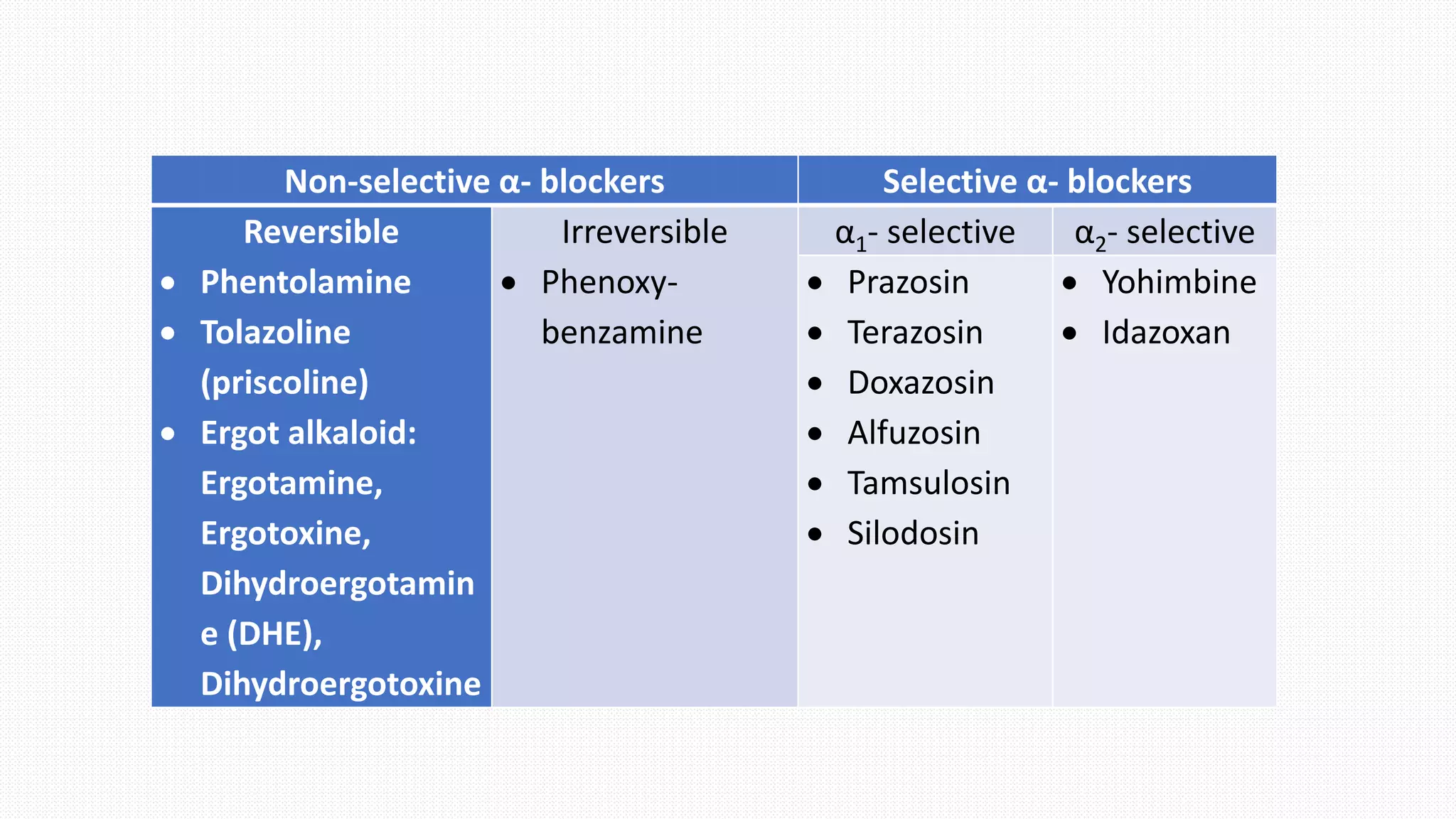
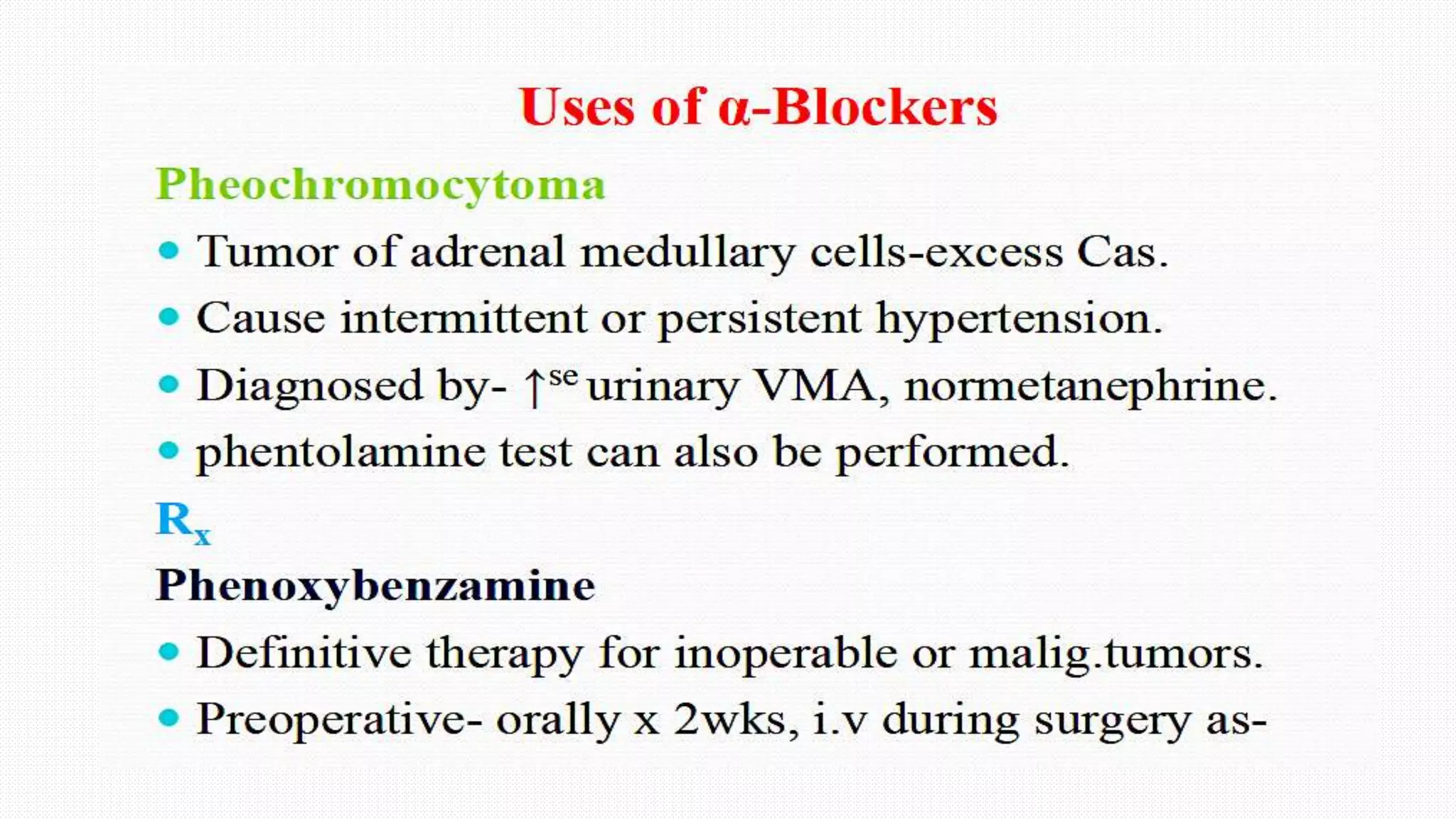
This document summarizes adrenergic receptor antagonists. It describes the different types of α-adrenergic receptors and how they mediate various physiological functions. It discusses selective and non-selective α-blockers, their mechanisms of action, and examples of commonly used drugs for each category. Specific drugs discussed include prazosin, terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin, yohimbine, and phentolamine. The document also reviews uses of α-blockers for conditions like hypertension, Raynaud's phenomenon, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and treatment of pheochromocytoma.