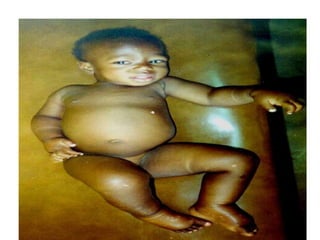
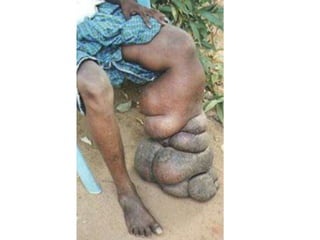
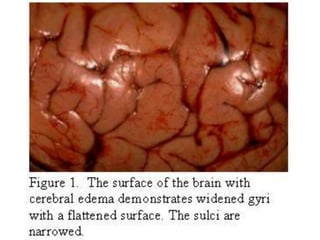
1. Hemodynamic disorders include edema, hemostasis, thrombosis, embolism, and shock. Edema is excess fluid in tissues and can result from increased capillary pressure, decreased plasma proteins, lymphatic obstruction, sodium retention, or increased capillary permeability.
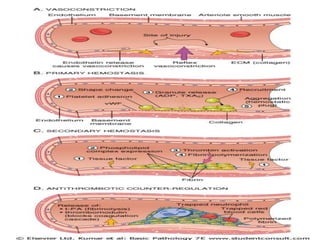
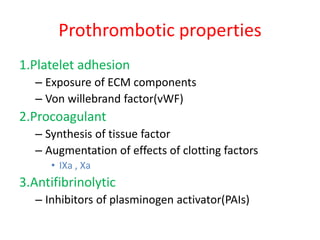
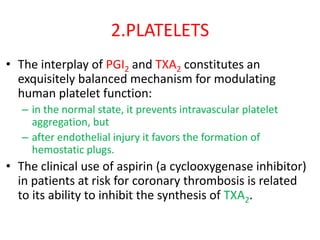
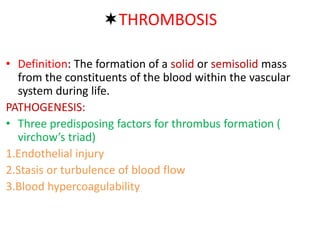
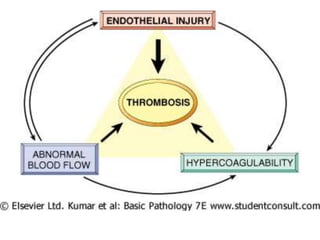
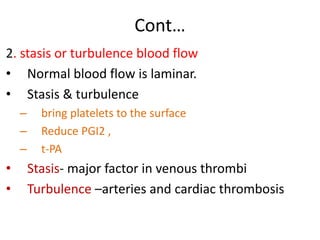
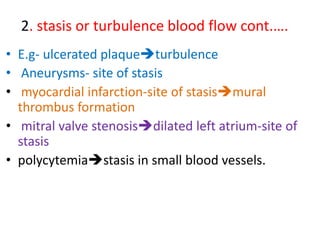
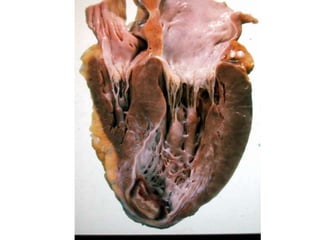
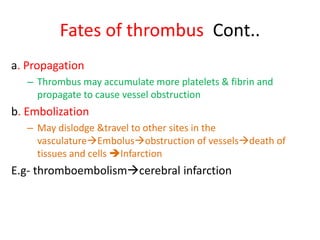
2. Hemostasis and thrombosis involve the vascular wall, platelets, and coagulation cascade. Thrombosis occurs when the clotting process is inappropriately activated, forming clots in uninjured vessels.
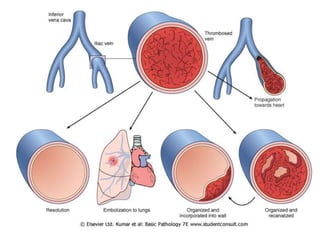
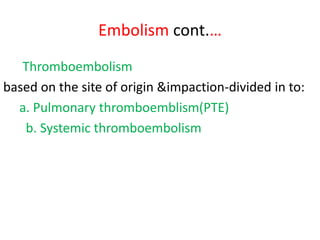
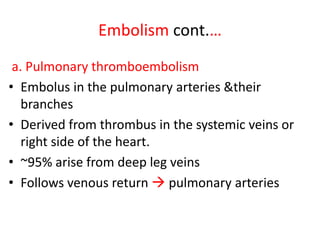
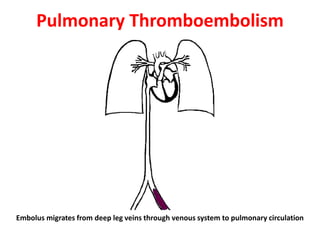
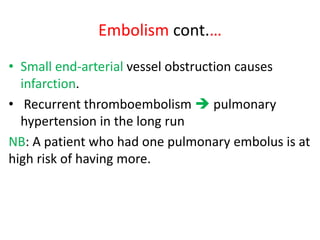
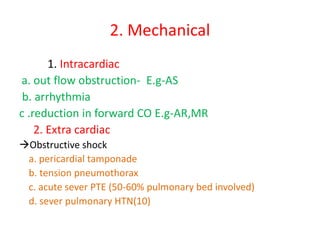
3. Embolism occurs when a detached mass such as a thrombus is carried by the bloodstream to obstruct vessels elsewhere. Pulmonary embolism is a common type that arises from deep vein