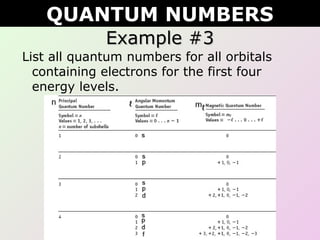
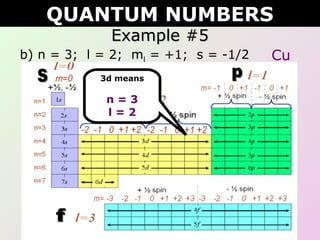
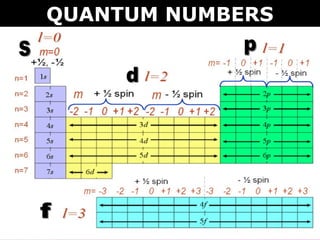
This document discusses quantum numbers which describe the location of electrons within an atom. There are four quantum numbers: 1) the principal quantum number (n) indicates the energy level, 2) the azimuthal quantum number (l) indicates the orbital type, 3) the magnetic quantum number (ml) represents a specific orbital based on the l value, and 4) the spin quantum number (s or ms) indicates the spin direction of the electron as either up or down. Examples are provided to demonstrate writing the full set of quantum numbers for various atoms.