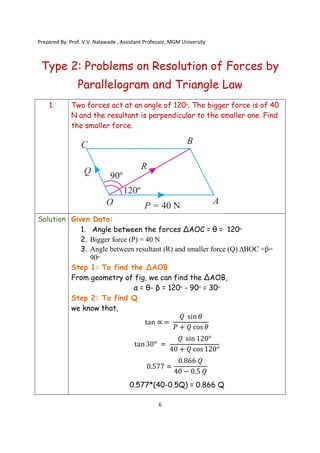
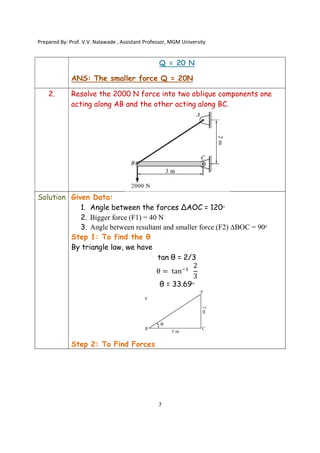
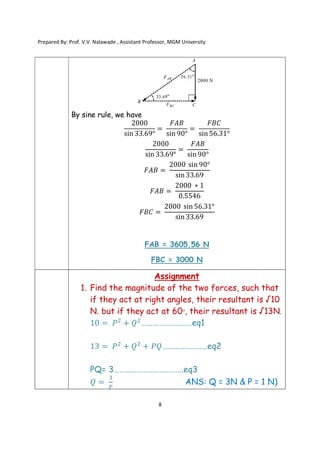
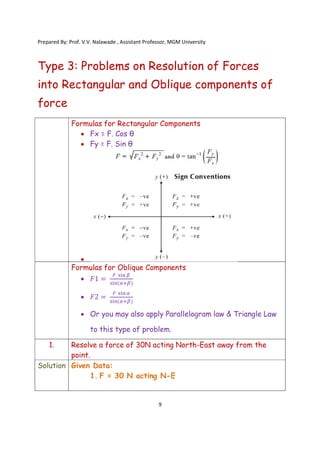
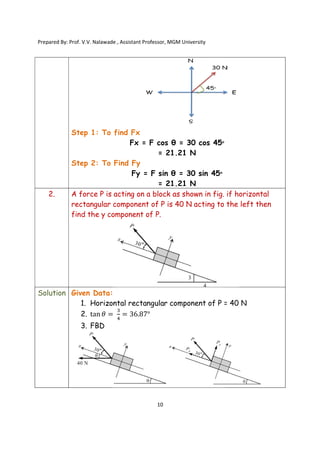
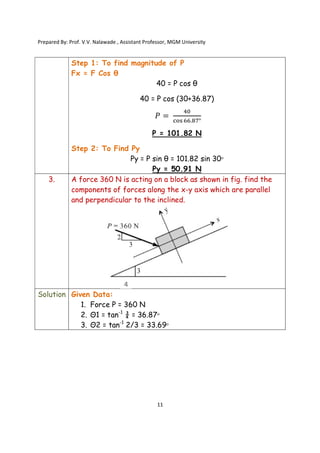
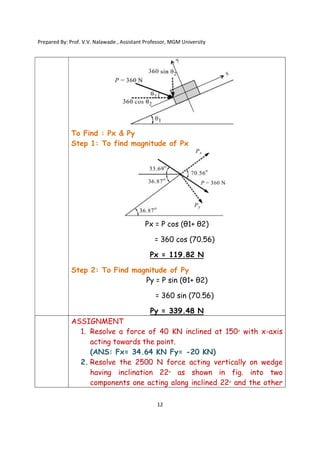
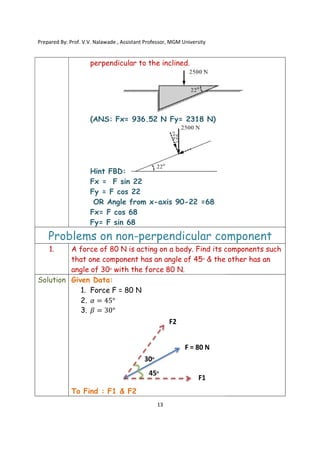
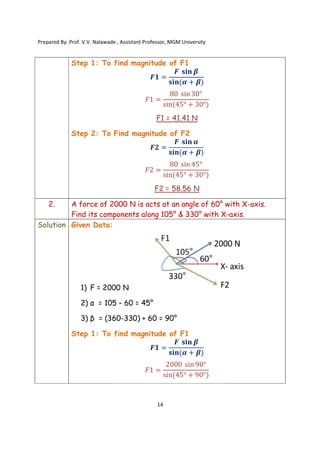
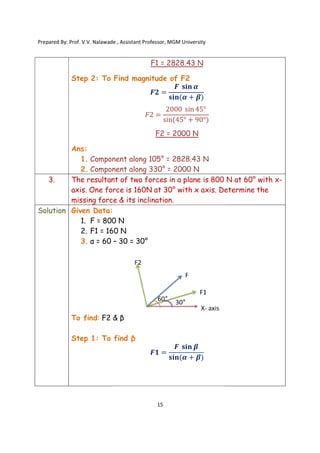
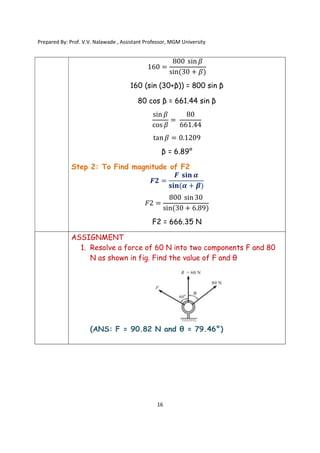
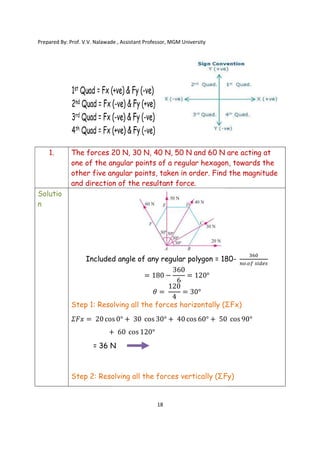
