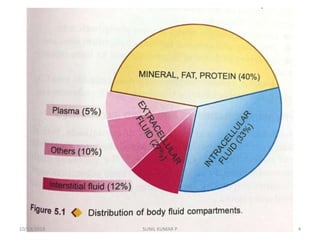
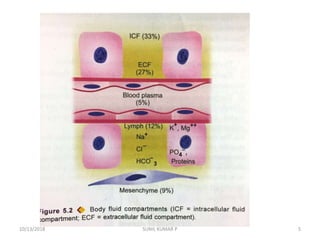
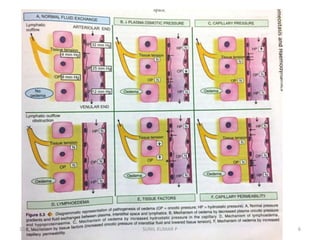
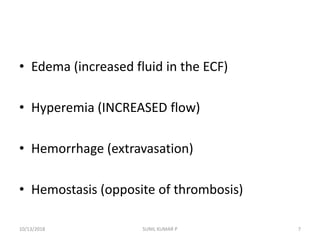
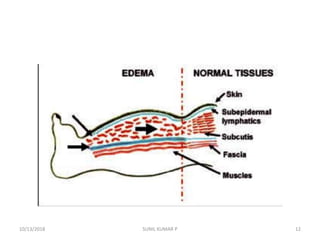
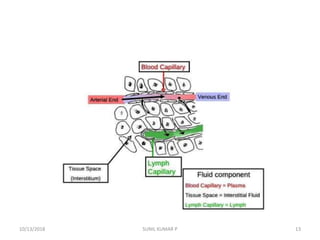
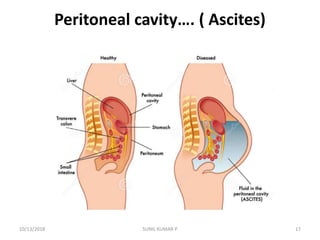
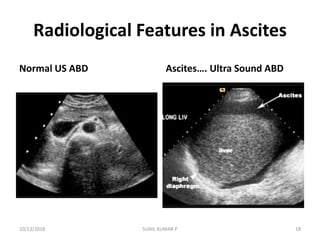
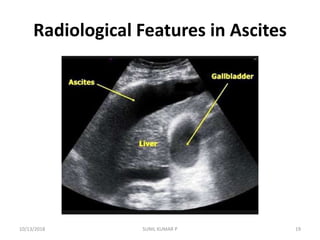
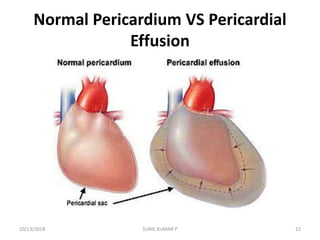
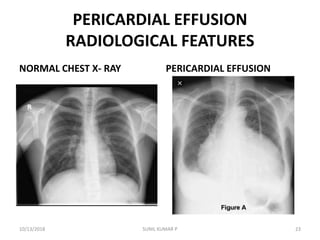
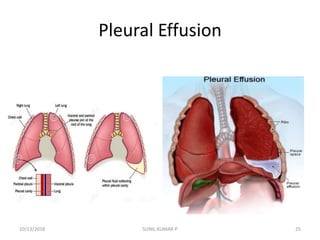
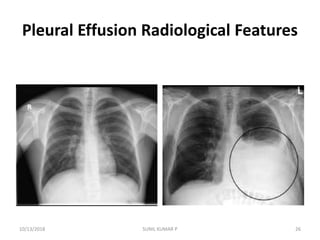
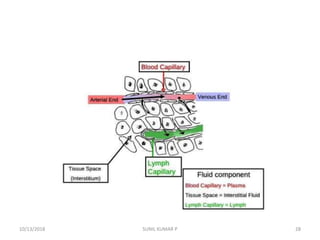
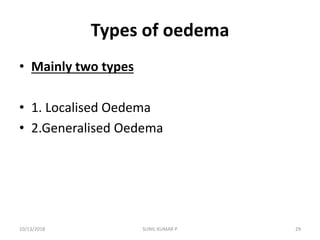
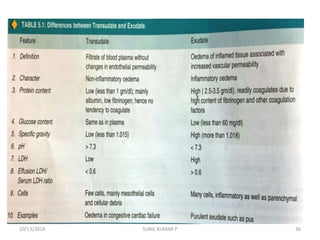
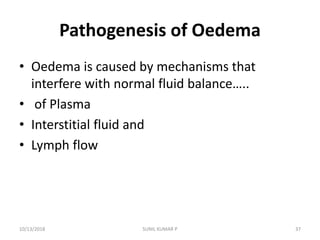
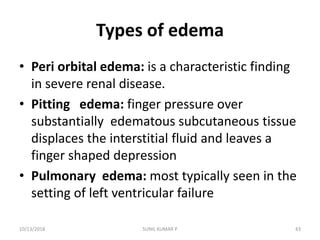
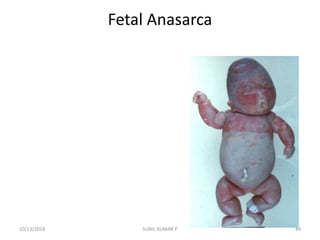
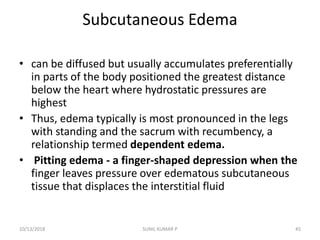
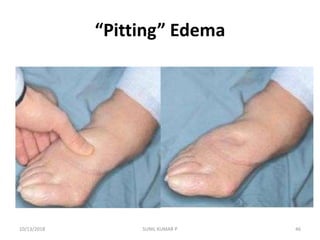
