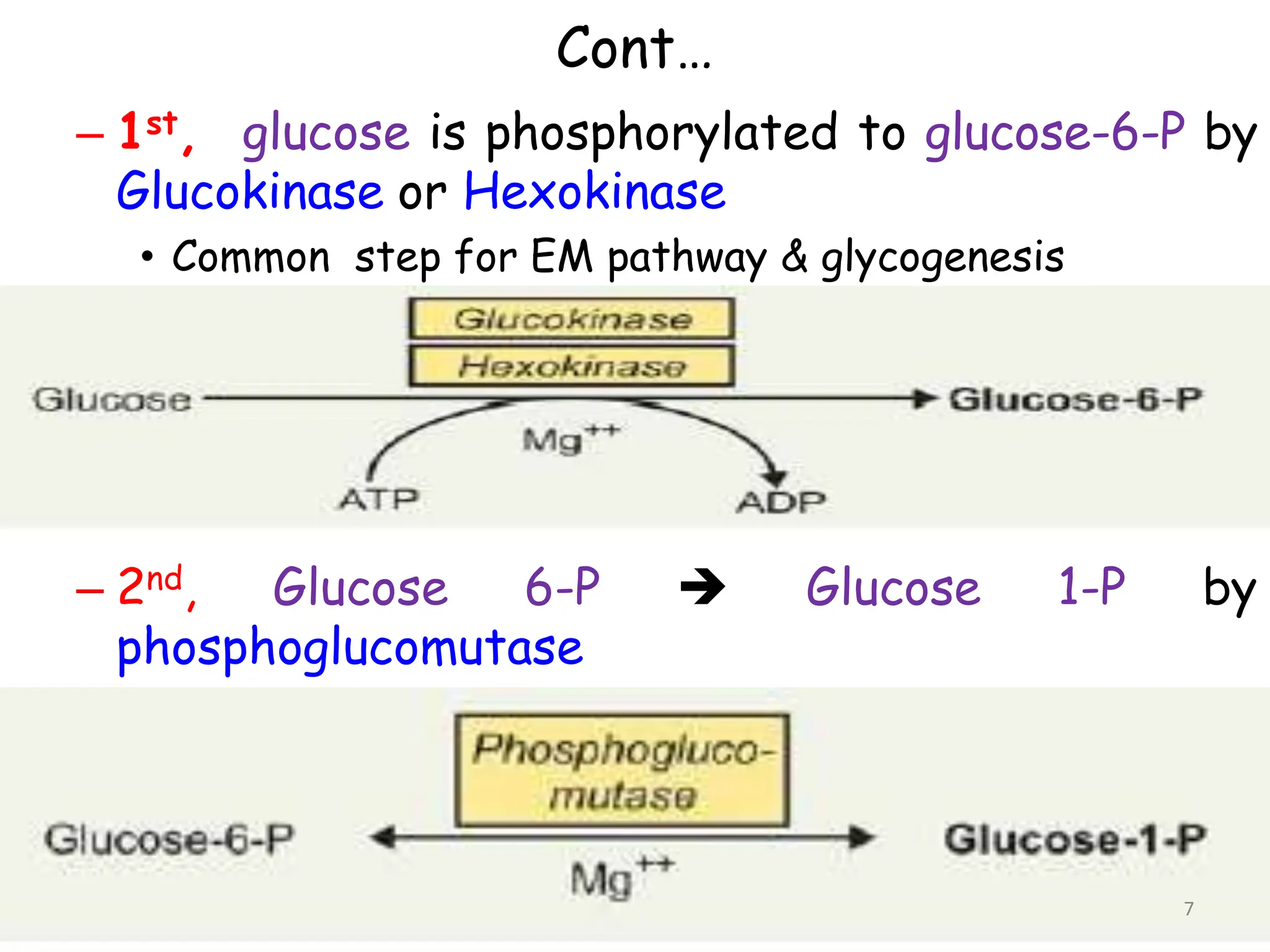
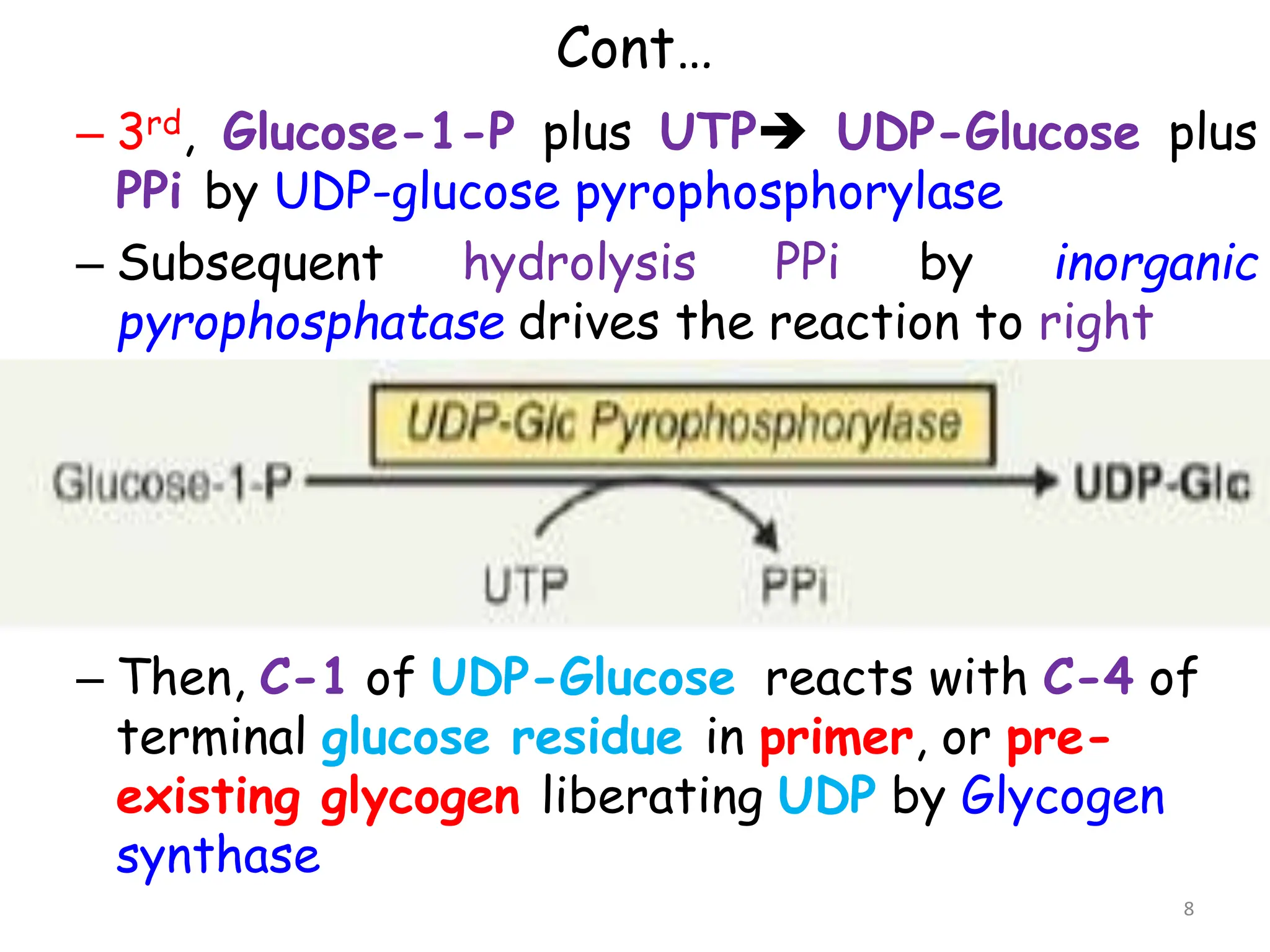
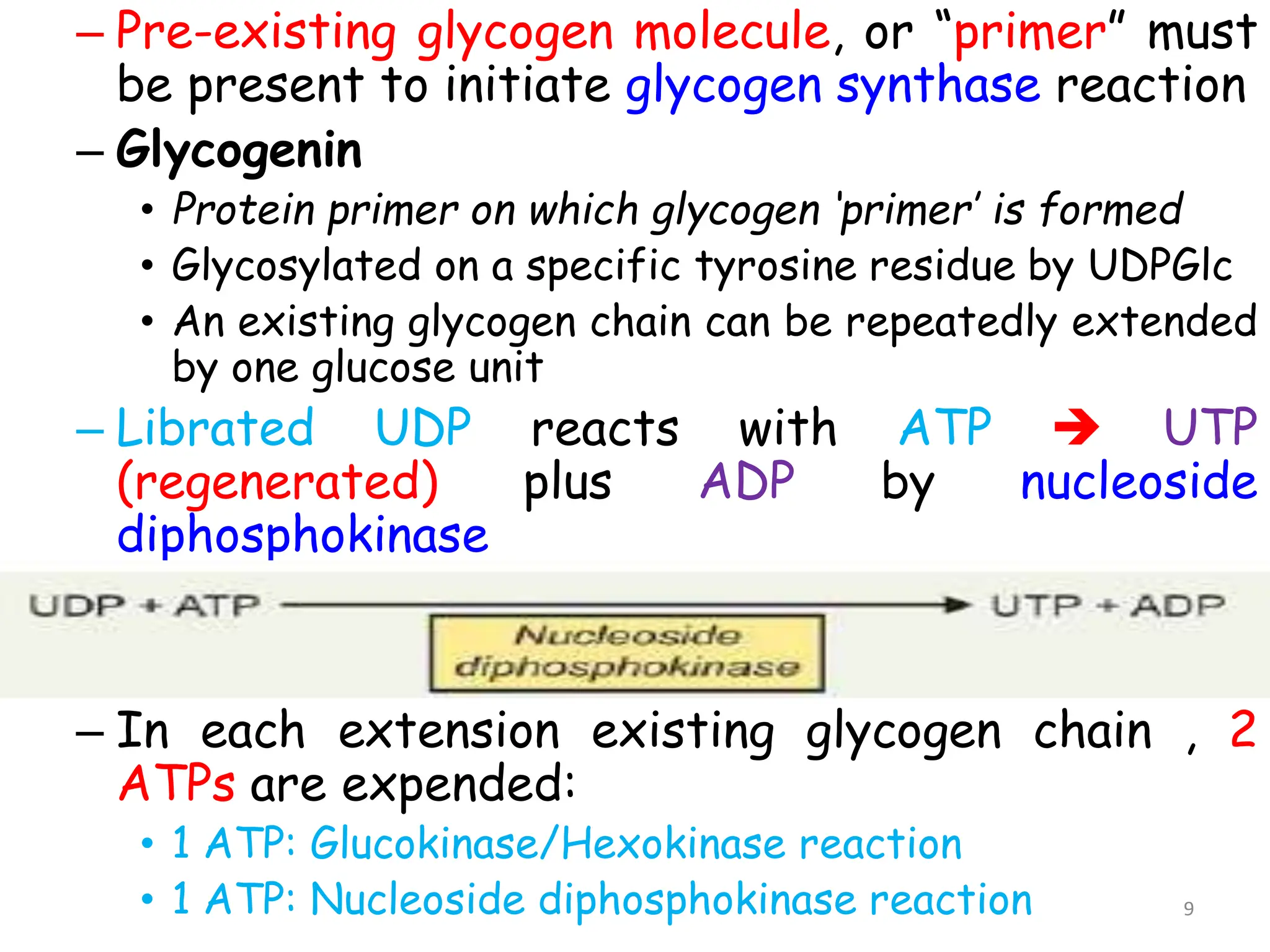
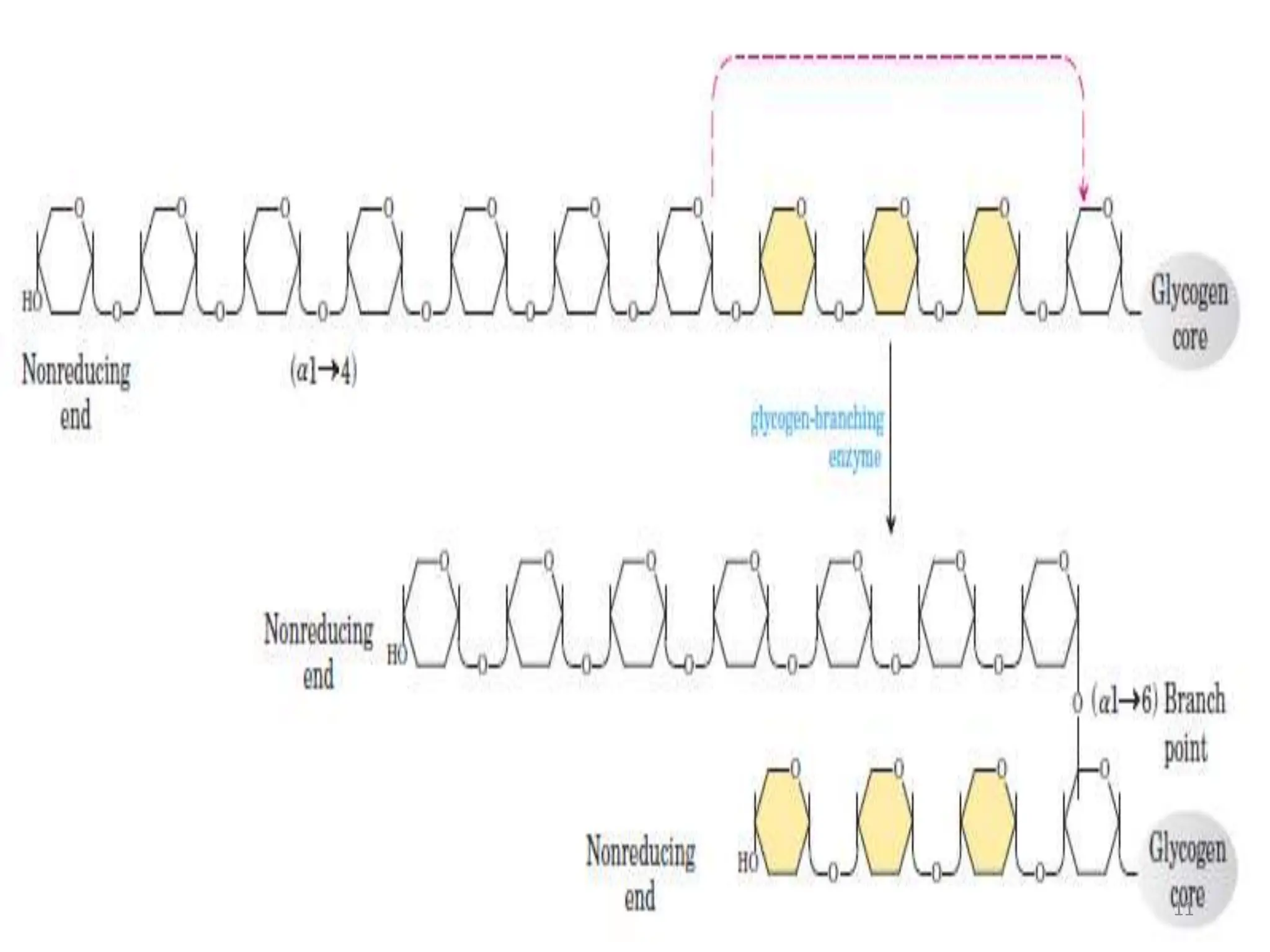
