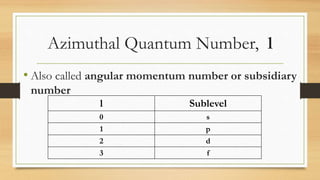
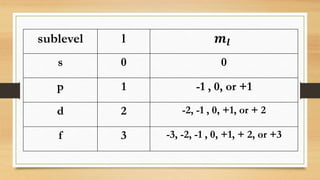
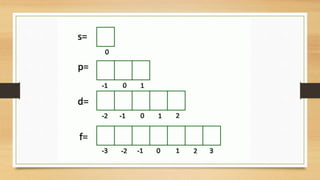
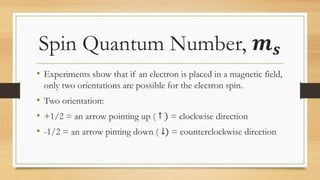
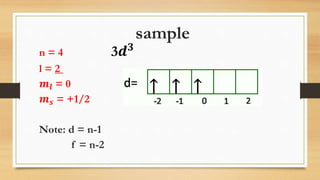
The document discusses the four quantum numbers - n, l, ml, and ms - that are used to describe an electron orbital. The principal quantum number n refers to the main energy level, the azimuthal quantum number l describes the sublevel shape, the magnetic quantum number ml gives the orientation in space, and the spin quantum number ms has two possible orientations of +1/2 or -1/2. Together the four quantum numbers uniquely specify an electron orbital in an atom.