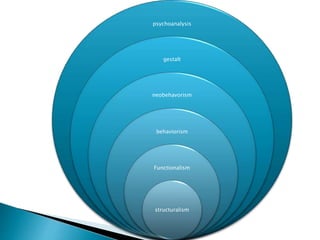
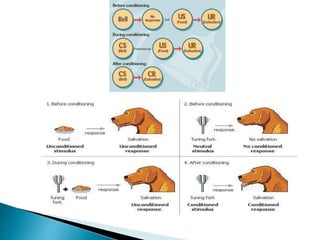
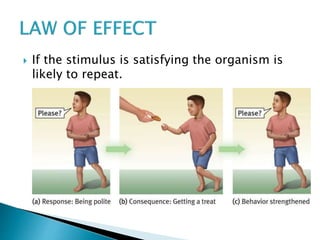
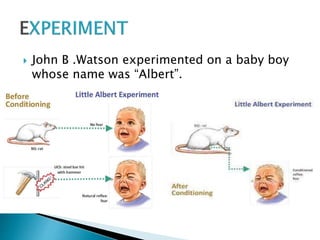
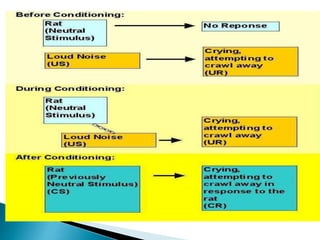
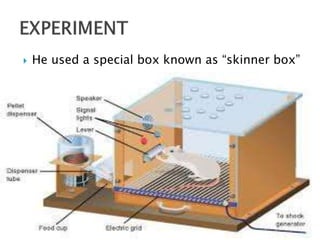
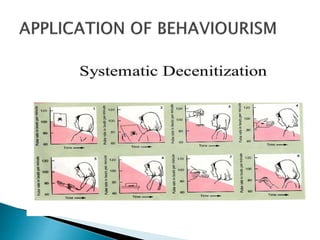
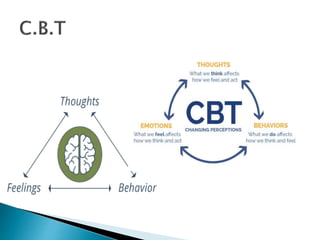
The document discusses several influential psychologists and their theories, including Ivan Pavlov and his work on classical conditioning using dogs, John B. Watson who believed environment shapes behavior and conducted experiments on conditioning in infants, and B.F. Skinner who introduced the theory of operant conditioning and used Skinner boxes to study reinforcement. It also mentions Edward Thorndike's law of effect and Ivan Sechenov and his studies on reflexes in the brain.