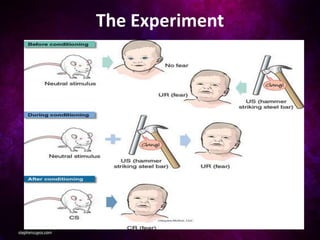
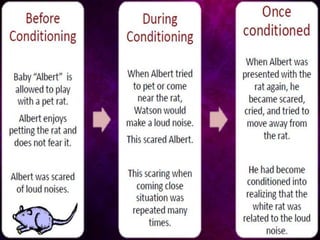
John B. Watson and his assistant Rosalie Rayner conducted an experiment on a 9-month old boy called Little Albert to study emotional learning and stimulus generalization. They showed Albert neutral stimuli like a white rat while making a loud noise, causing him to become afraid of the rat and other similar objects. Unfortunately, they returned Albert to his mother without undoing the conditioning, and he died at age 6 still fearful without understanding why. The experiment supported Watson's behaviorist theory that all behaviors are learned through conditioning and reinforcement.