Embed presentation
Downloaded 877 times
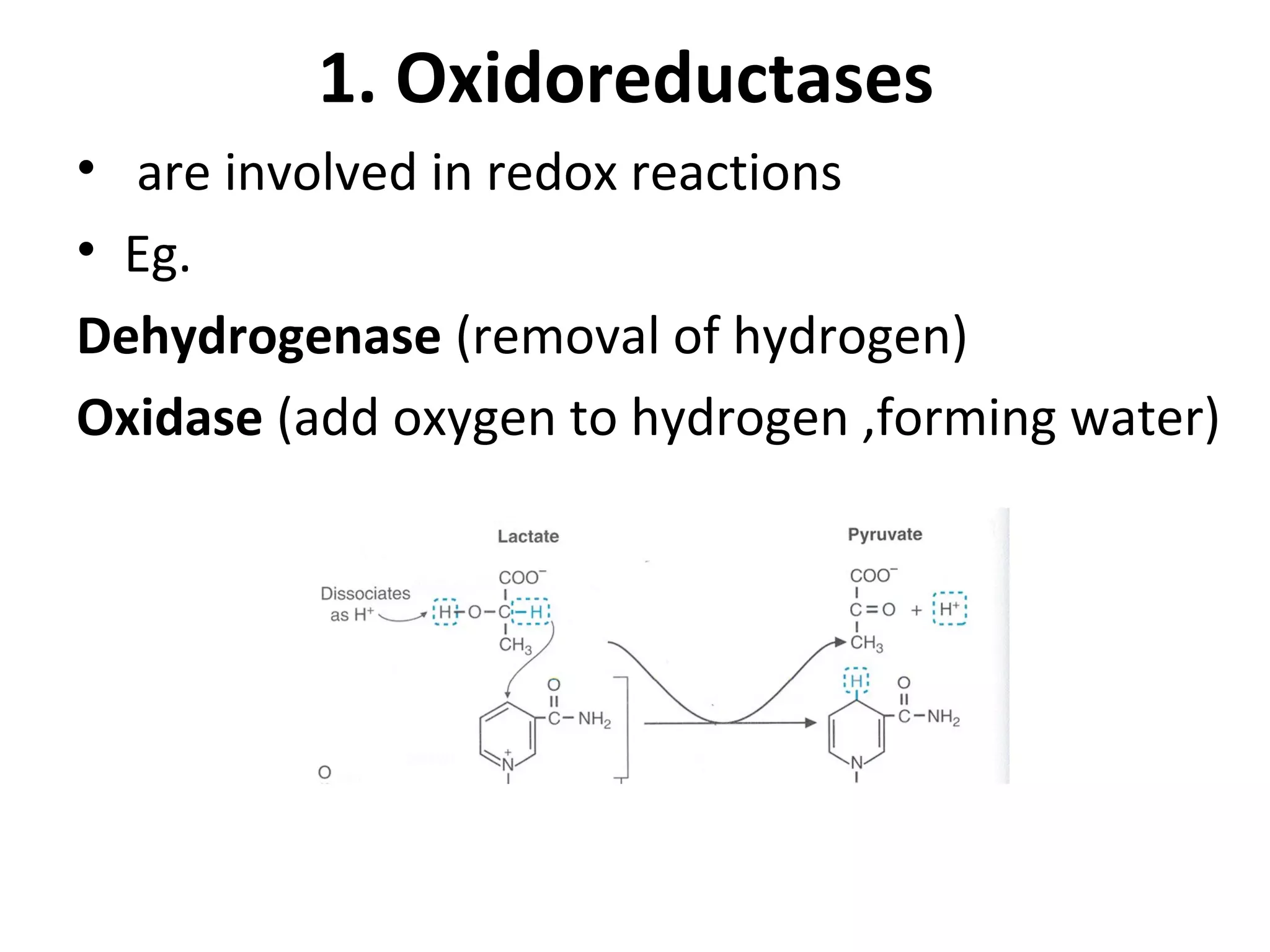
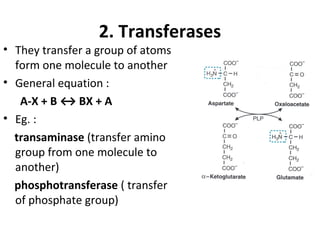


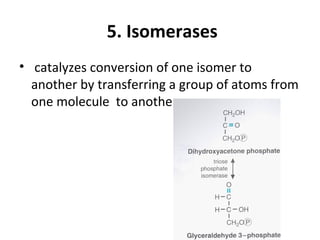

This document categorizes enzymes into six main classes based on their catalytic activity: 1) Oxidoreductases catalyze redox reactions such as dehydrogenation and oxidation. 2) Transferases transfer atomic groups between molecules, like transaminases transferring amino groups. 3) Hydrolases catalyze hydrolysis reactions by adding water, as seen in maltase breaking maltose into glucose. 4) Lyases break chemical bonds without water, such as decarboxylases removing carboxyl groups. 5) Isomerases catalyze conversion between isomers by moving atomic groups. 6) Ligases catalyze bond formation using ATP, for example DNA ligase in DNA synthesis.






