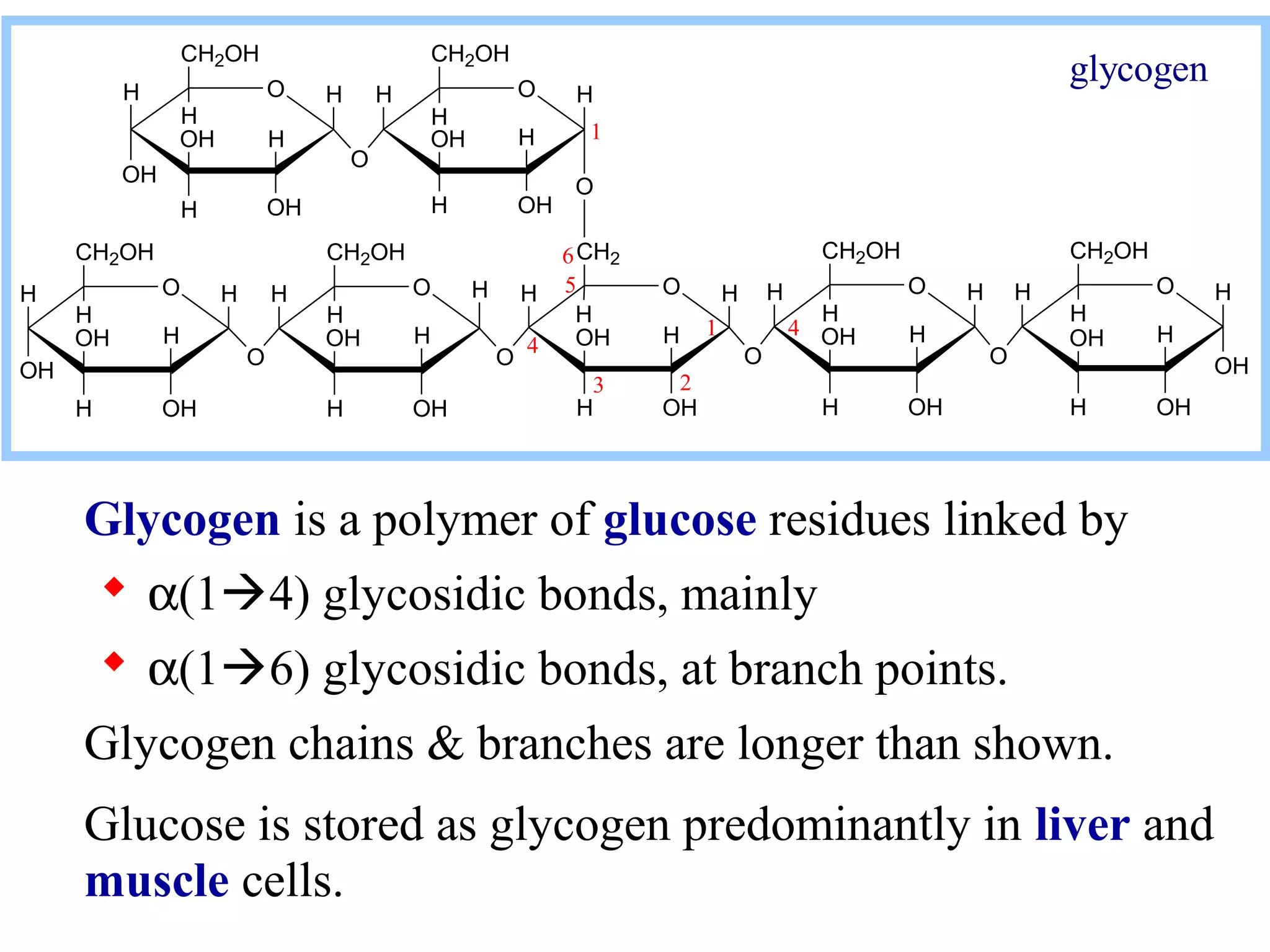
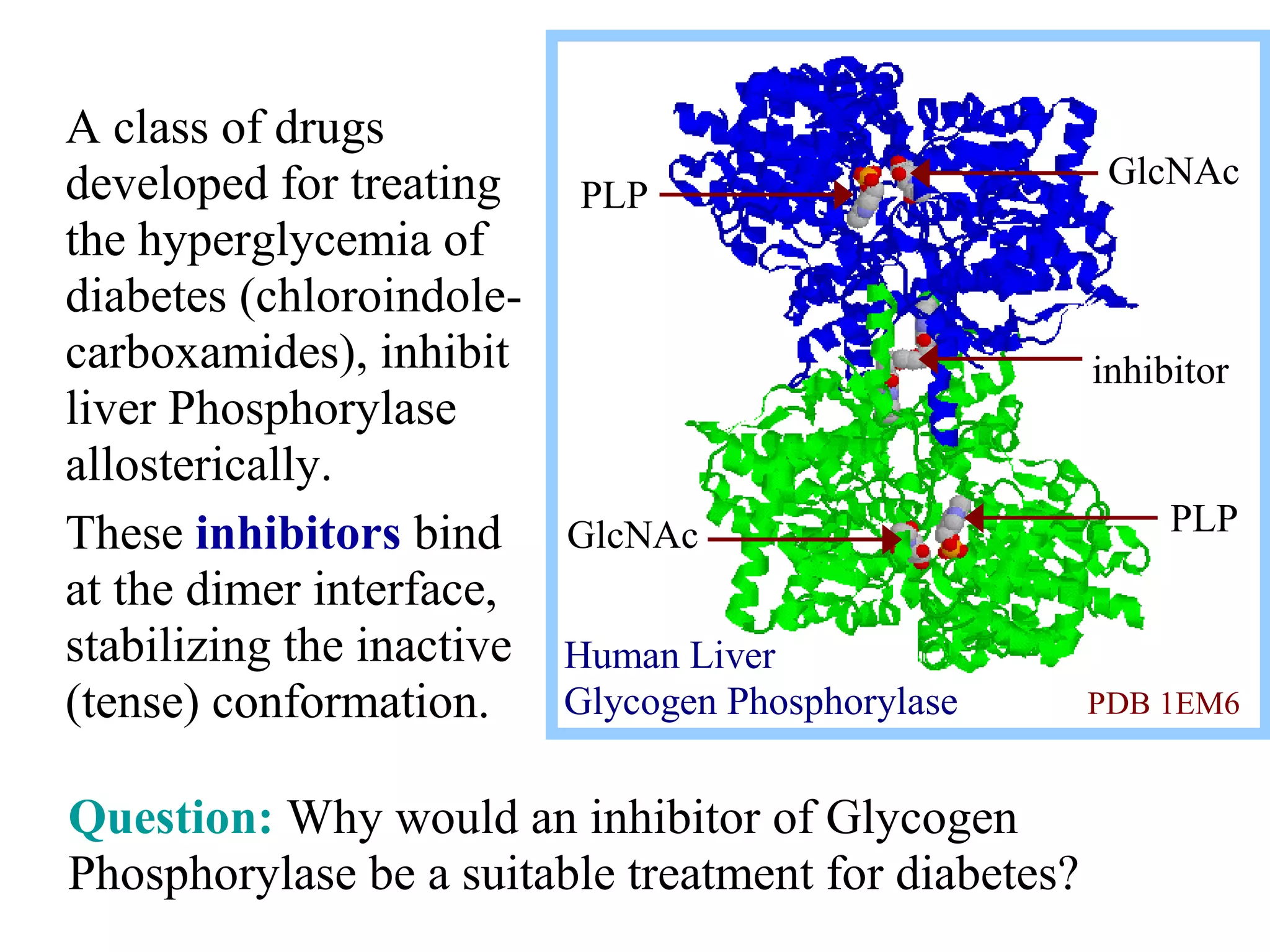
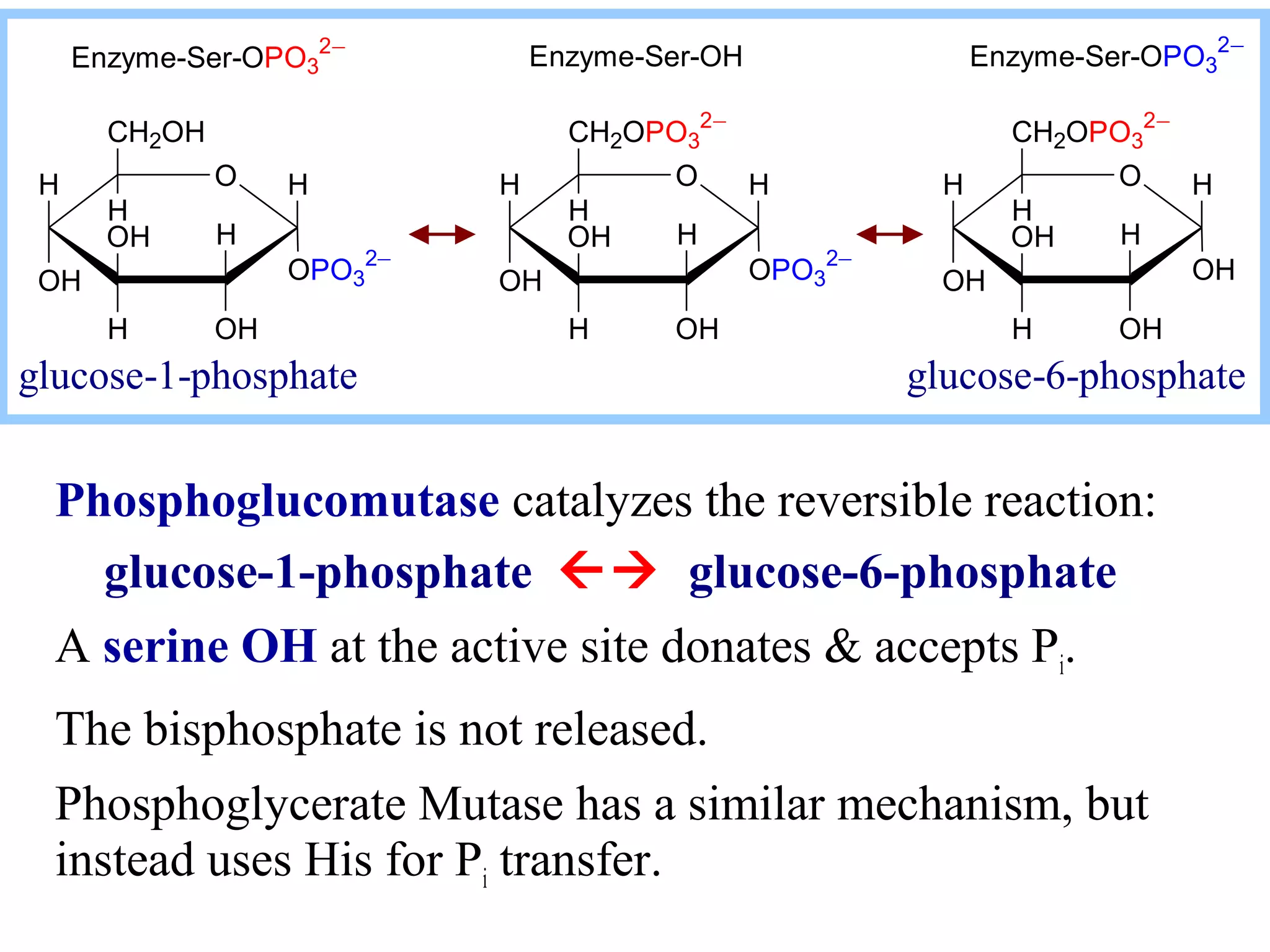
