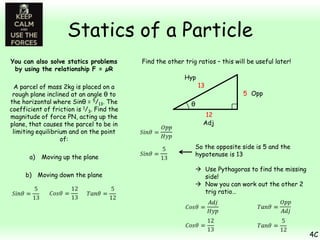
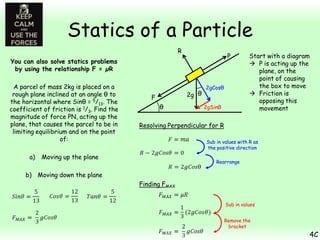
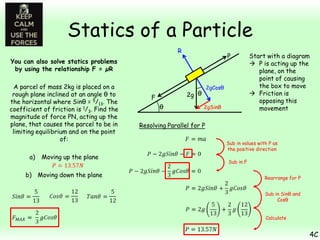
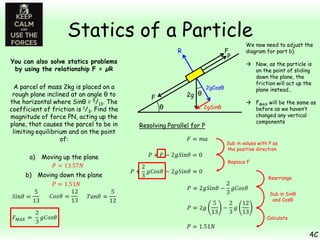
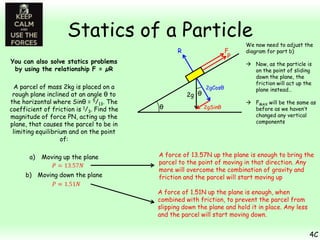
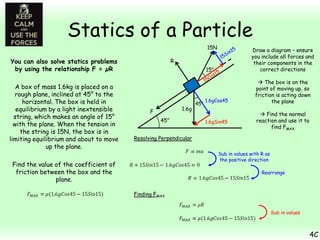
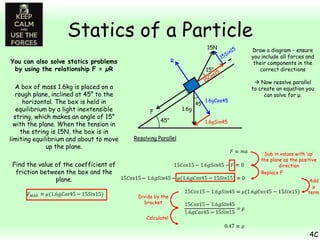
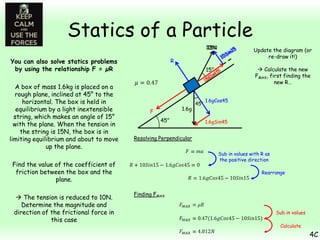
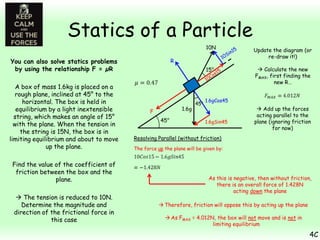
This chapter focuses on objects in static equilibrium, where the net force and net torque on the object are both zero. Solving static equilibrium problems involves drawing free body diagrams showing all external forces acting on the object, then resolving forces into components and setting the sums of forces in each direction equal to zero. Three examples are given of solving static equilibrium problems involving particles under the influence of multiple forces. The problems are solved by resolving forces into horizontal and vertical or parallel and perpendicular components, setting the component force equations equal to zero, and solving the equations to determine the magnitudes of unknown forces. Key steps include drawing diagrams, resolving forces, setting force sums to zero, and solving the resulting equations.