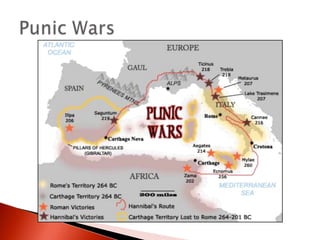
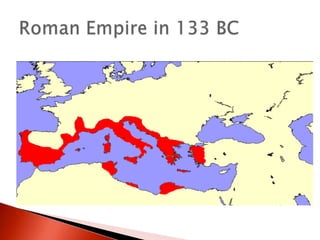
Rome's conquest of Italy brought it into conflict with Carthage, leading to the Punic Wars between 264-146 BC. Rome defeated Carthage in the Third Punic War, destroying the city and selling survivors into slavery. Rome then expanded across the Mediterranean, establishing control over the Greek empires and becoming masters of the western world by 133 BC. However, internal problems grew as wealthy landowners displaced small farmers and inequality increased, sparking reform efforts and civil wars. Order was restored under Augustus, the first emperor, who established a stable government and 200 years of Pax Romana.