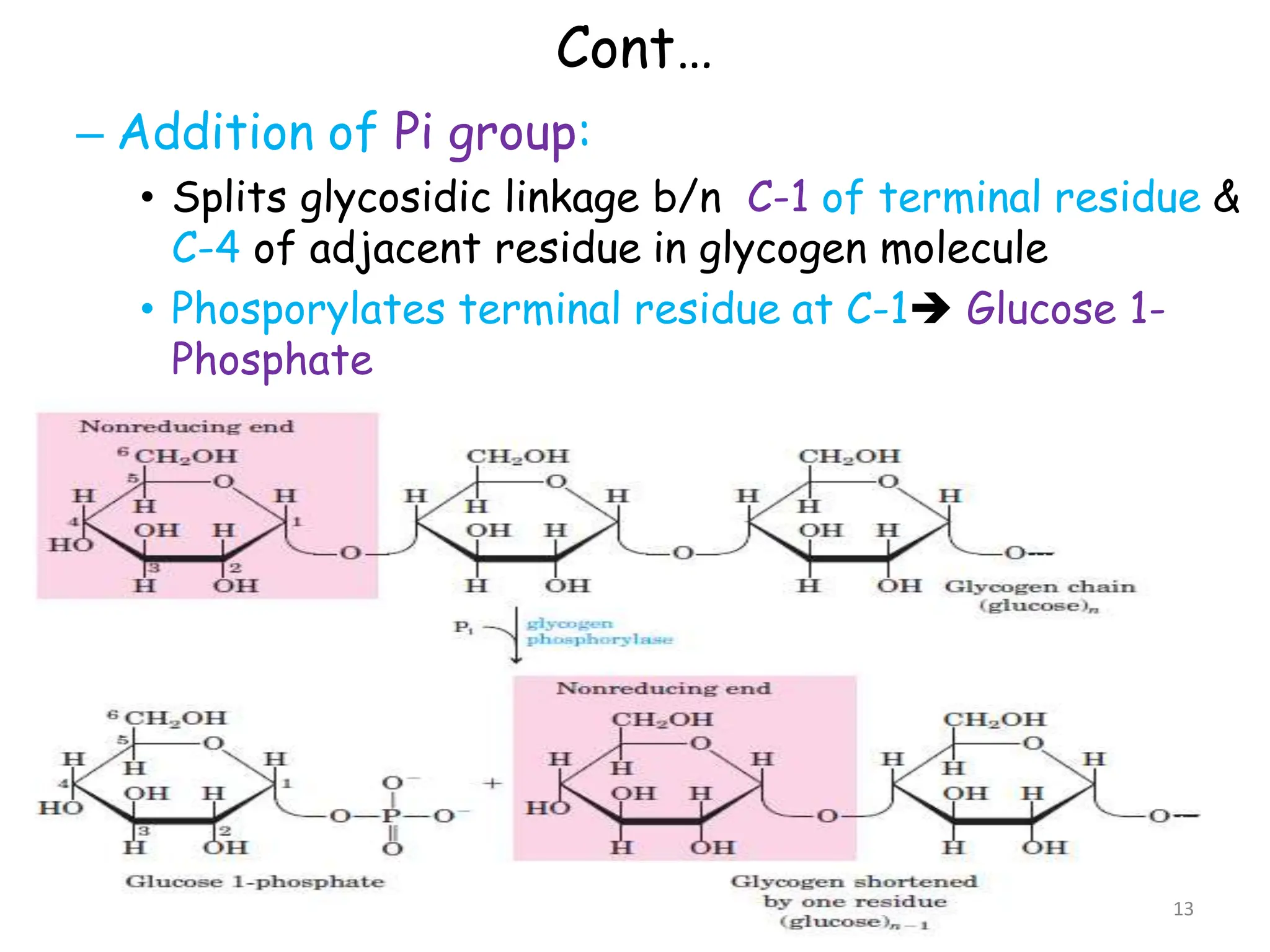
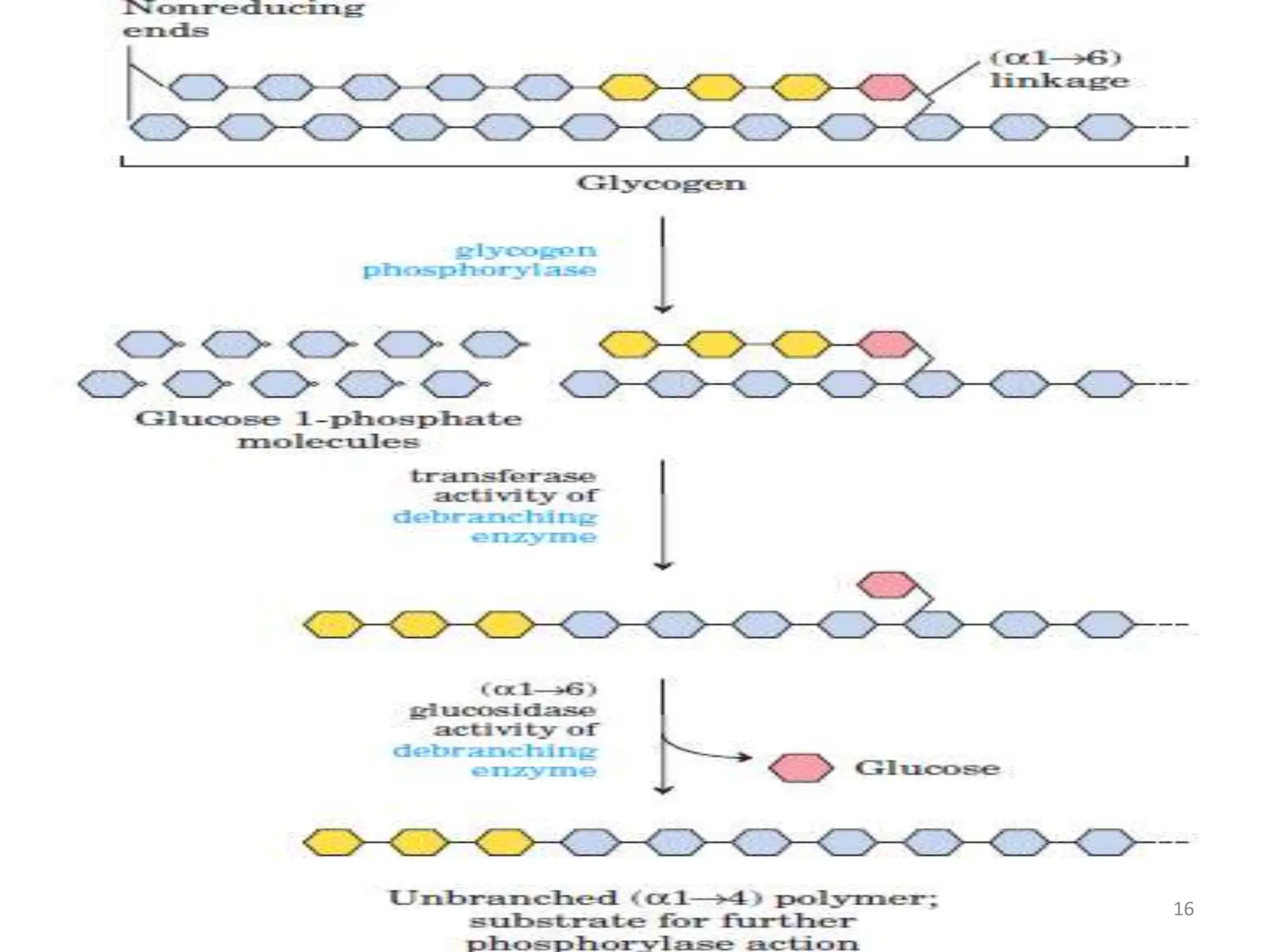
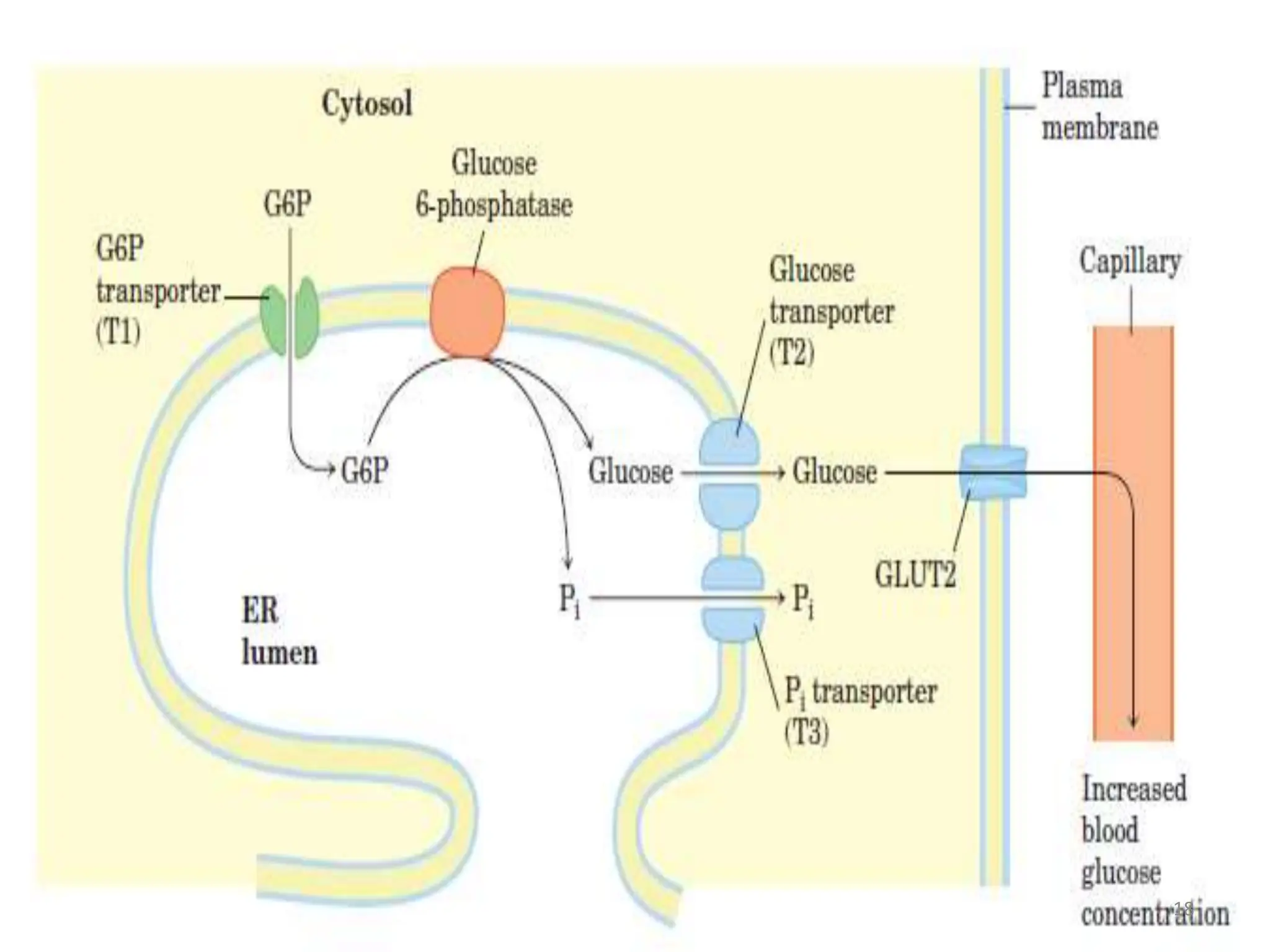
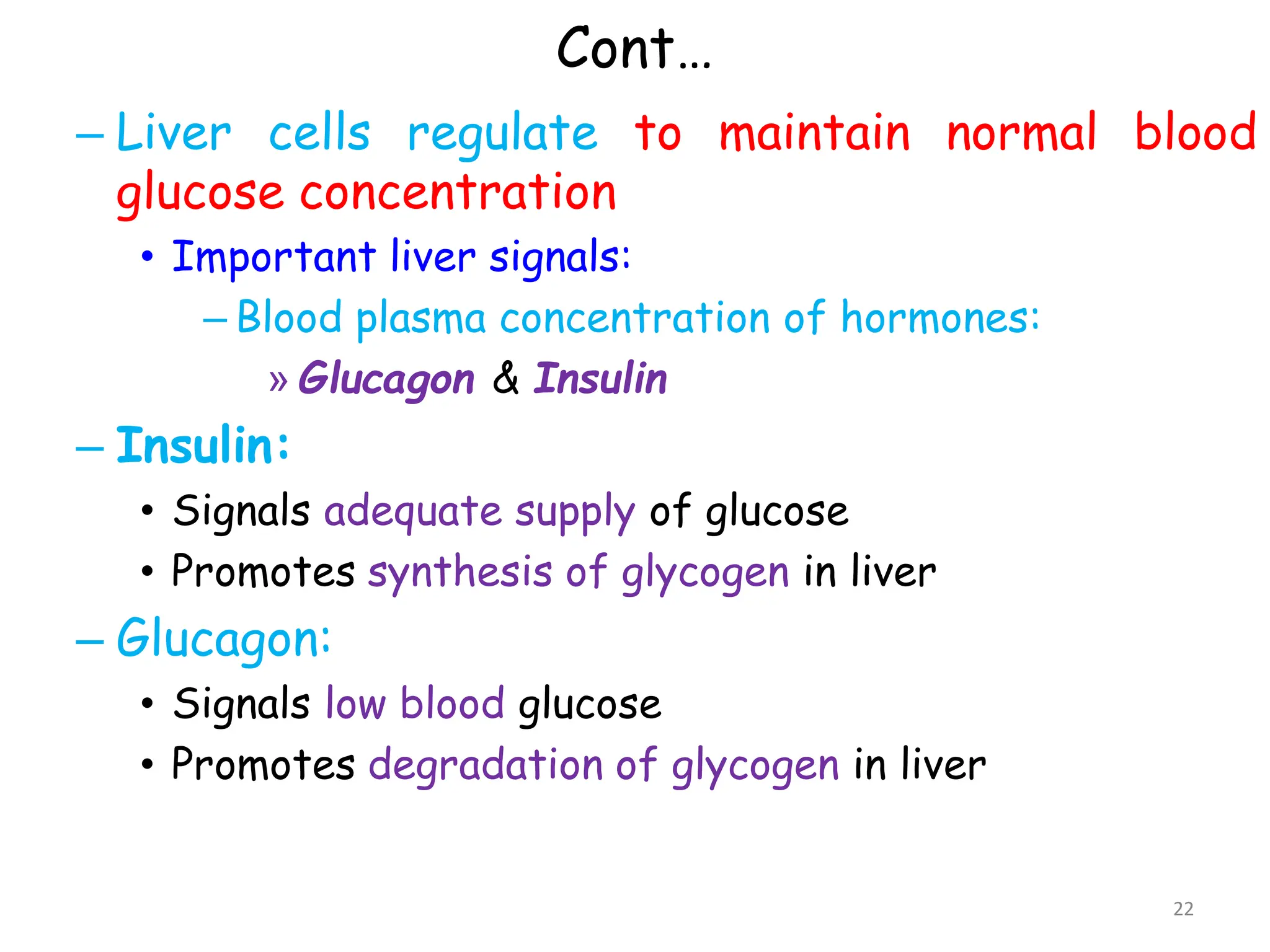
