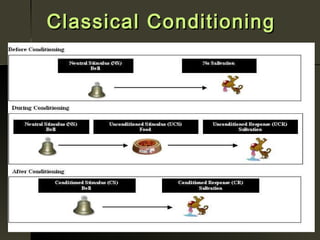
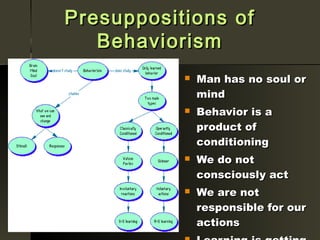
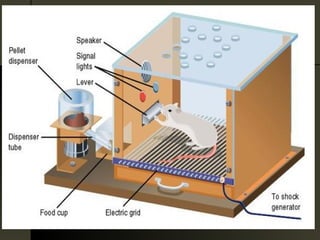
Behaviorism is a philosophy of psychology that views human and animal behavior as observable actions that can be studied scientifically without reference to internal mental states. Key principles include classical conditioning proposed by Ivan Pavlov, operant conditioning developed by B.F. Skinner involving reinforcement and punishment, and the idea that psychology should be an objective, experimental science of observable behavior.