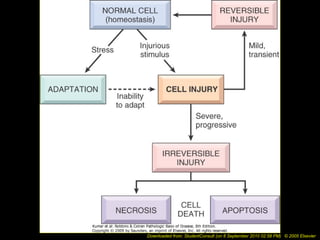
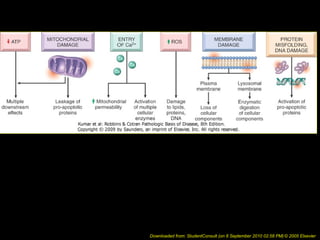
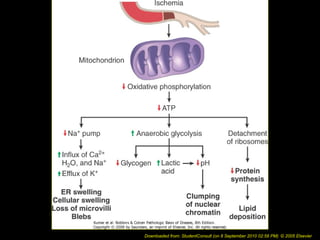
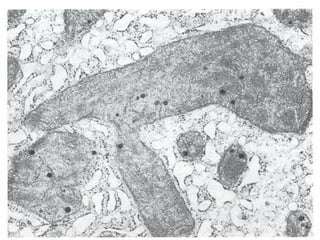
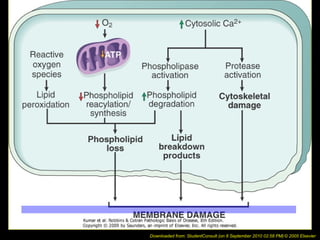
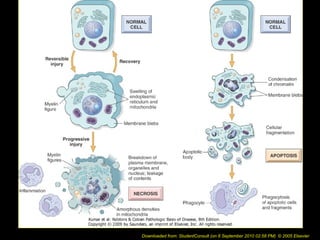
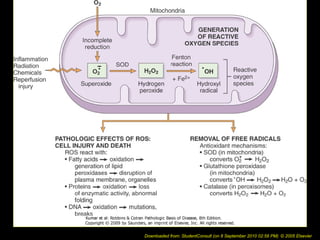
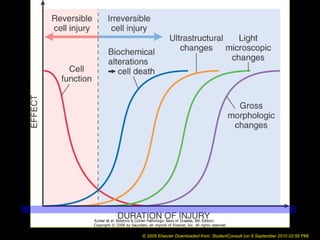
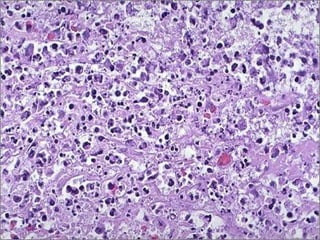
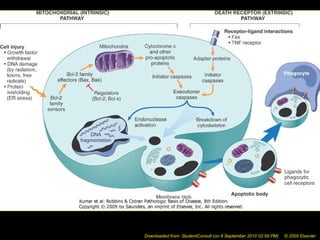
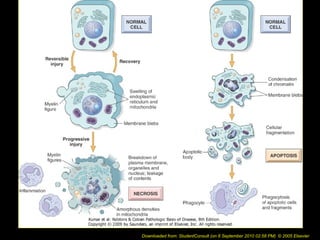
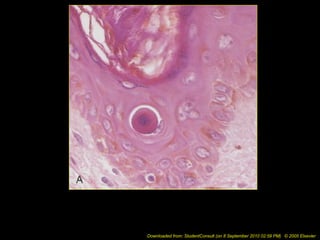
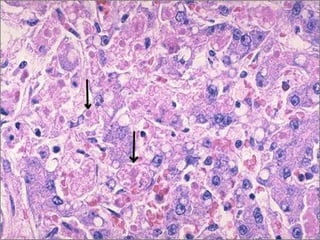
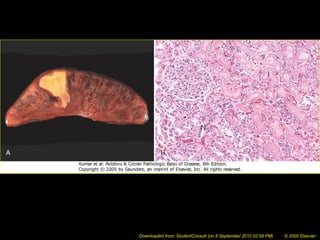
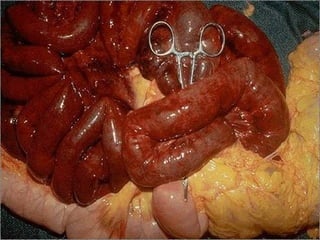
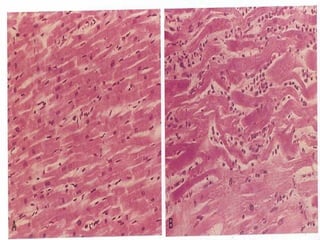
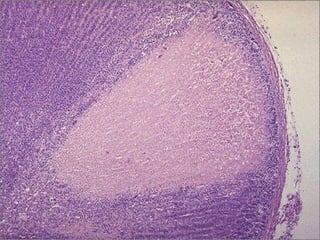
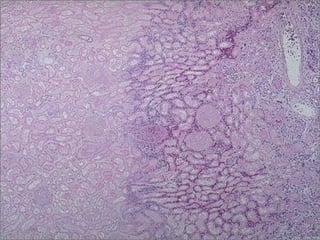
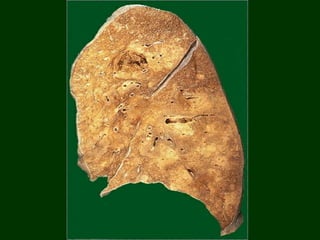
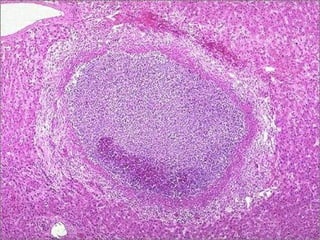
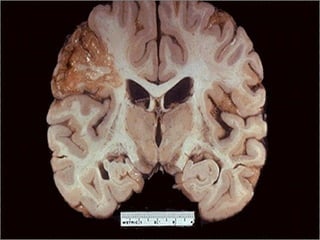
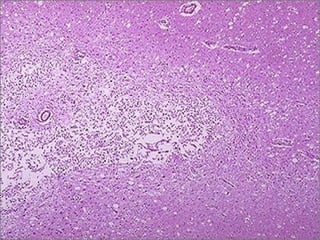
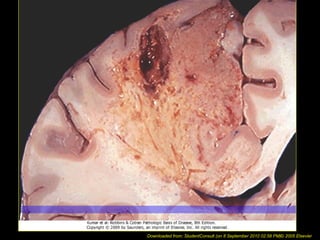
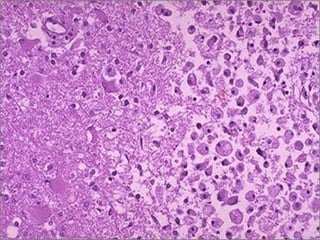
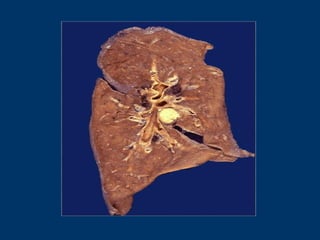
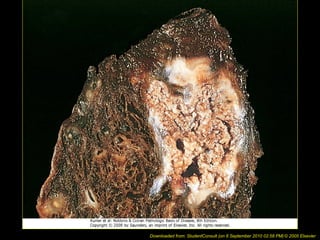
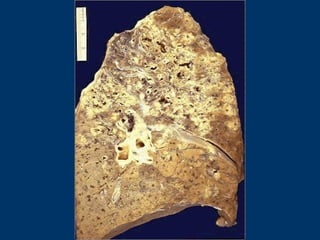