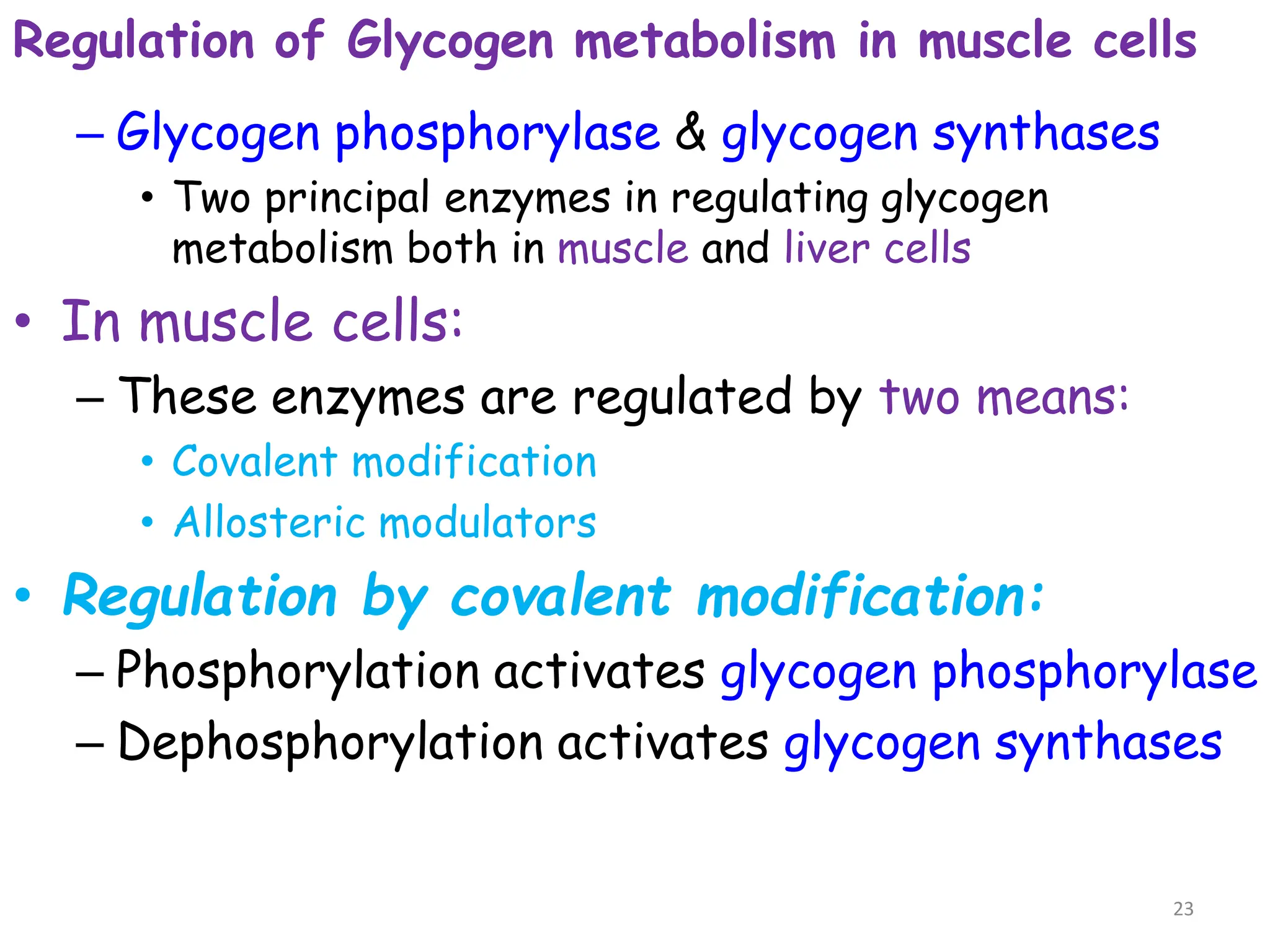
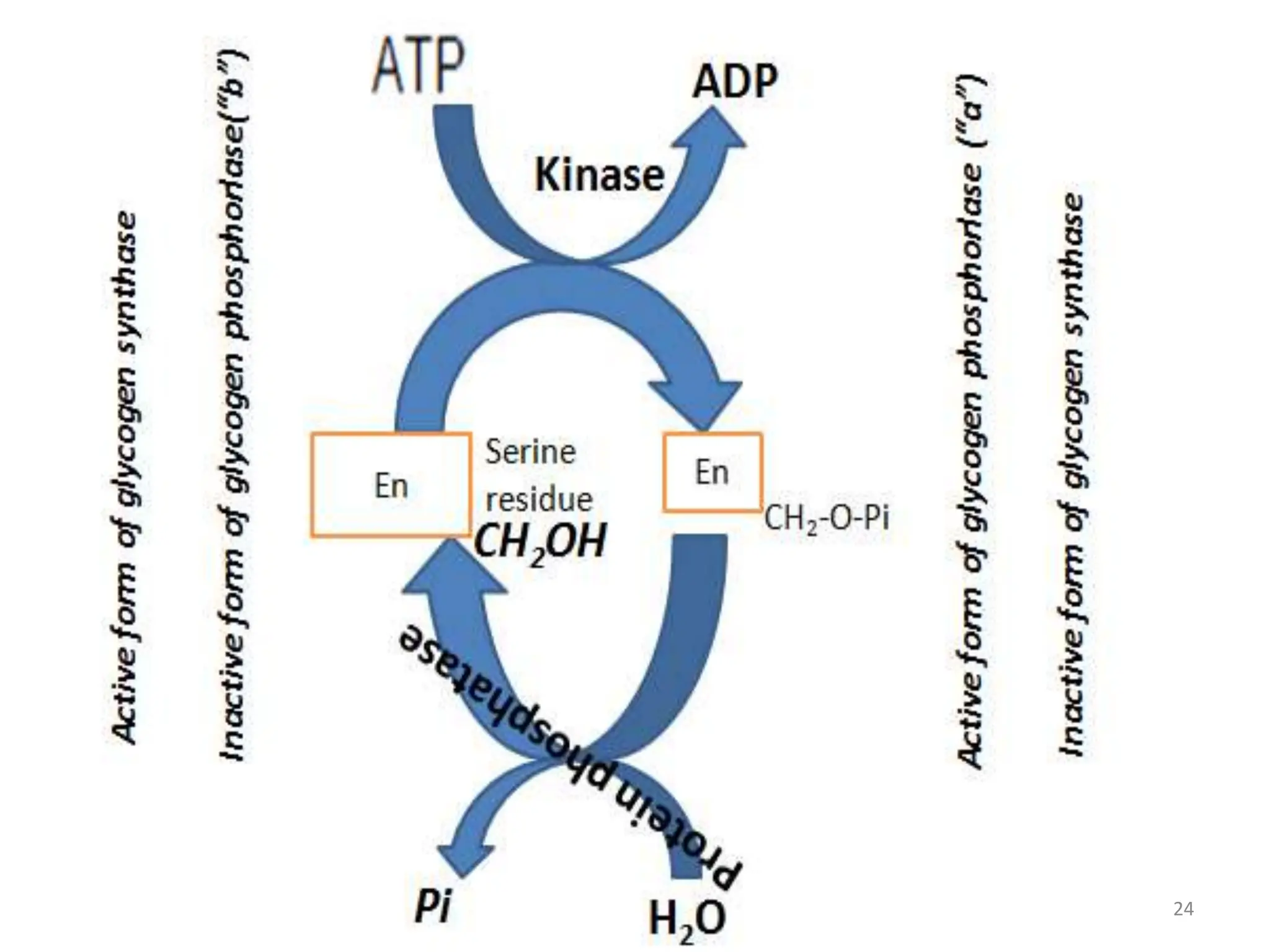
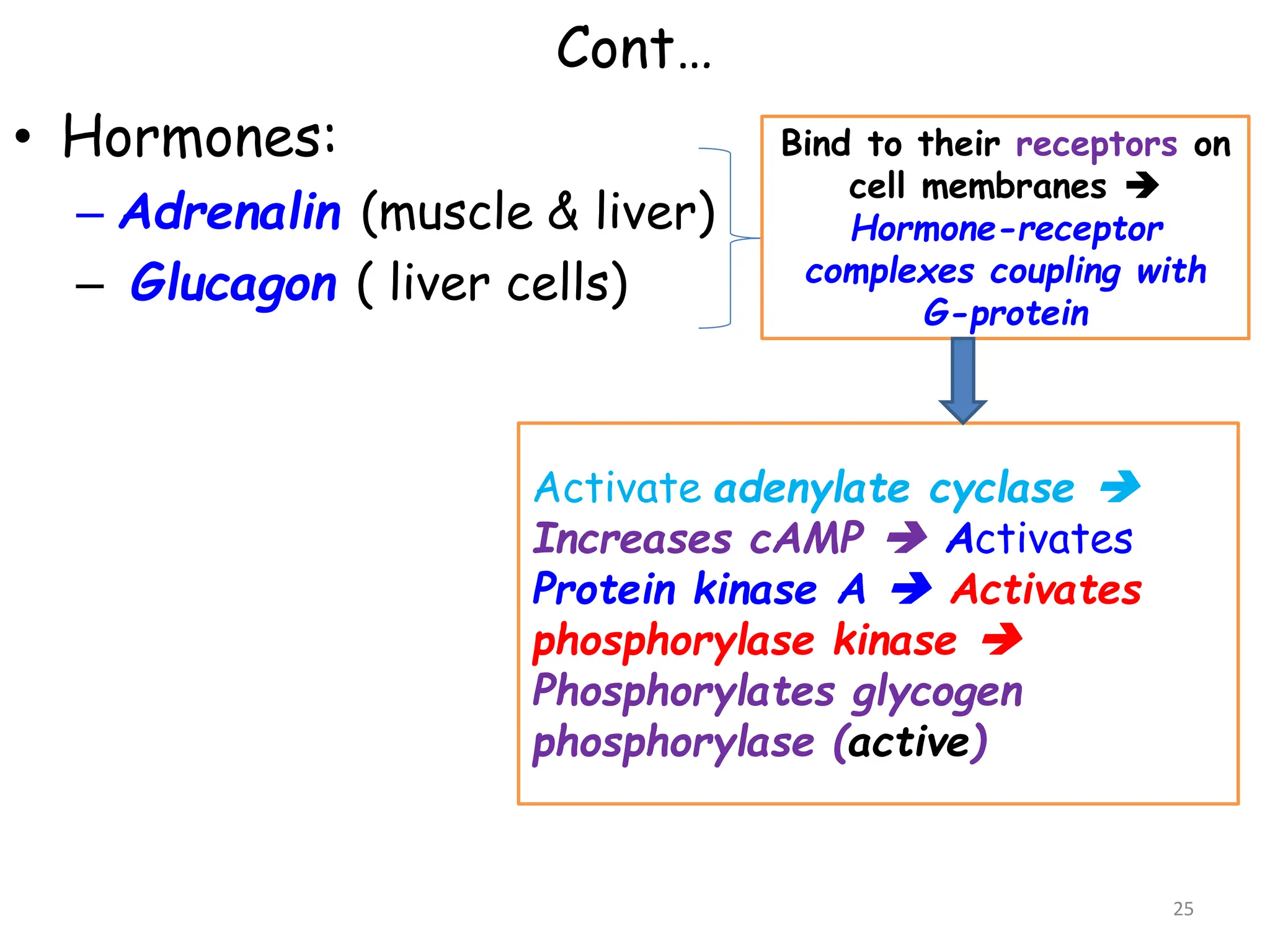
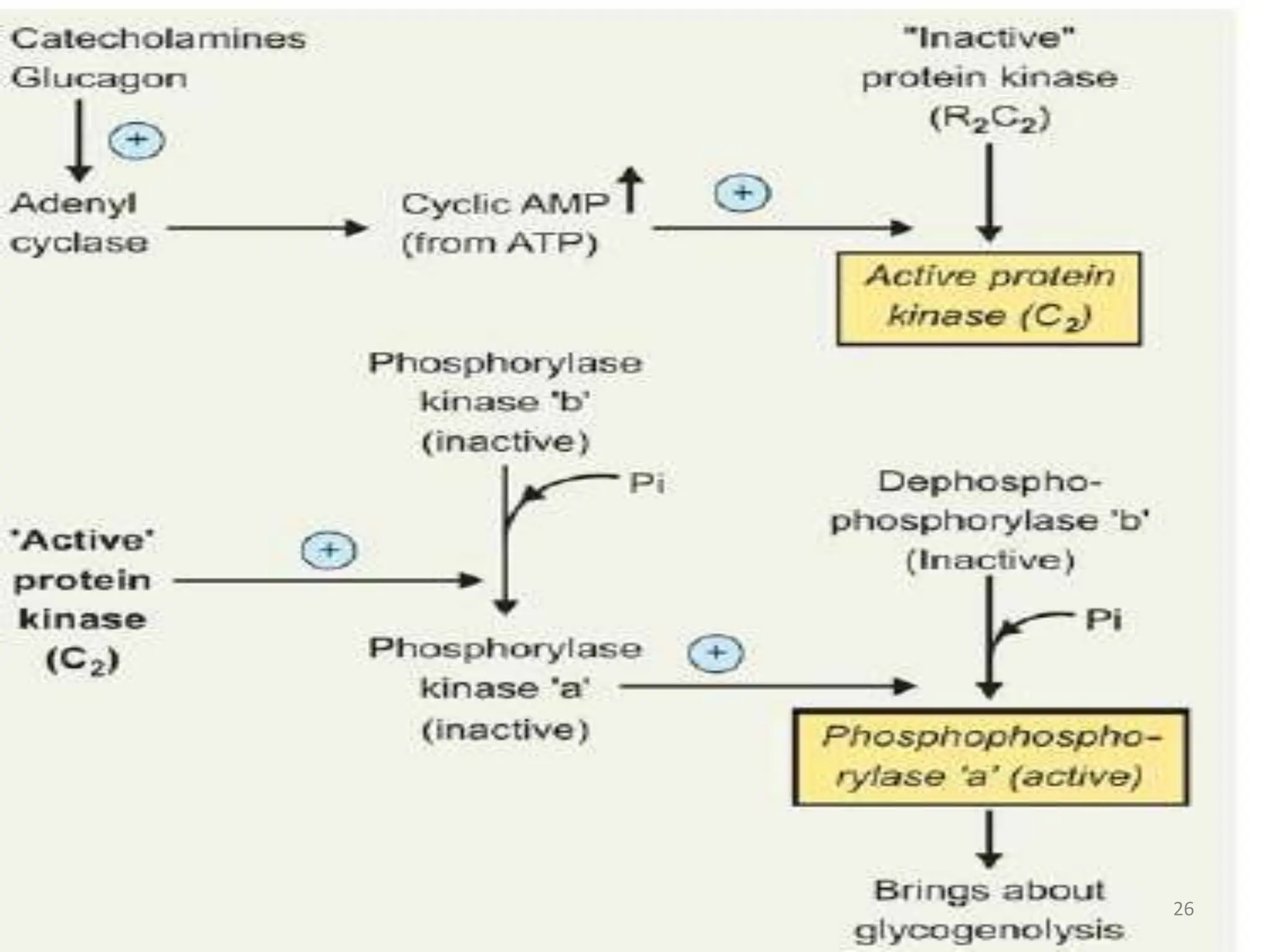