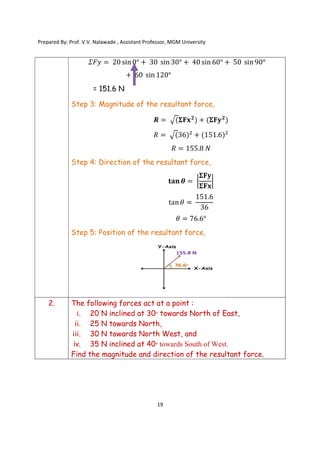
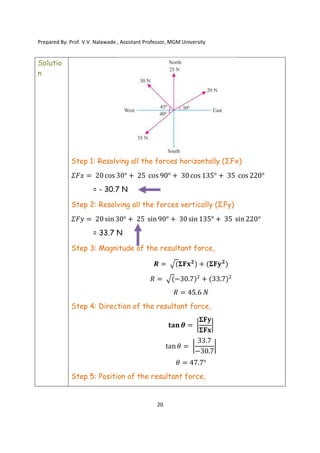
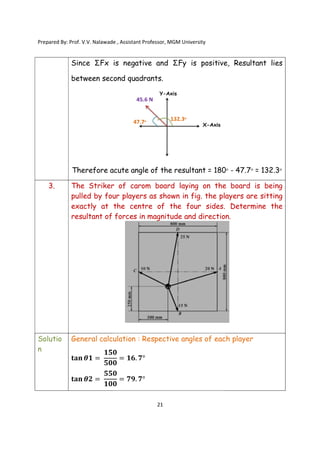
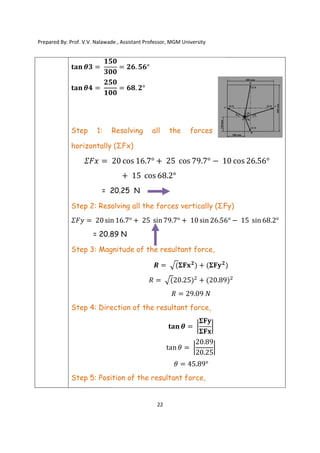
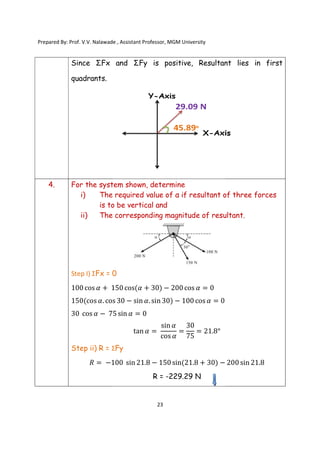
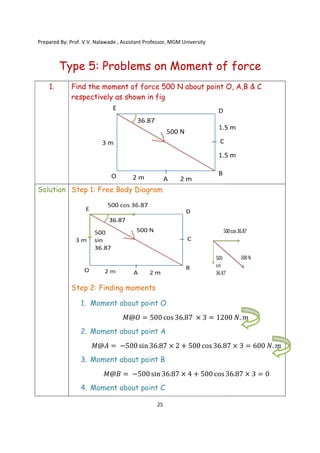
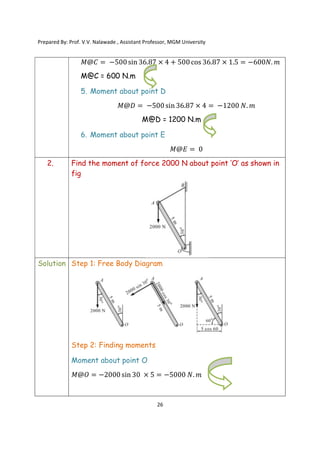
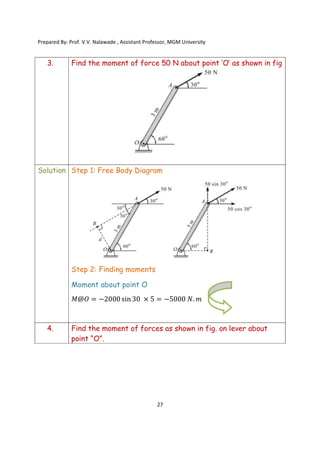
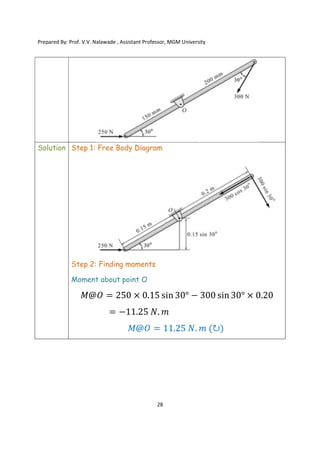
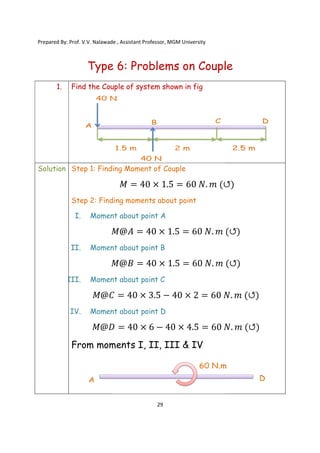
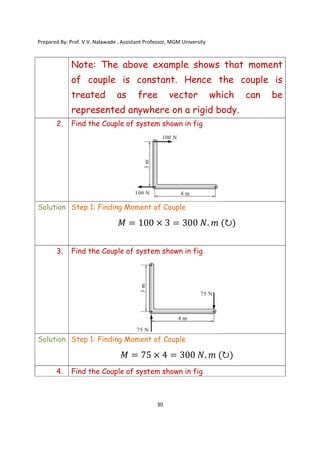
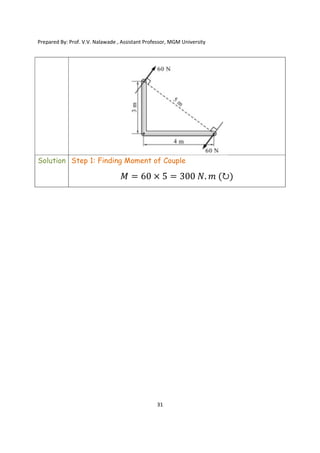
