1) Behaviourism is a learning theory that proposes that behaviour can be modified through consequences like reinforcement or punishment. It focuses on observable behaviours rather than internal mental states.
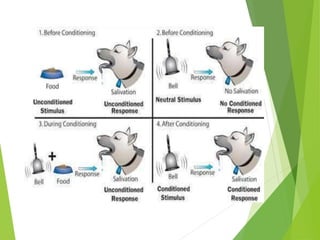
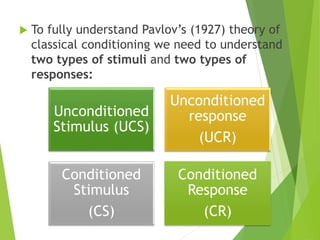
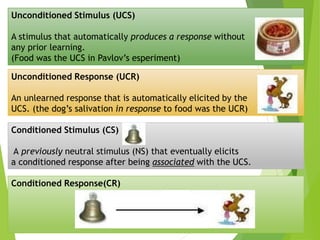
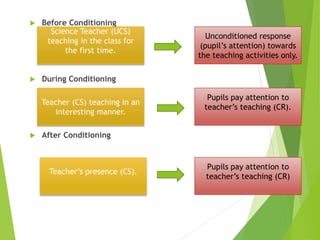
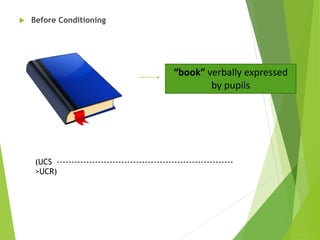
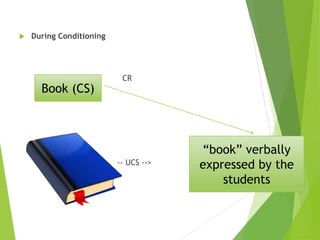
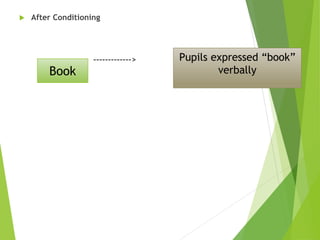
2) Classical conditioning involves associating an unconditioned stimulus that naturally elicits a response with a neutral conditioned stimulus to produce a conditioned response. Pavlov's famous experiment conditioned dogs to salivate when a bell was rung.
3) Operant conditioning, proposed by Skinner, is learning through reinforcement and punishment of behaviours. Positive reinforcement strengthens behaviours by rewarding them, while negative reinforcement removes an unpleasant stimulus to increase a behaviour.