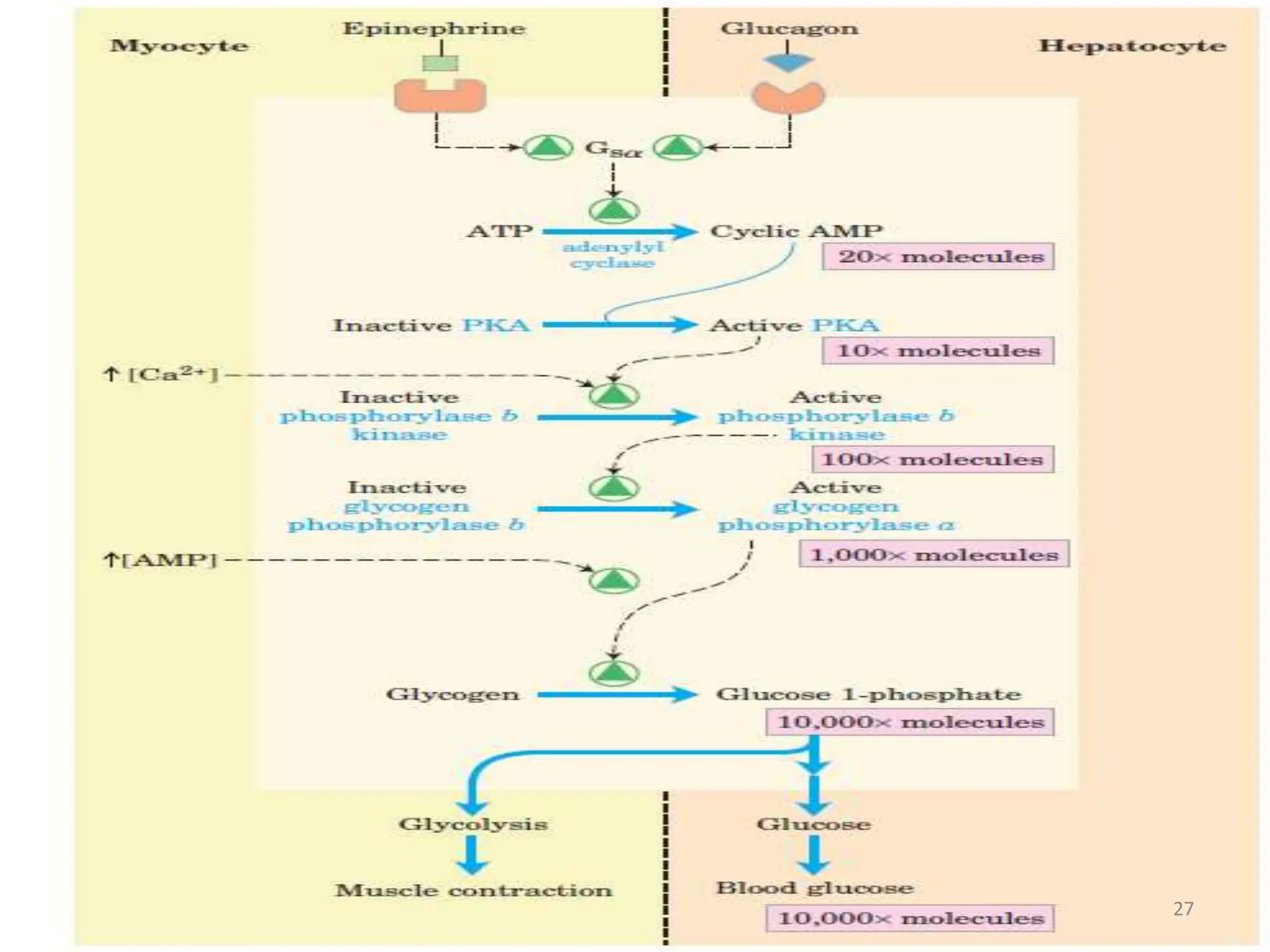
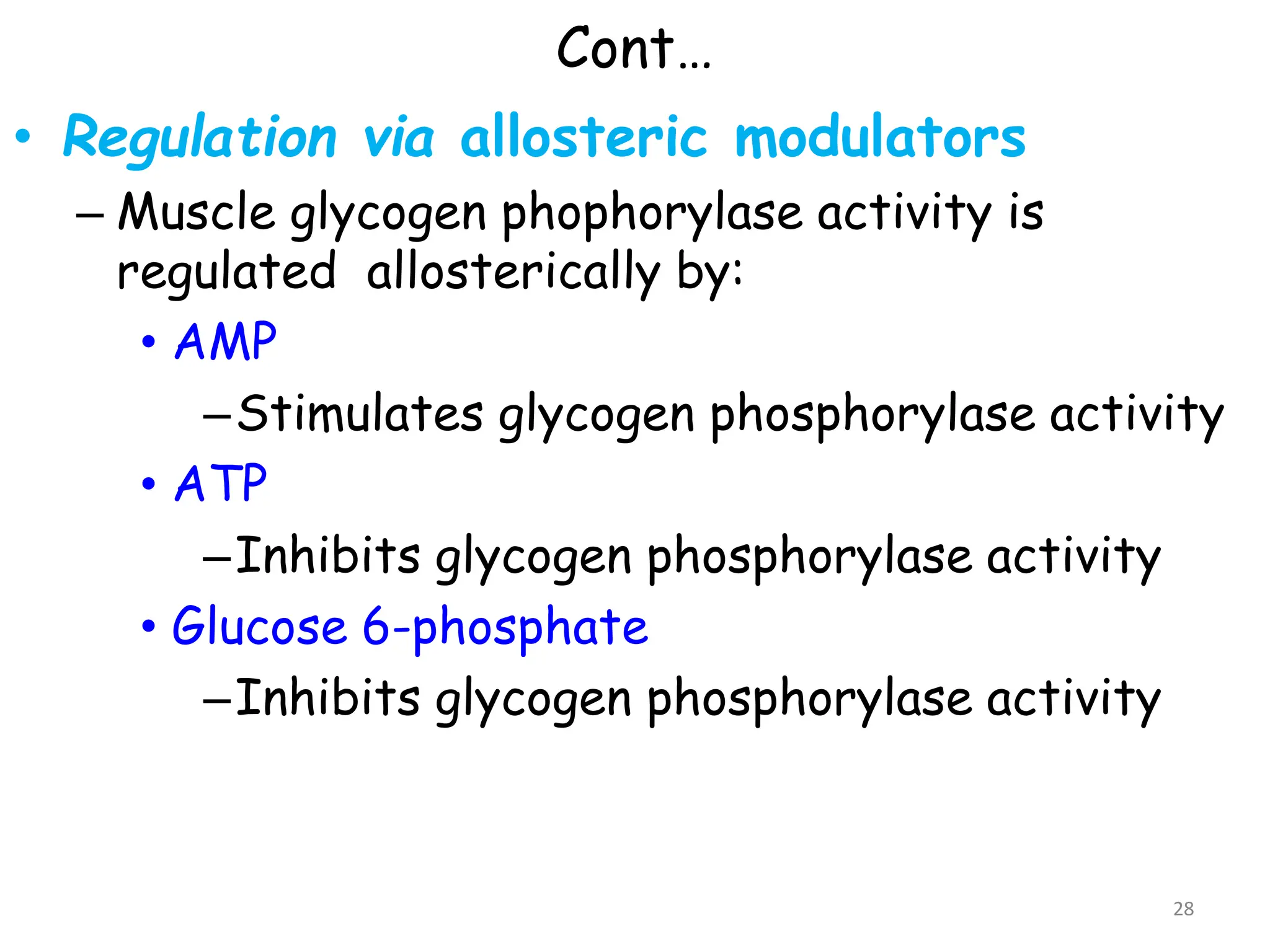
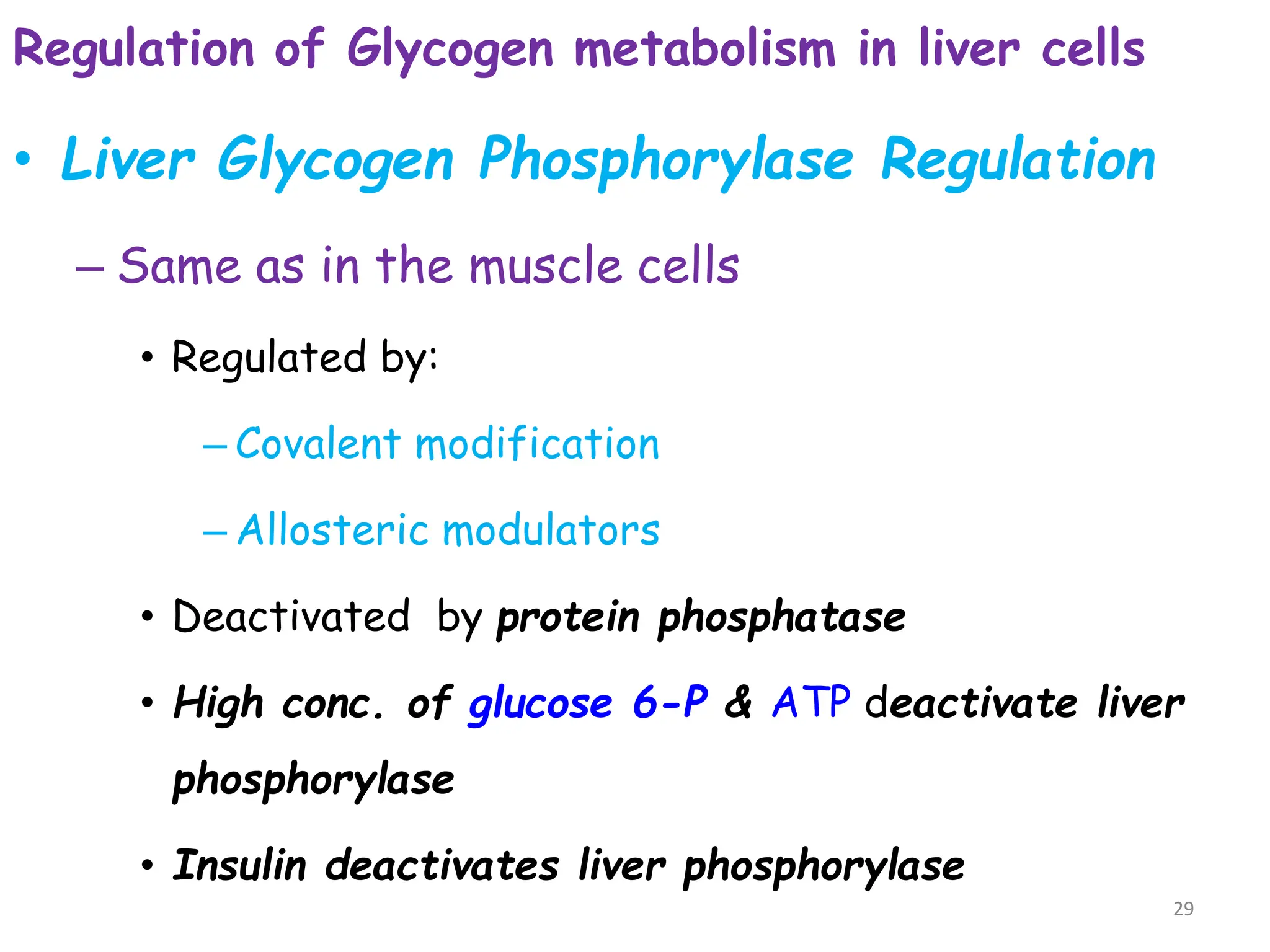
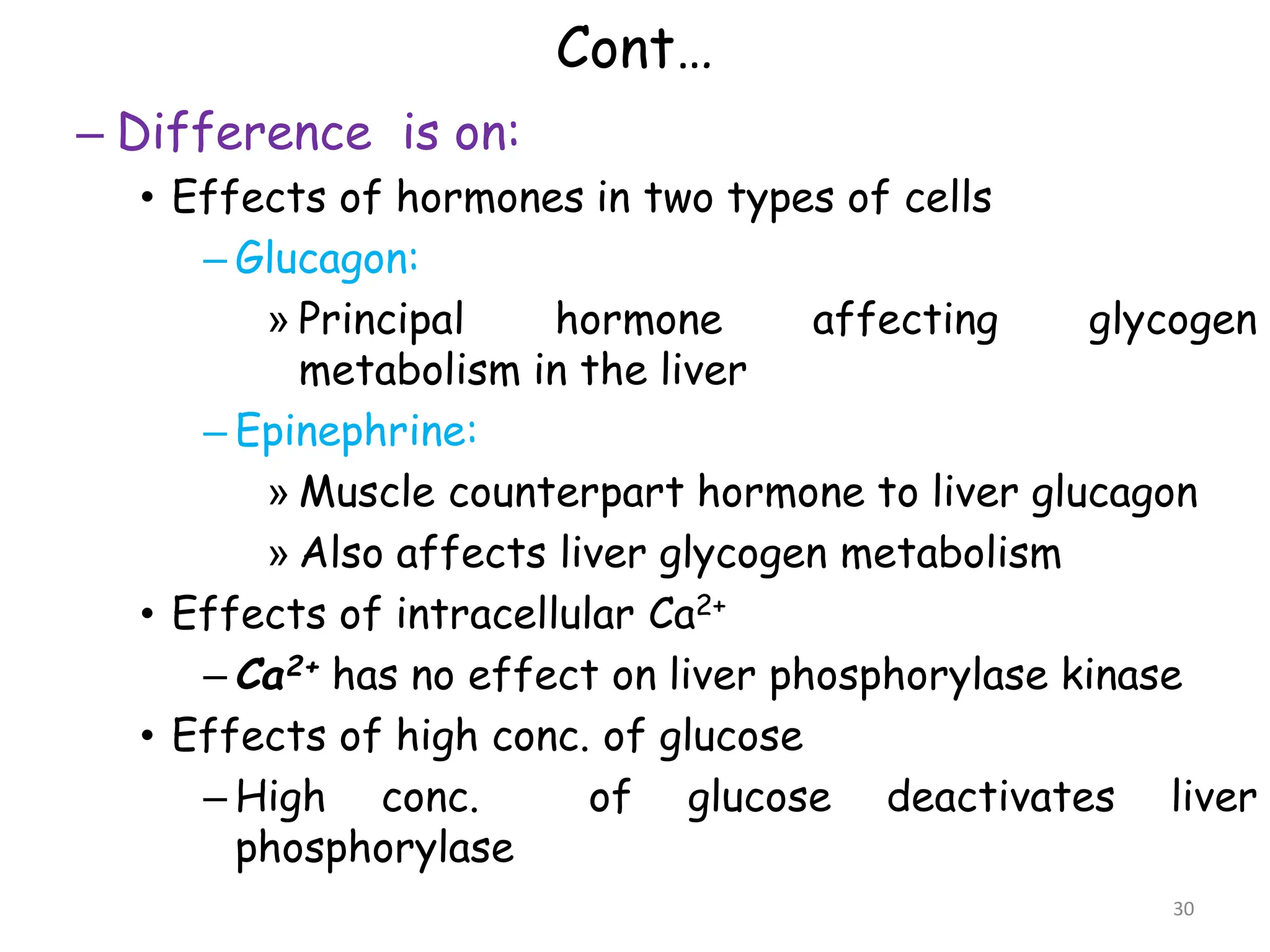