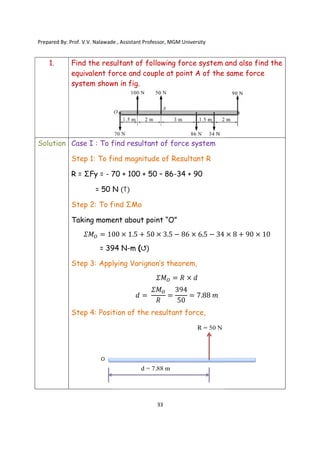
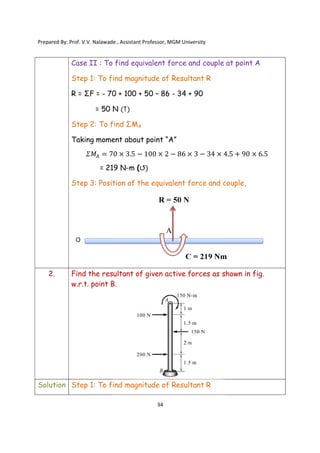
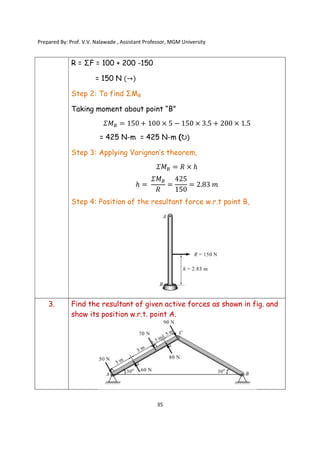
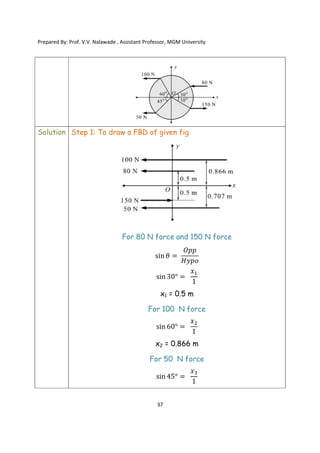
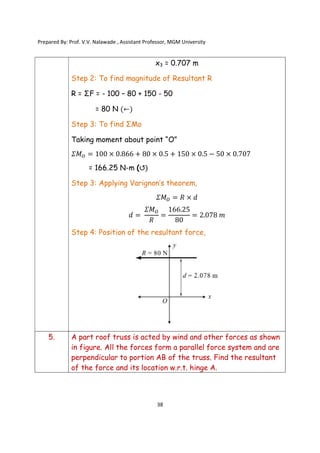
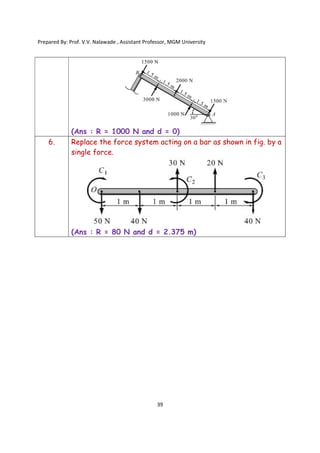
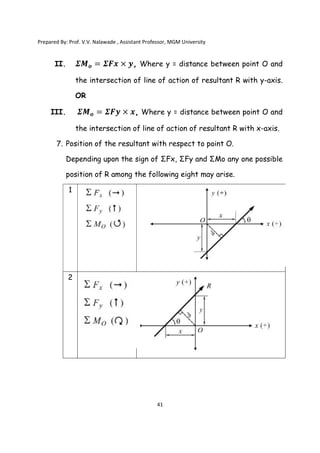
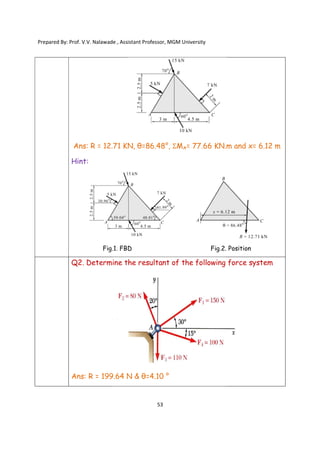
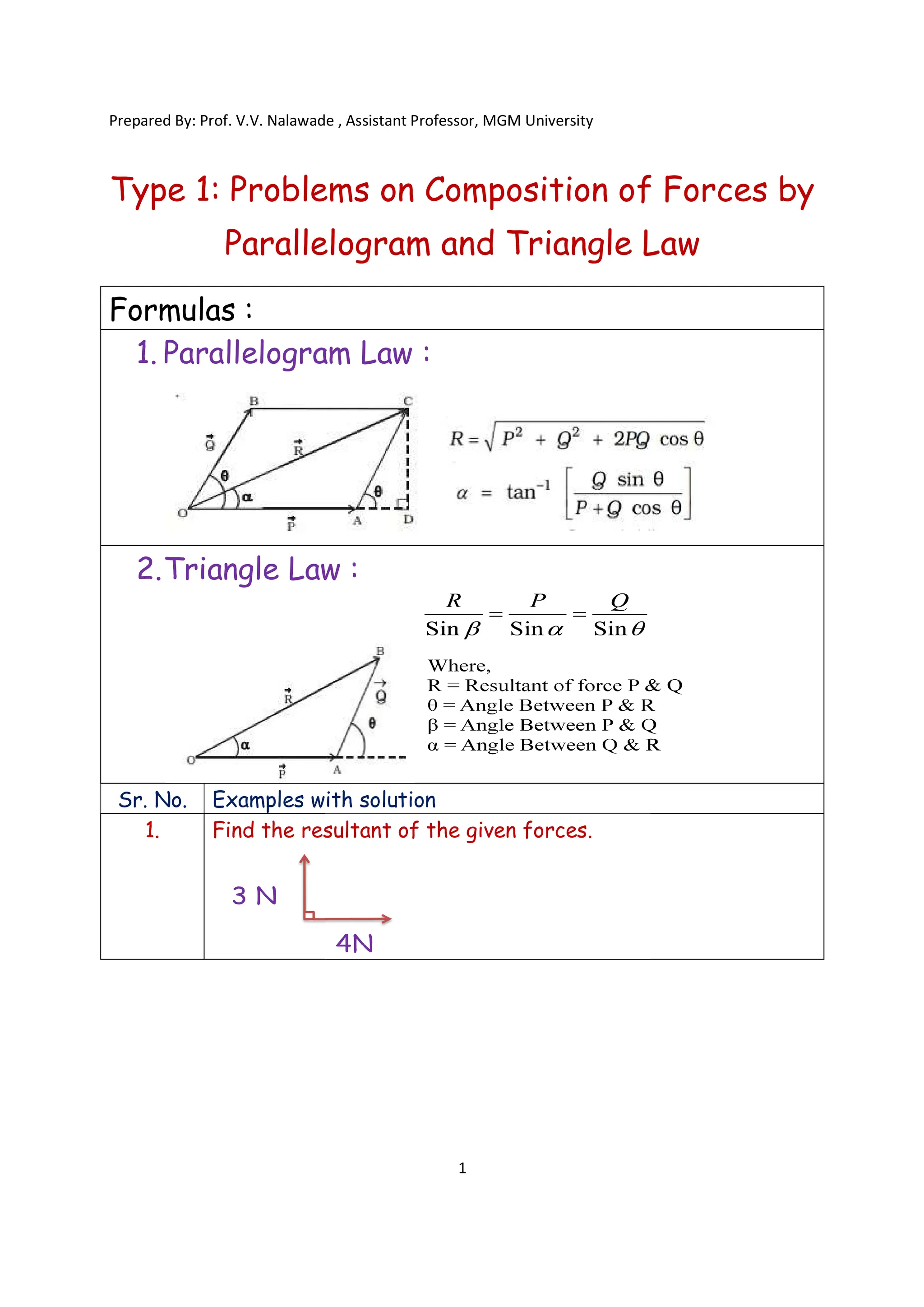
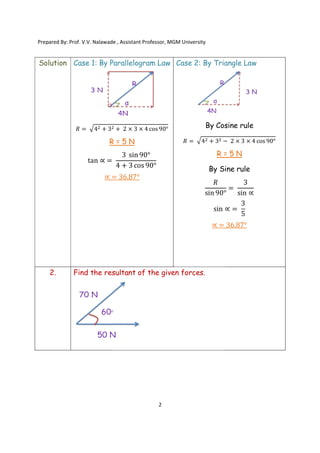
