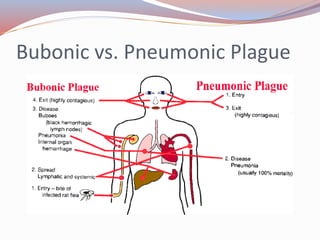
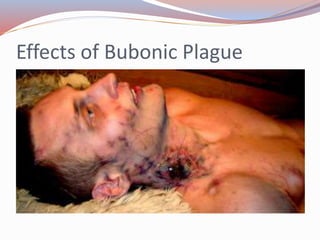
The document summarizes key events and effects of the Black Death pandemic in Europe during the 14th century. It describes how the plague originated in Italy and was caused by Yersinia pestis bacteria spread by fleas on rats. At its peak, it was killing over 7,000 people per day in Cairo. The pandemic led to widespread death, social unrest, accusations against Jewish people, an economic downturn, and religious upheaval including the questioning of the Catholic Church's authority. It took over 100 years for Europe's population and economy to fully recover from the Black Death.