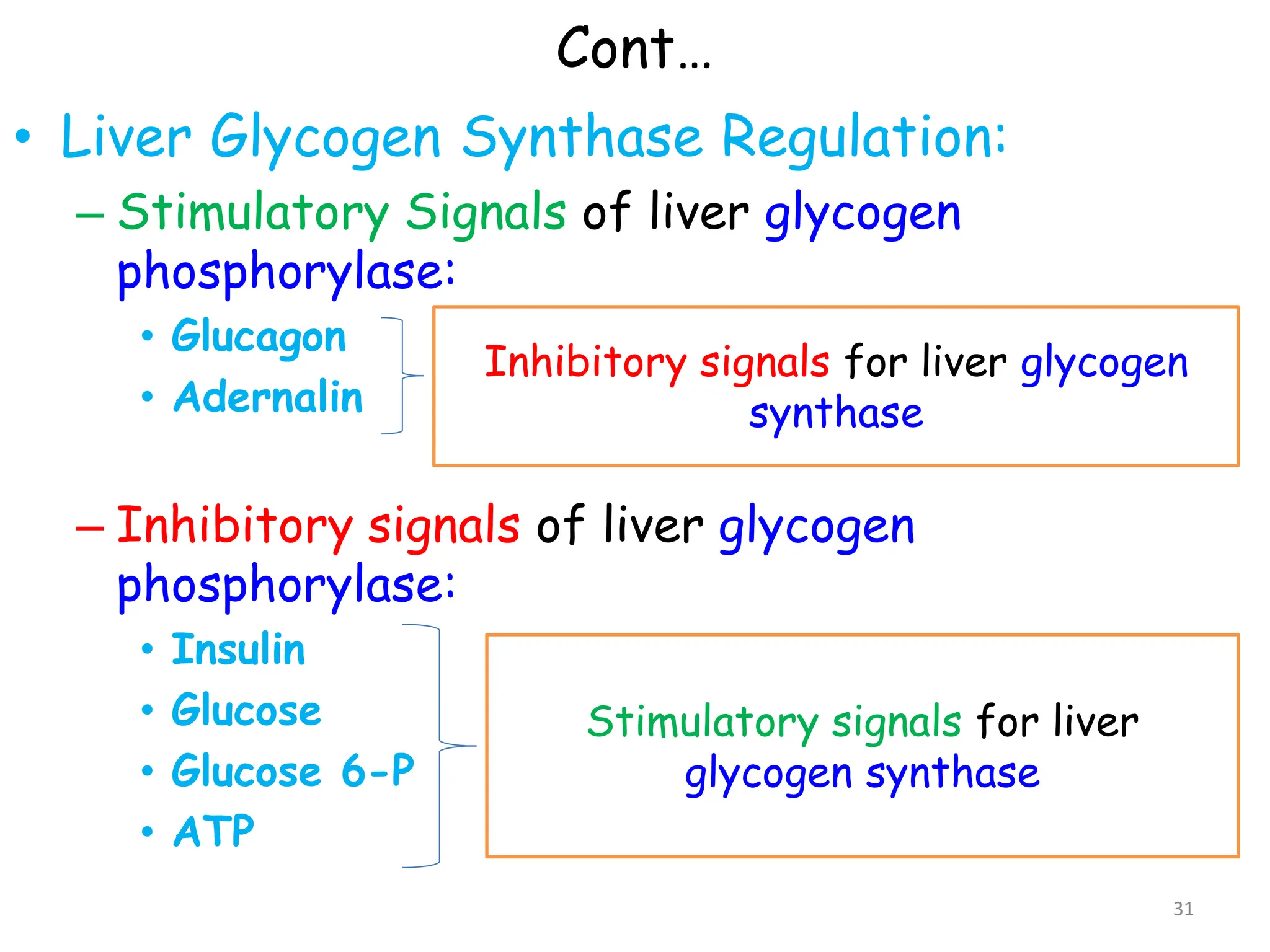
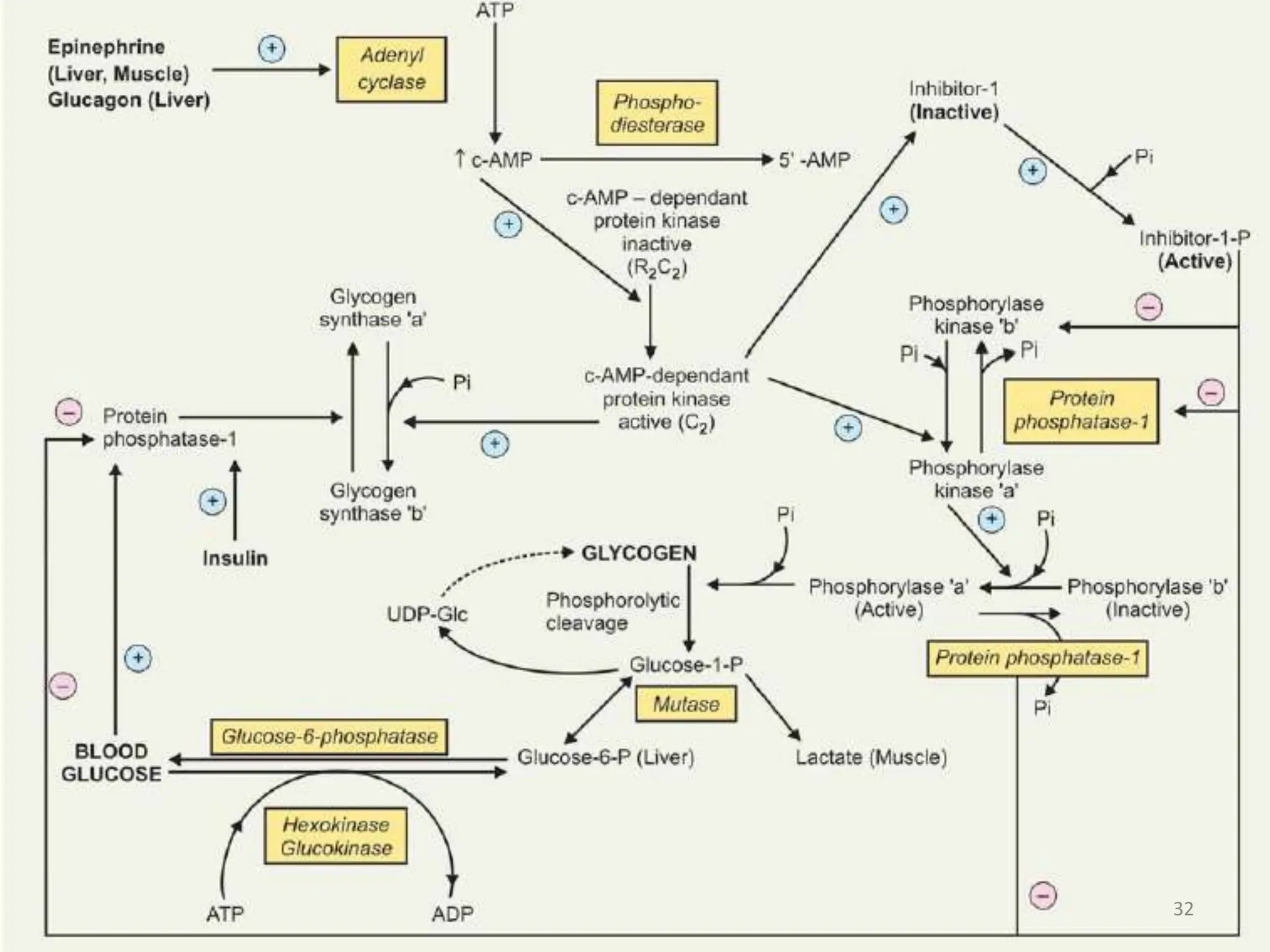
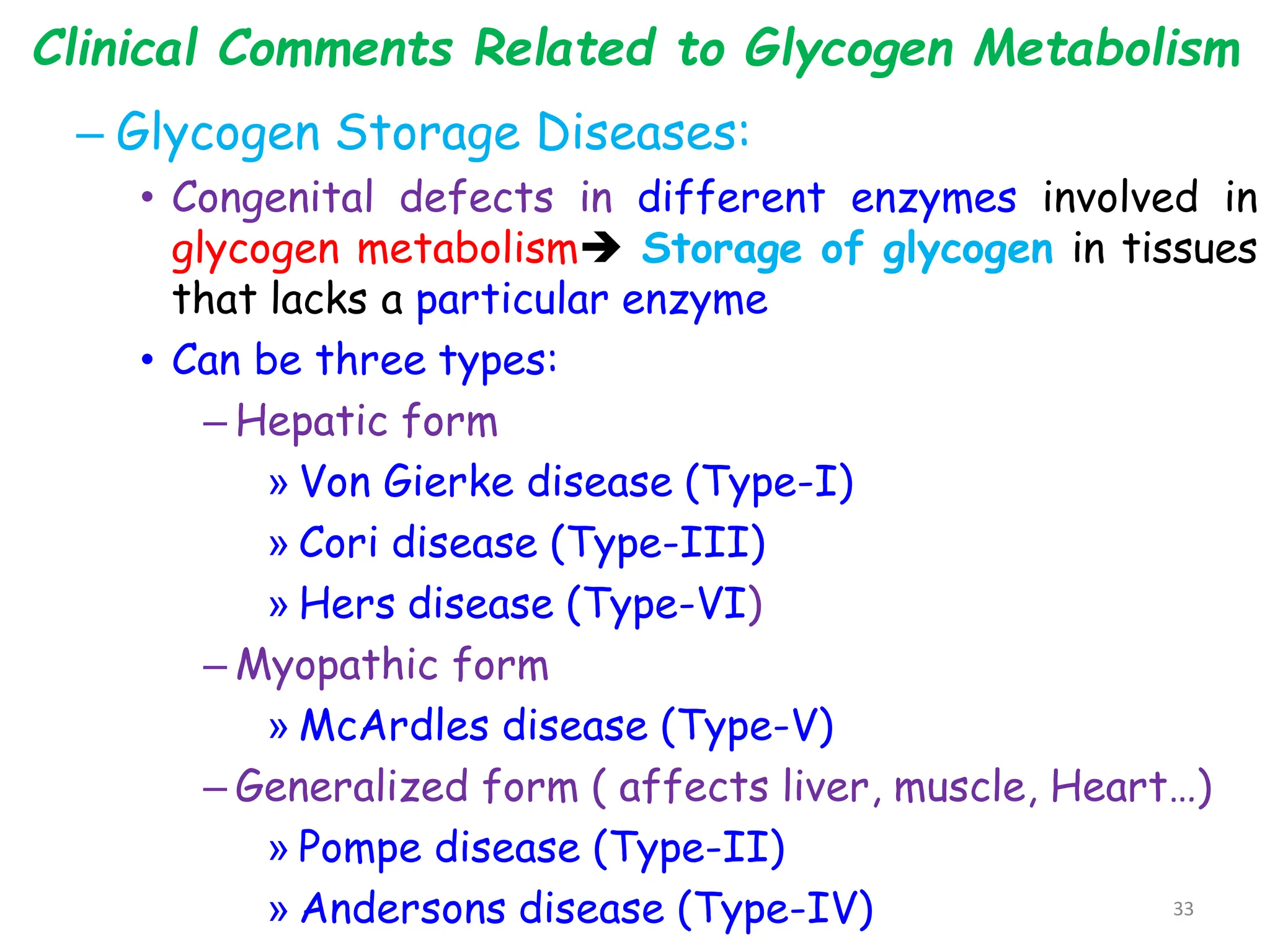
