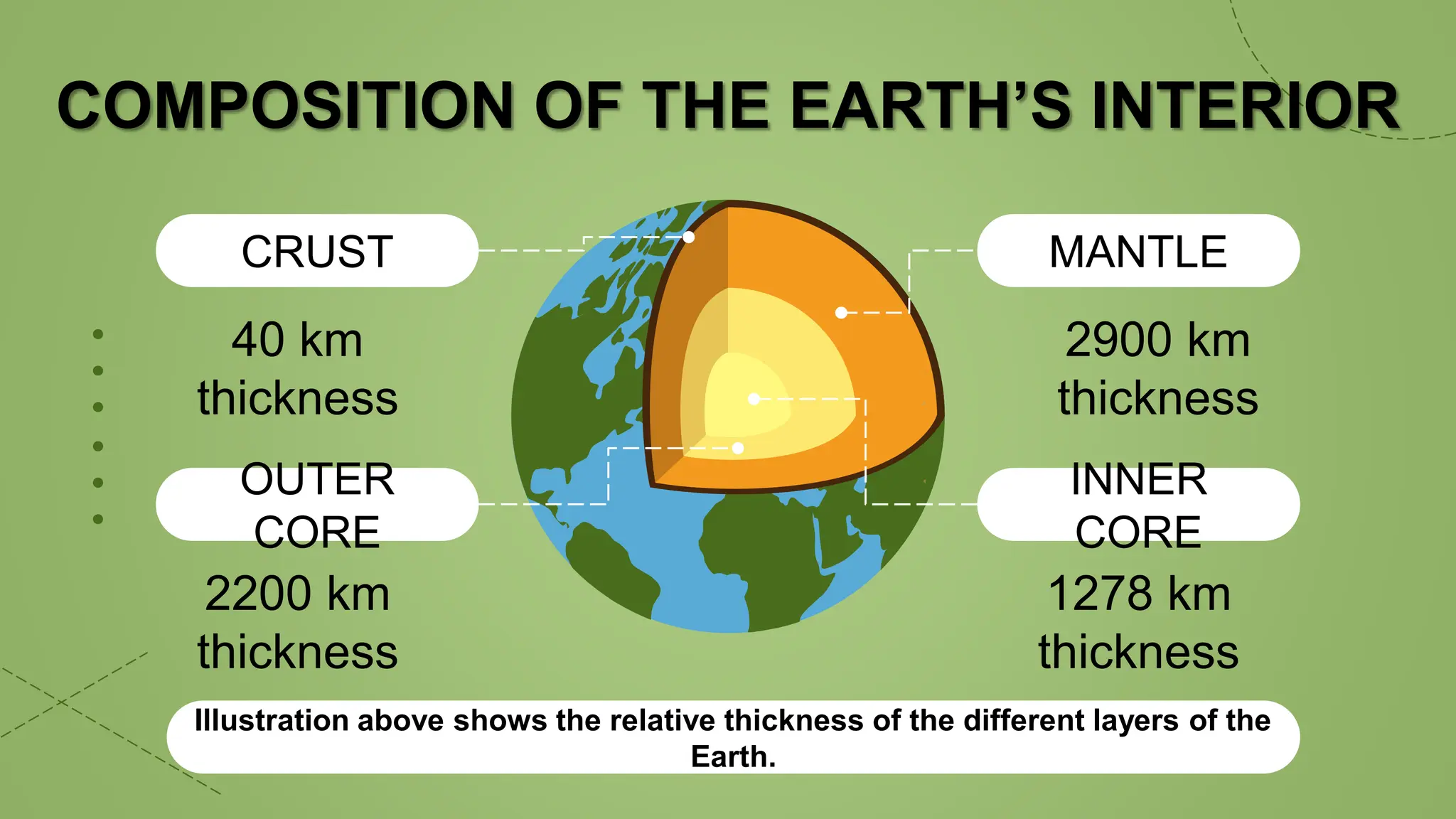
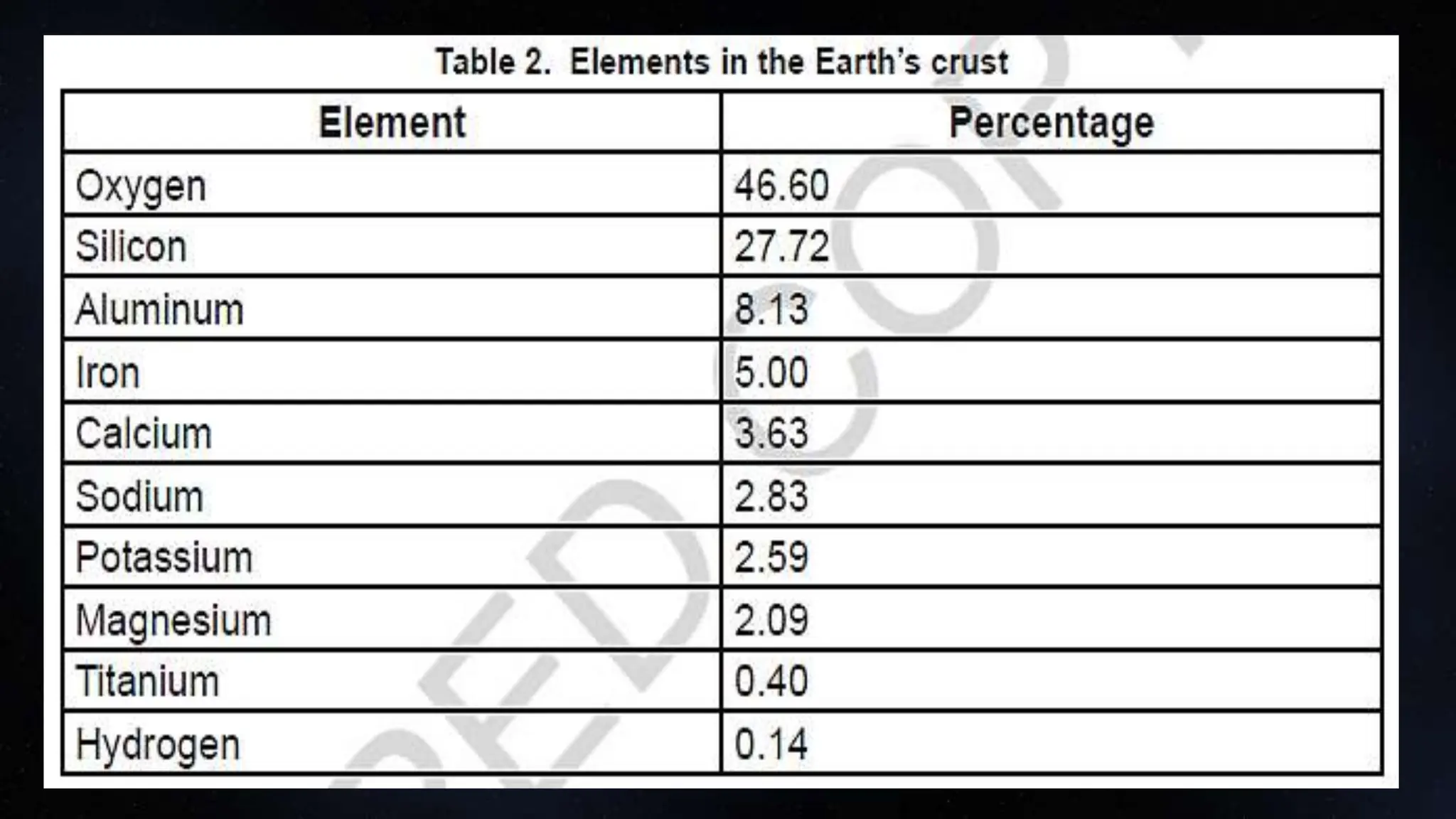
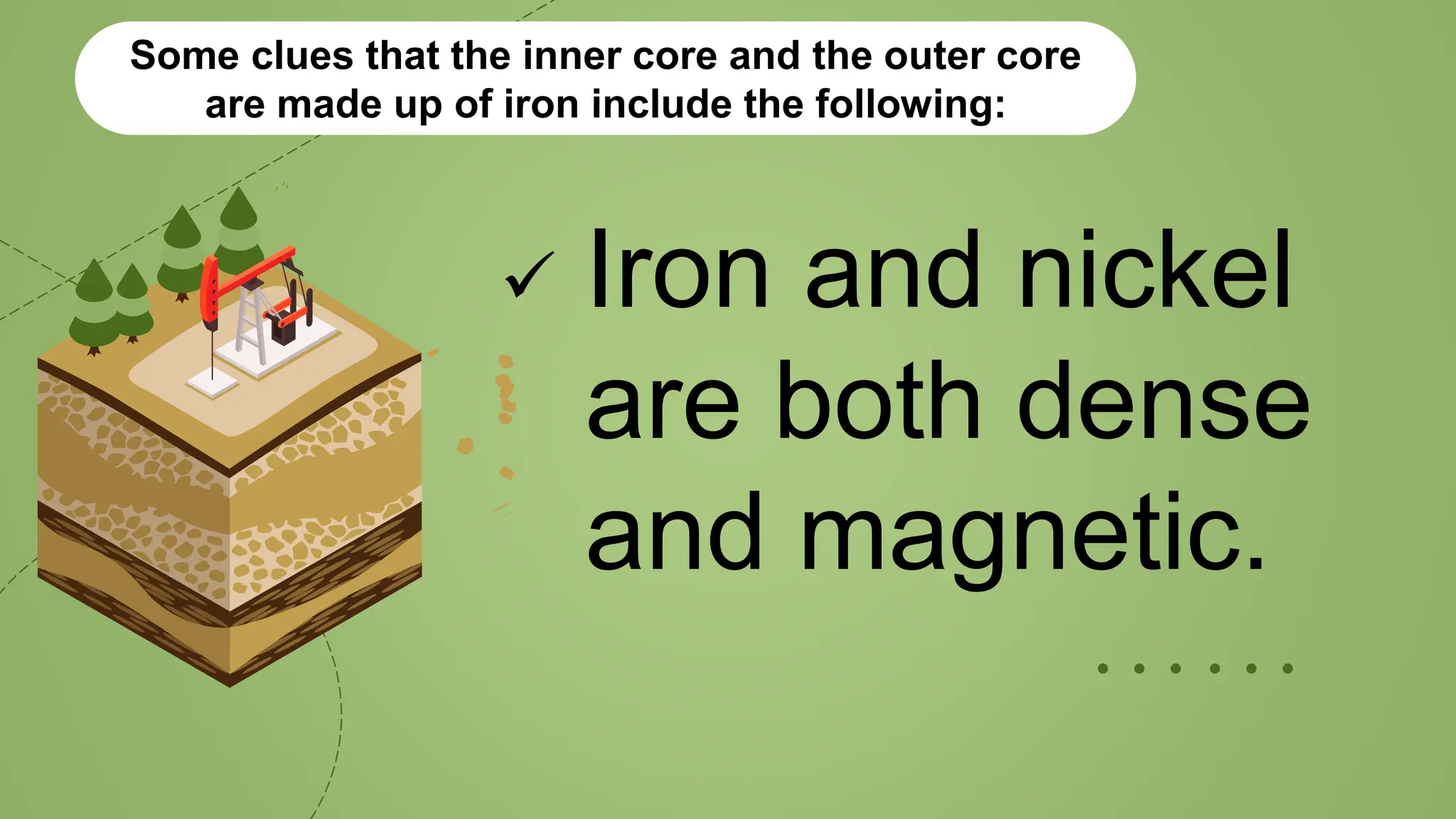
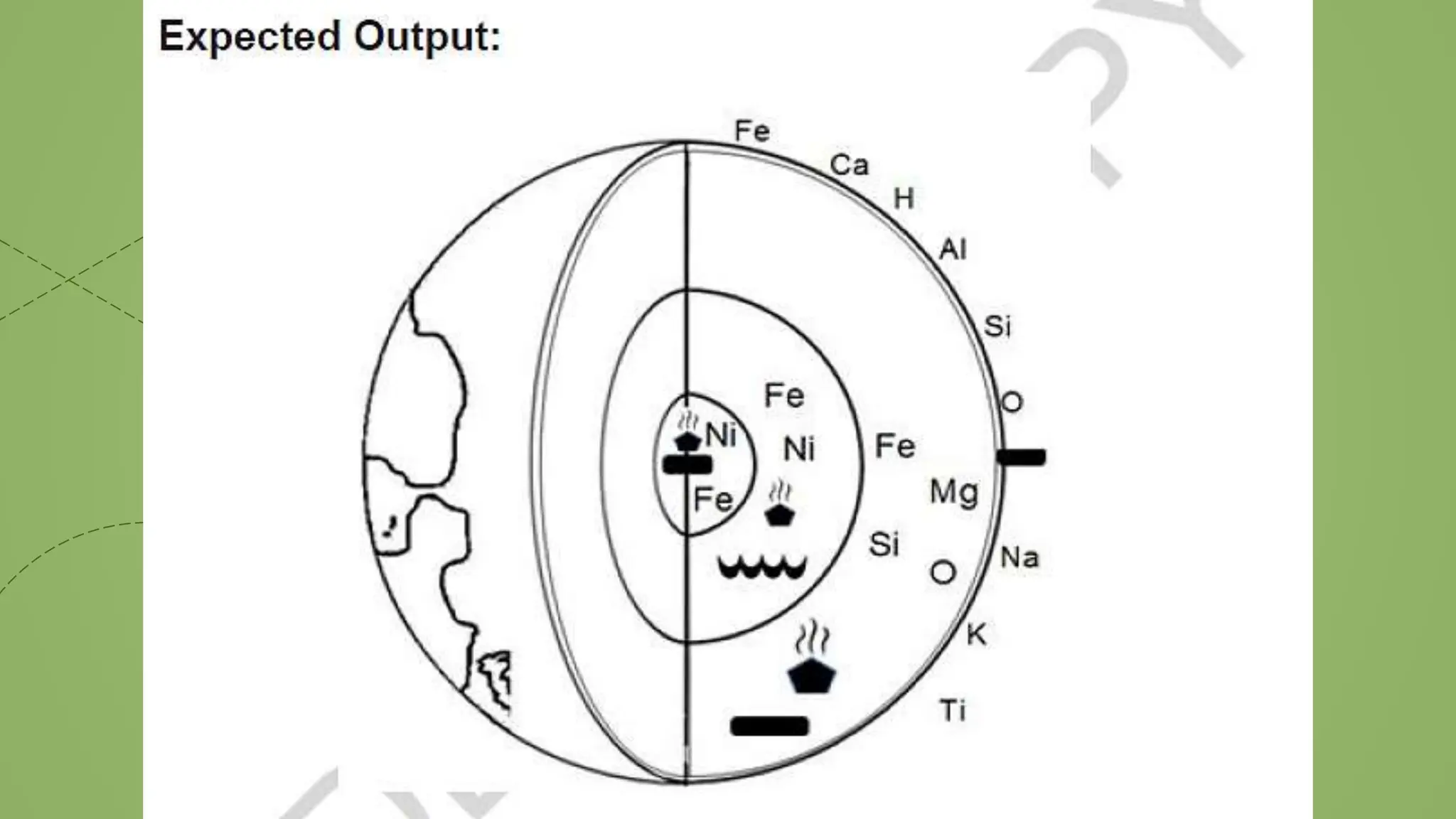
This document provides information about the internal structure of the Earth. It begins with objectives to describe the Earth's interior and the process of convection currents in the mantle. It then provides details on the composition and thickness of each layer, including the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. It describes concepts like density, temperature, and convection currents. The document contains diagrams illustrating the layers and quizzes to test comprehension. In summary, it outlines the layers within the Earth and some of the geological processes occurring in its interior.