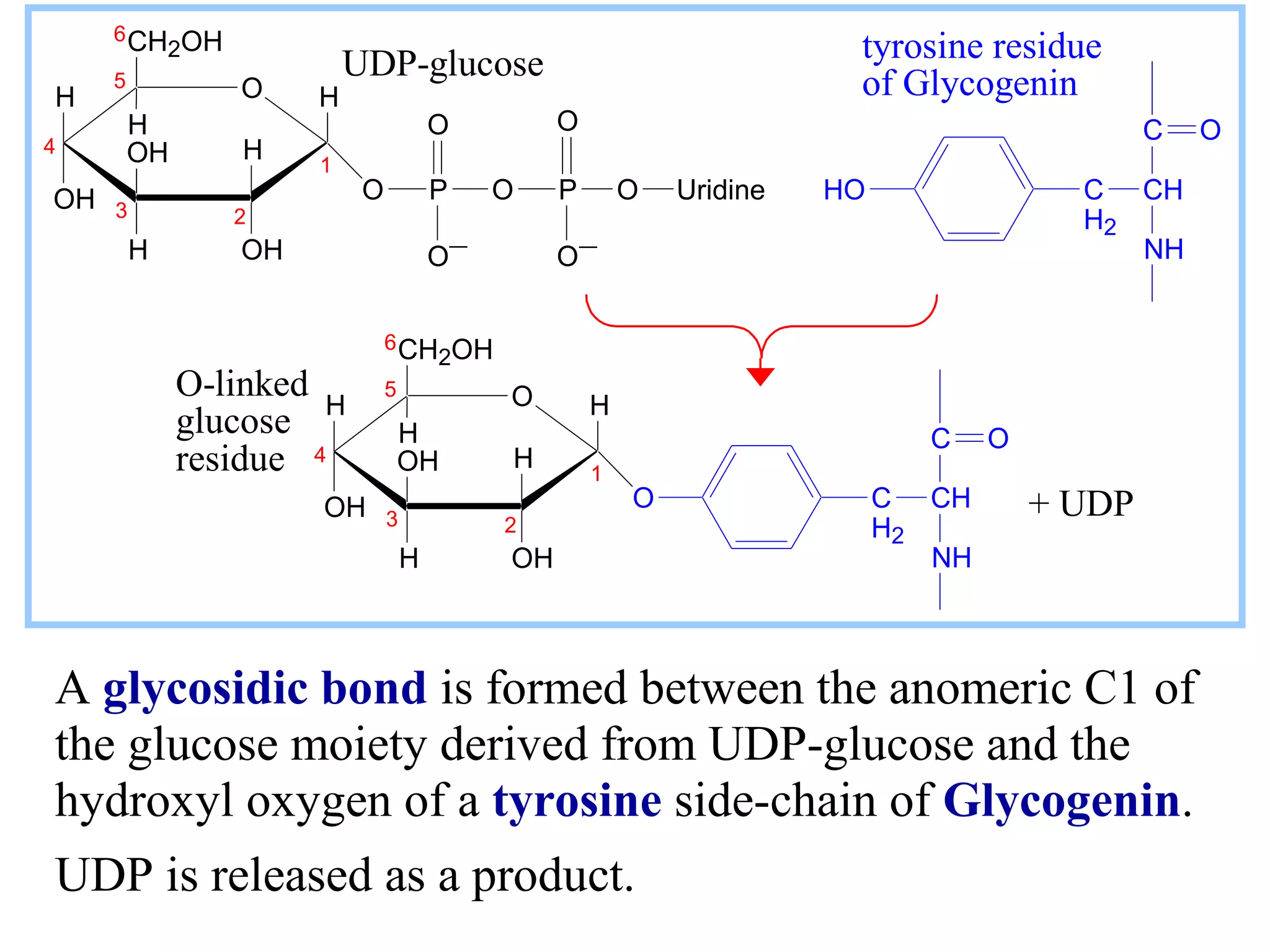
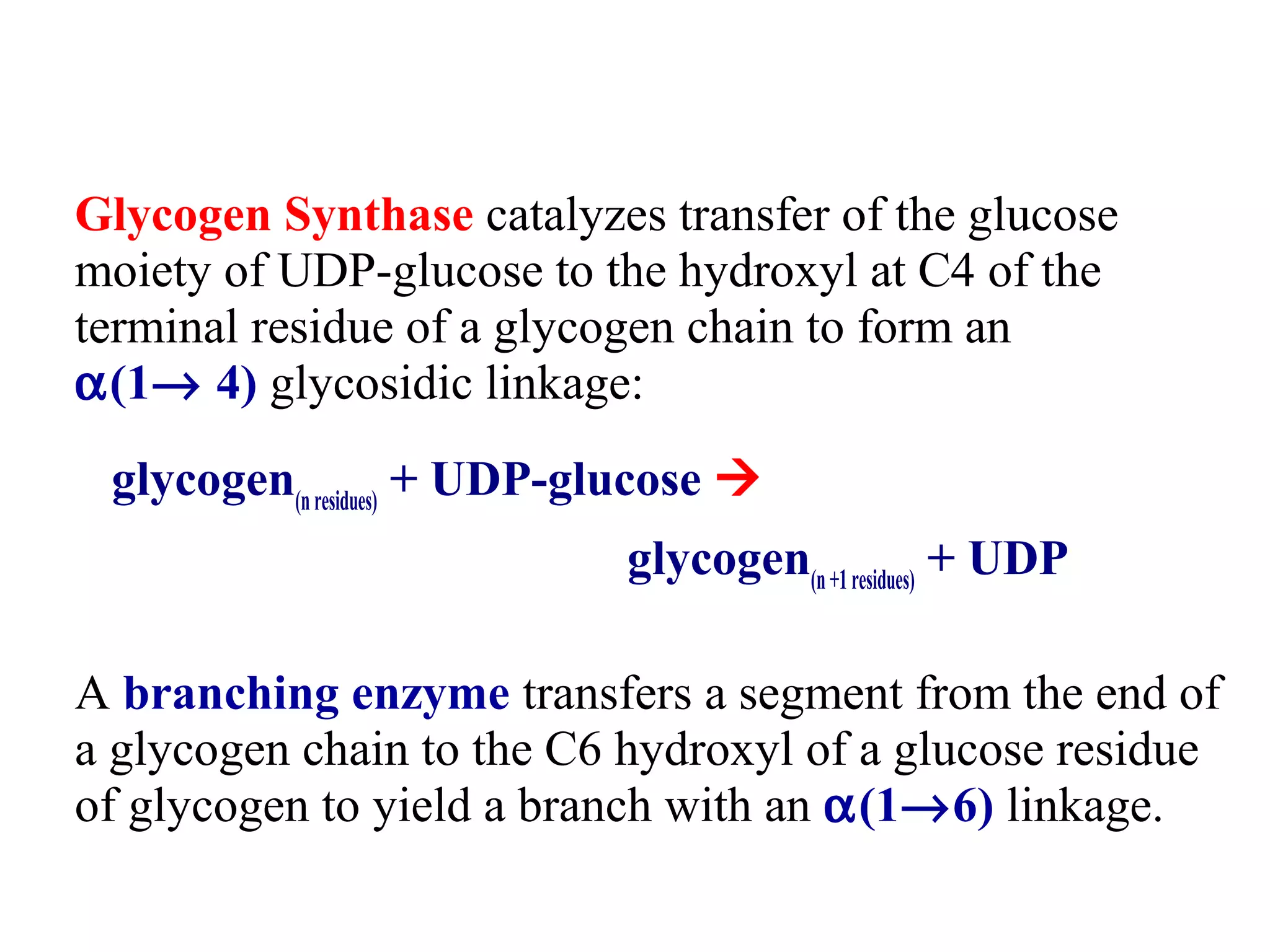
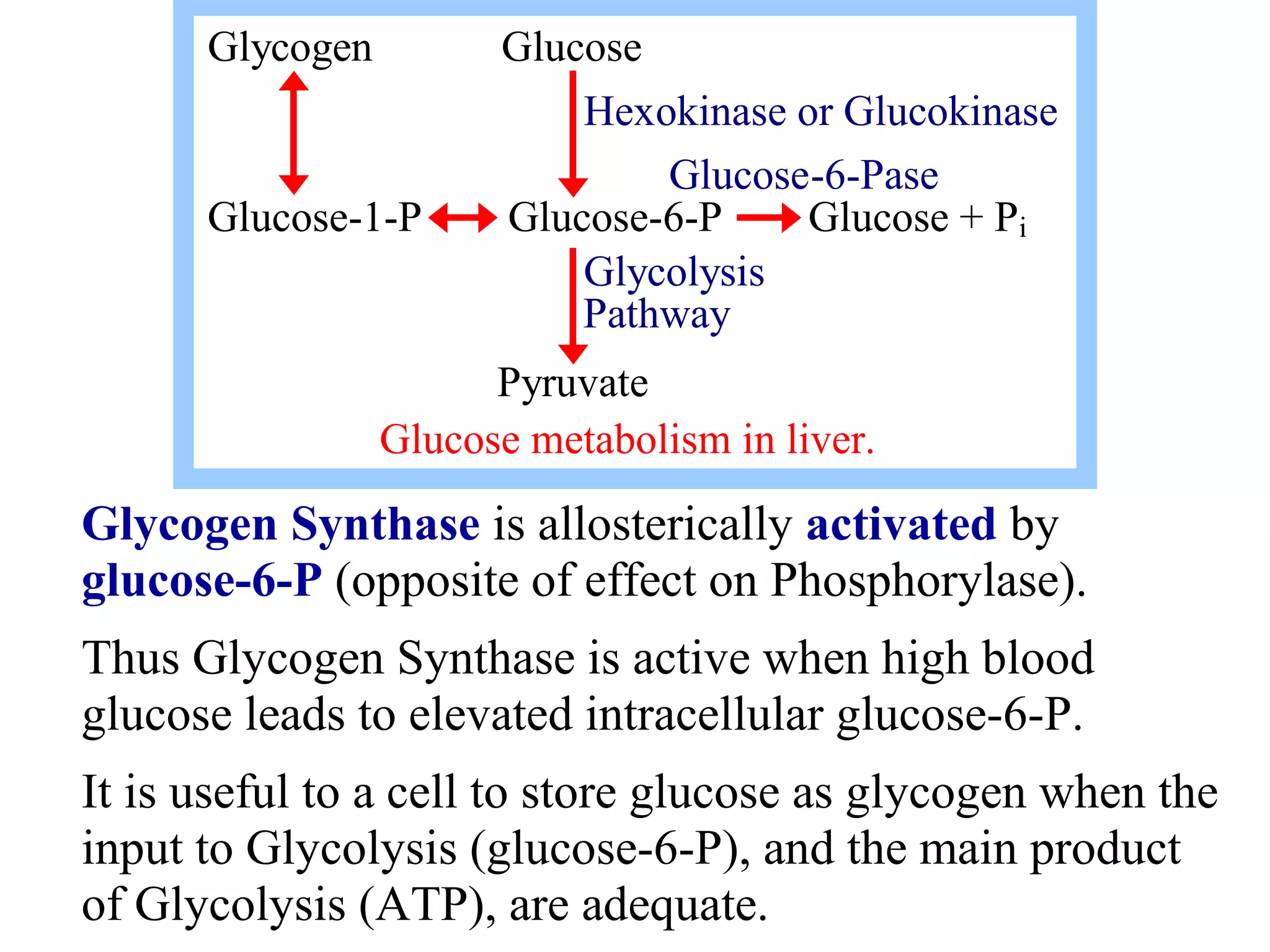