The document contains various problems and solutions on the composition and resolution of forces using the parallelogram and triangle laws. It covers multiple cases with detailed examples and computations, including resultant forces and angles. Prepared by Prof. V.V. Nalawade, the content serves as educational material on physics principles related to force compositions.
![Prepared By: Prof. V.V. Nalawade , Assistant Professor, MGM University
4
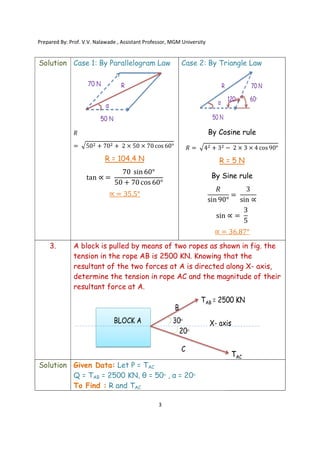
By using Parallelogram Law
Magnitude of resultant is given as
𝑅 = 𝑃 + 2500 + 2 × 𝑃 × 2500 cos 50°
Squaring on both sides
𝑅 = 𝑃 + 2500 + 2 × 𝑃 × 2500 cos 50°………………eqn
1
Direction of resultant is given by
tan 20° =
2500 sin 50°
𝑃 + 2500 cos 50°
Cross multiplication gives
[𝑃 + 2500 cos 50°] tan 20° = 2500 sin 50°
0.3639 P + 584.88 = 1915.11
𝑃 =
1915.11 – 584.88
0.3639
P = 3656.69 KN
Put value of P in eqn
1 we get
𝑅 = 3656.69 + 2500 + 2 × 3656.69 × 2500 cos 50°
R = 5601.22 KN
Final Answer:
1. Tension in Rope AC = 3656.69 KN
2. Magnitude of Resultant R = 5601.22 KN
Assignment:
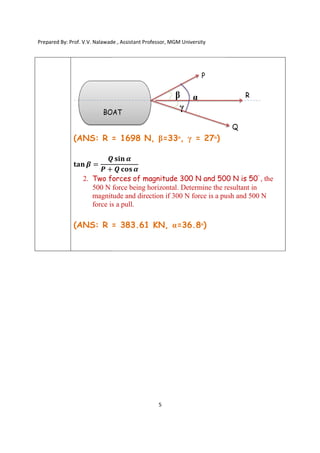
1. A boat is moved uniformly along a canal by two horses
pulling with forces P = 890 N and Q = 1068 N acting at
an angle α = 60ᵒ as shown in the fig. Determine magnitude of
the resultant pull on the boat and the angle β and γ as shown.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solvedproblemsonforcesystem-240328110705-688f382f/85/Unit-1-force-system-solved-problems-on-force-system-pdf-4-320.jpg)