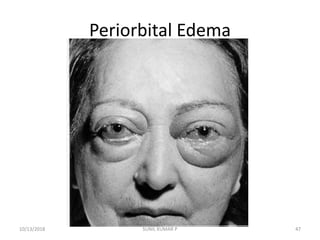
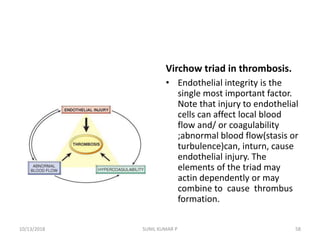
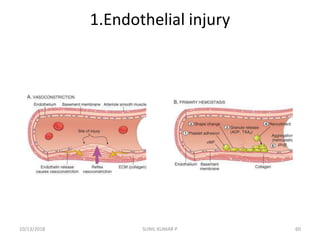
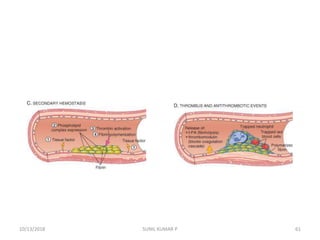
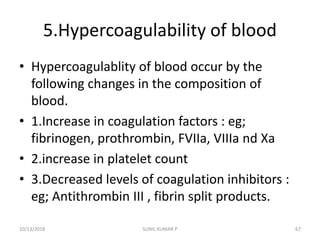
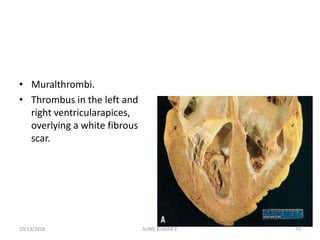
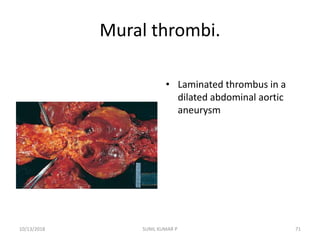
This document discusses hemodynamic disorders such as edema, thrombosis, embolism, and infarction. It focuses on edema, defining it as abnormal accumulation of fluid in interstitial tissues or body cavities. Edema fluid can be a transudate or exudate depending on its protein content. The document examines the pathogenesis of edema including increased hydrostatic pressure, decreased plasma oncotic pressure, lymphatic obstruction, sodium retention, and inflammation. It also discusses specific types of edema like pulmonary and cerebral edema.