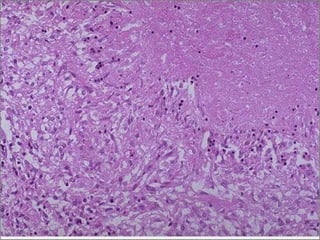
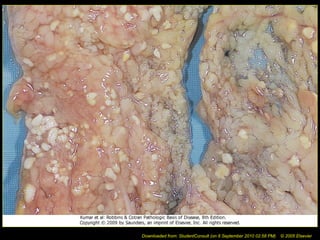
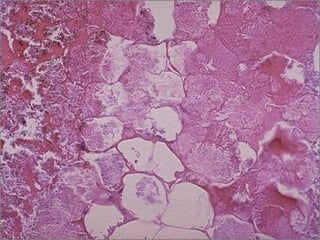
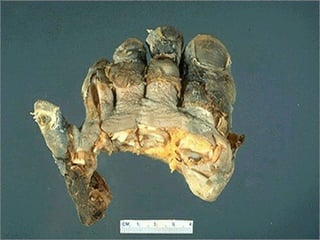
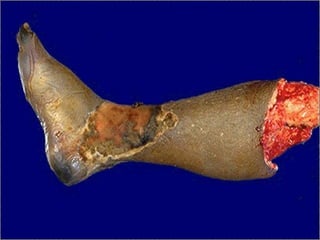
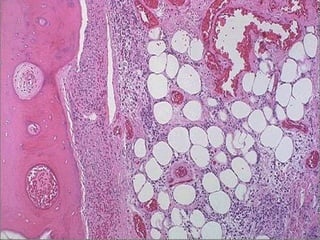
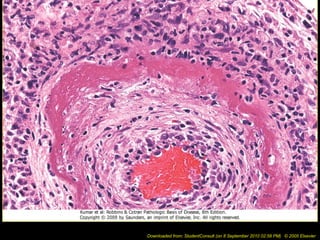
This document discusses cell injury and cell death. It notes that cells have a normal steady state of homeostasis but stress can force adaptation or injury. Cell injury can be reversible or irreversible, depending on the severity and duration of the stress. Irreversible injury leads to cell death. Mechanisms of injury include damage to membranes, respiration, protein synthesis, and DNA. Causes include hypoxia, free radicals, chemicals, infections, and physical or immunological stresses. Reversible injury disrupts mitochondria and ATP production, while irreversible injury severely damages membranes and organelles. The morphology of injury progresses from reversible changes like swelling to irreversible changes like membrane breaks and nuclear fragmentation. Types of cell death include apoptosis and various forms