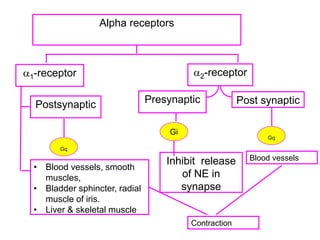
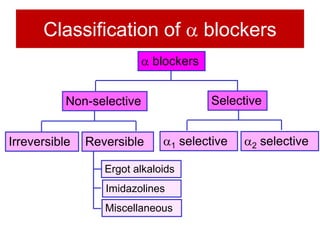
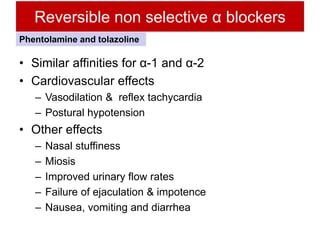
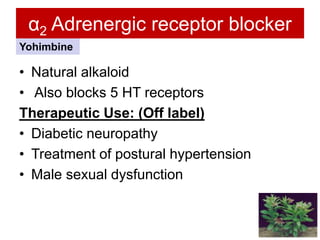
Alpha blockers work by blocking alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. They can be classified as non-selective or selective. Non-selective alpha blockers like phentolamine cause vasodilation and reduce blood pressure but can also cause side effects like nasal congestion and hypotension. Selective alpha-1 blockers like prazosin, terazosin, and doxazosin are used to treat hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia as they cause less side effects. Newer drugs like tamsulosin and alfuzosin are more uroselective and effective for treating BPH with minimal effects on blood pressure. Alpha blockers have various clinical uses including treatment of phae