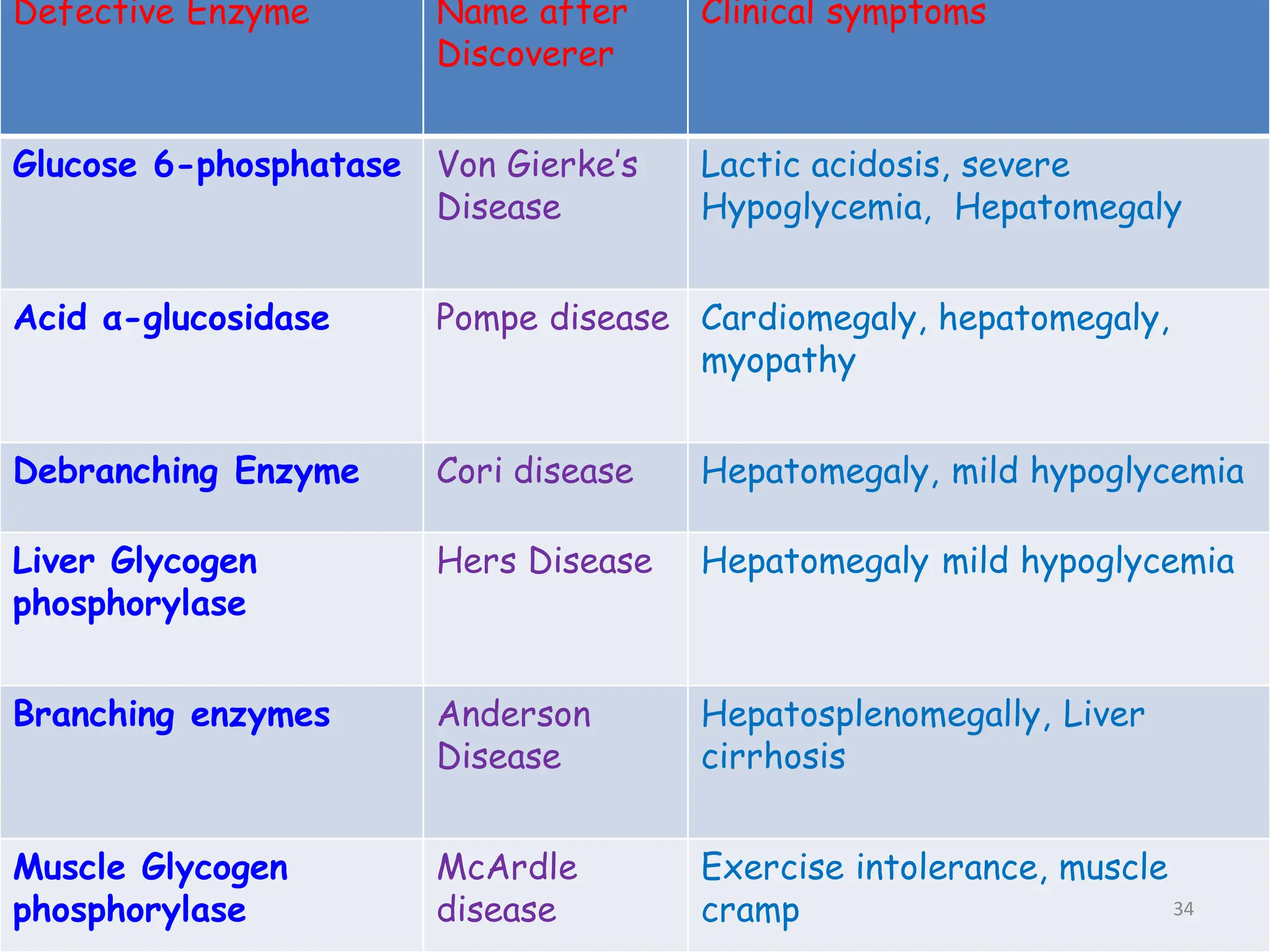
The document discusses glycogen metabolism, highlighting its role as a storage form of glucose in the liver and muscles, and how it is mobilized during energy needs. It details the processes of glycogenesis and glycogenolysis, along with the regulatory mechanisms involved in these phases influenced by hormones and intracellular signals. The document also addresses glycogen storage diseases related to enzyme deficiencies affecting glycogen metabolism.