1) Organisms require chemical energy stored in high-energy compounds for processes like muscle contraction and active transport.
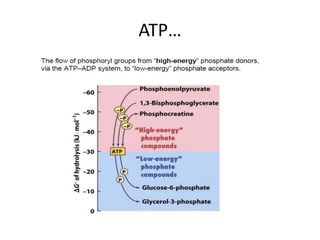
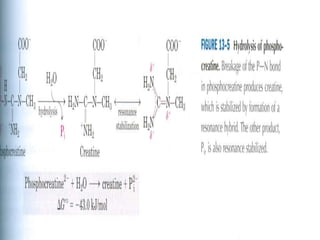
2) High-energy compounds include ATP, phosphoenolpyruvate, and acetyl-CoA, which contain high-energy bonds like phosphoanhydride and thioester bonds.
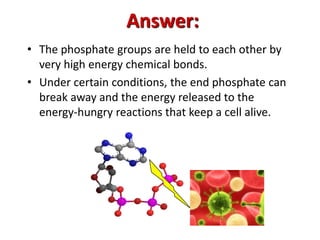
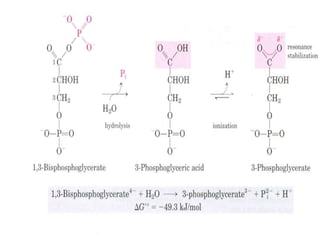
3) ATP is the most common energy currency in cells. It stores and transports chemical energy through its high-energy phosphoanhydride bonds, which are hydrolyzed to fuel energetic reactions.