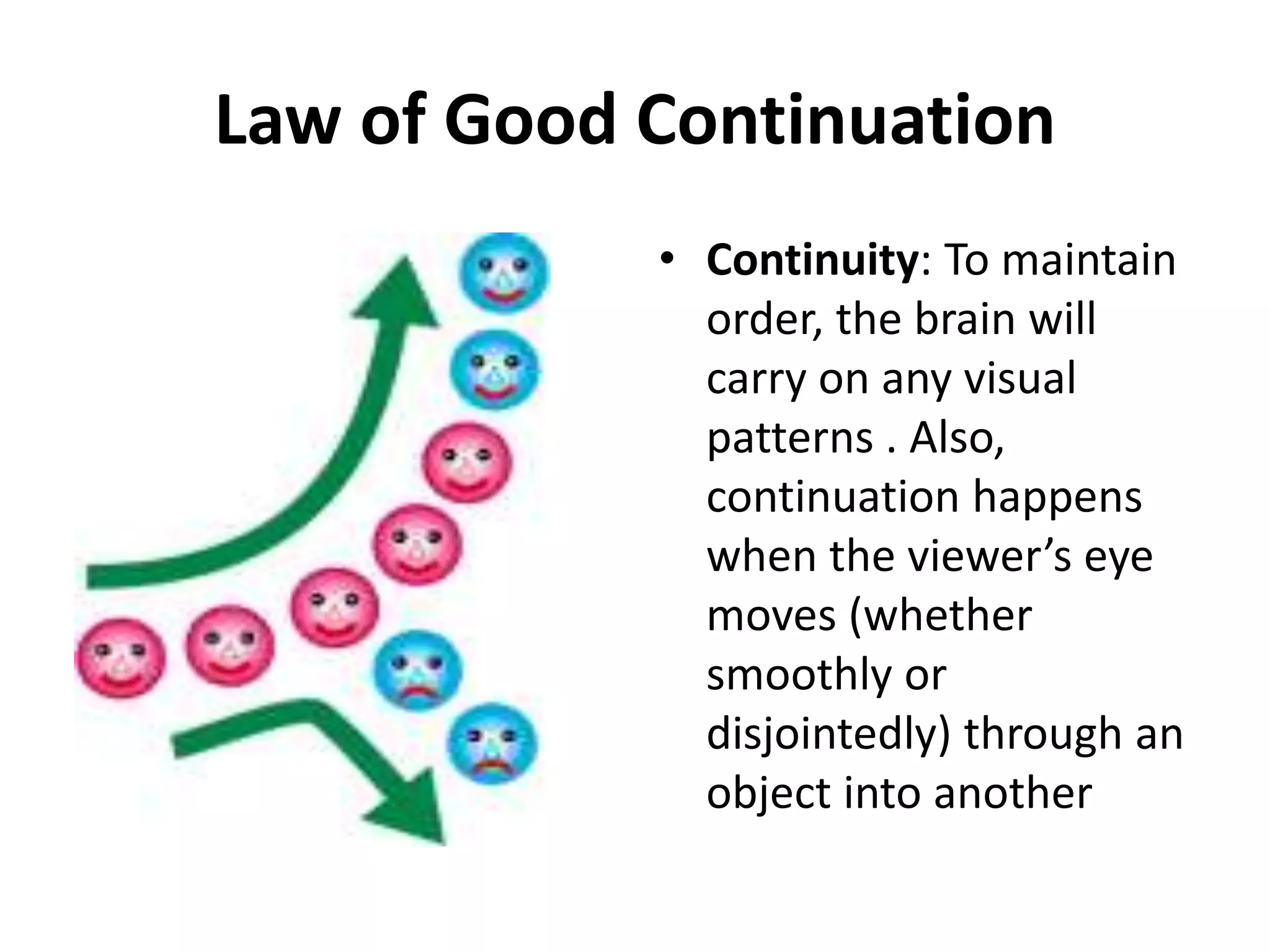
Gestalt psychology focuses on the idea that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. It was developed in the early 1900s and proposes that humans perceive things holistically rather than by individual elements. The key Gestalt principles include proximity, similarity, closure, good continuation, pragnanz, and figure/ground. These principles influence how humans group and perceive visual elements. Wolfgang Kohler also studied insight learning through experiments with apes solving problems. The Gestalt principles can be applied to education by considering how proximity, similarity, closure, continuity, simplicity, and emphasis impact teaching and learning.