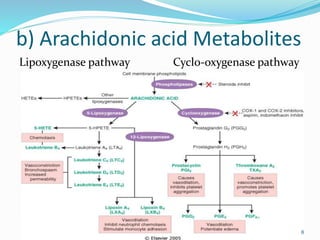
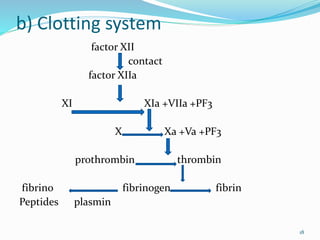
This document summarizes different mediators of inflammation. It describes cell-derived mediators like vasoactive amines (histamine, serotonin), arachidonic acid metabolites from cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways, lysosomal components, platelet activating factor, cytokines, and nitric oxide. It also discusses plasma-derived mediators including the kinin system, clotting system, fibrinolytic system, and complement system. These mediators cause effects like vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, adhesion of leukocytes, and chemotaxis during inflammation.