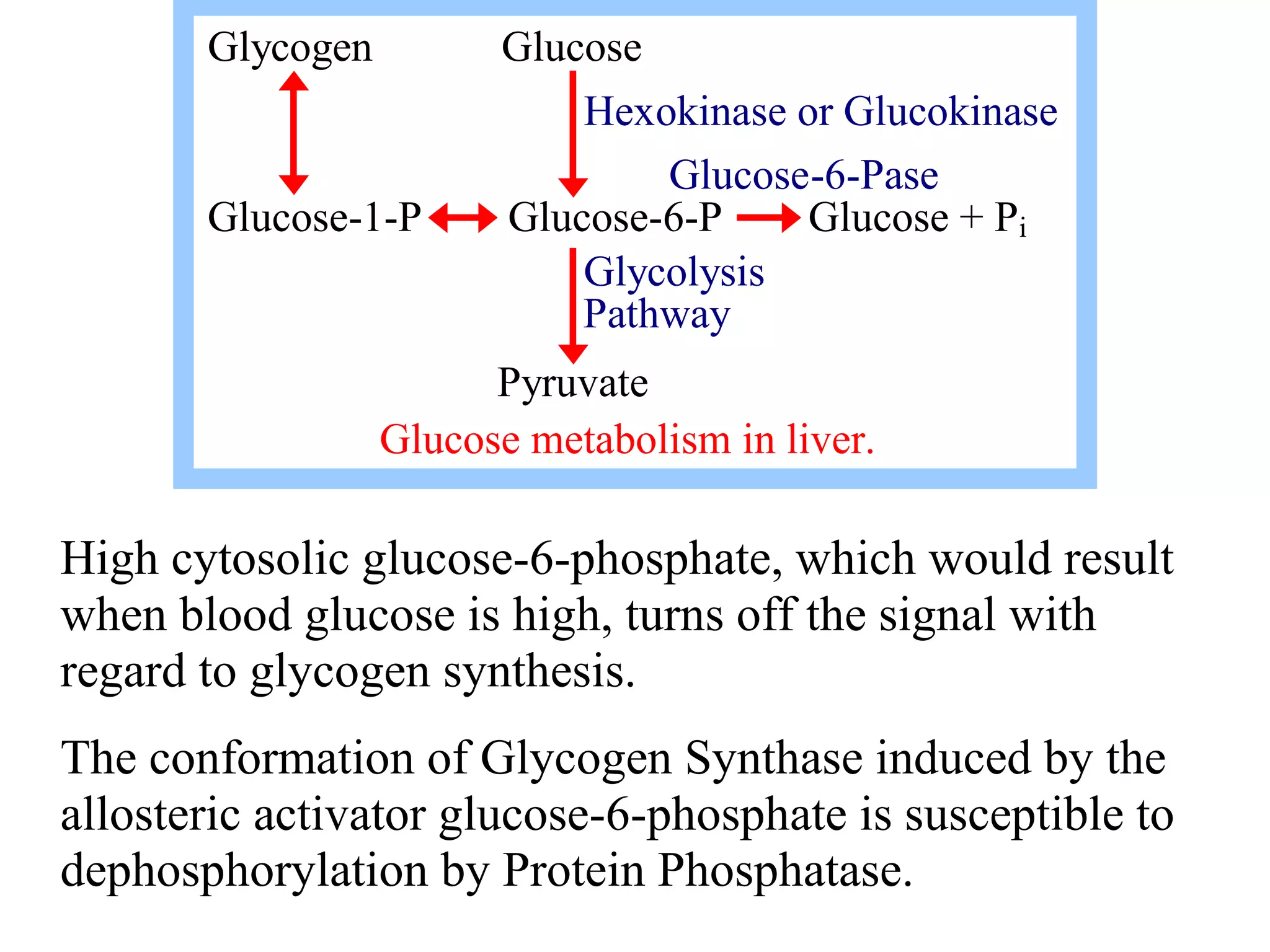
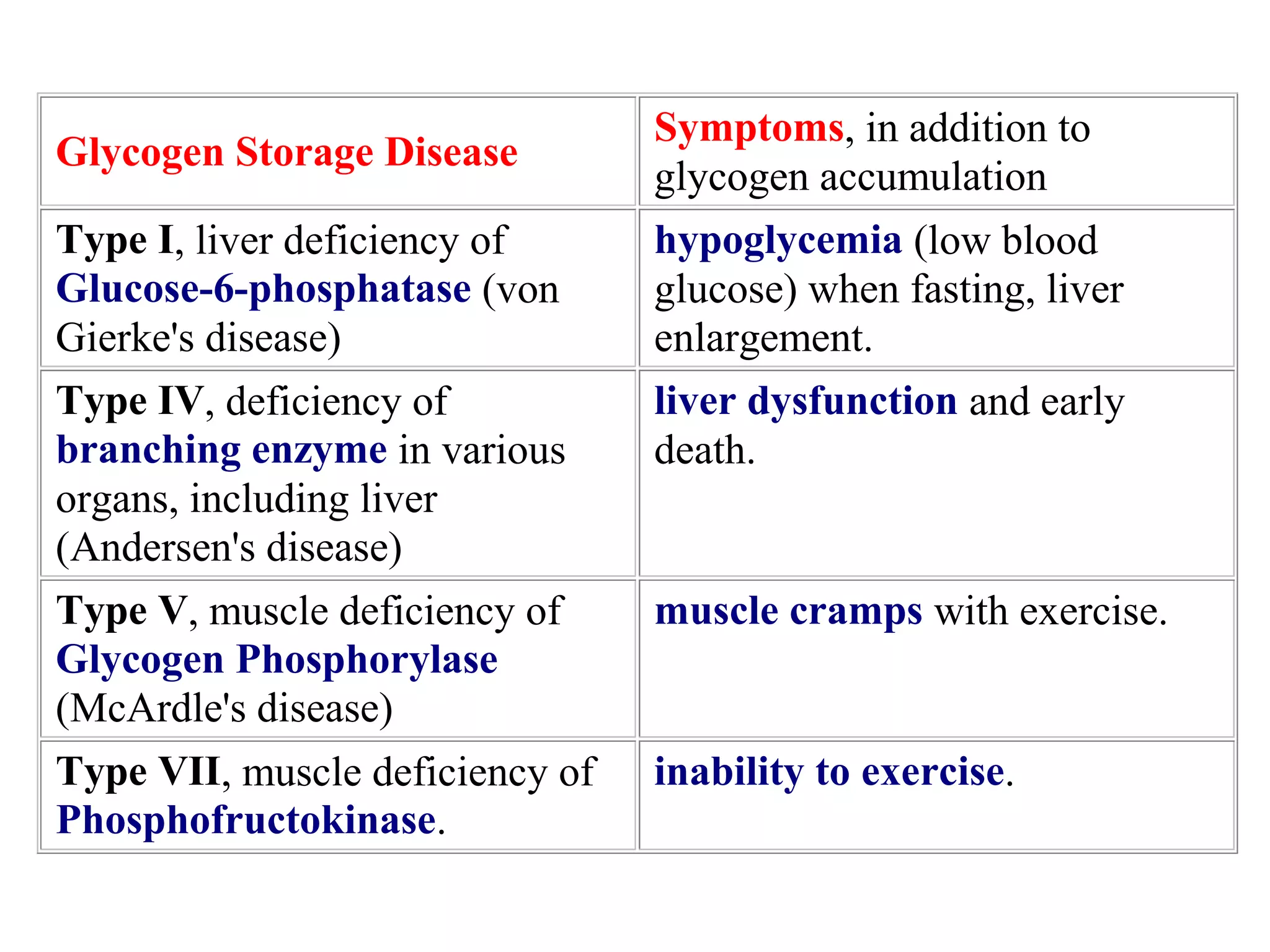
Glycogen is a branched polymer of glucose residues stored in liver and muscle cells. Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the phosphorolytic cleavage of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate. An inhibitor of glycogen phosphorylase would be a suitable treatment for diabetes by decreasing glycogen breakdown and lowering blood glucose levels. Glycogen synthesis utilizes UDP-glucose to add glucose residues via glycogen synthase. Glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen synthase activities are regulated by allosteric effectors and phosphorylation to prevent futile cycling between glycogen breakdown and synthesis.