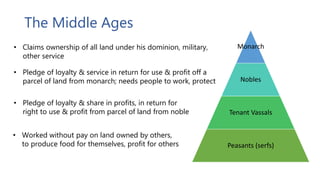
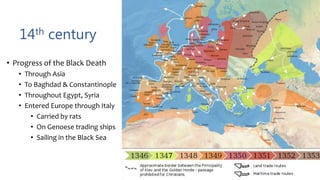
The document provides a historical overview of Europe from the Renaissance to 1815, focusing on the transition from feudalism during the Middle Ages to the emergence of modern society. It details the consequences of significant events such as the Hundred Years' War and the Black Death, which altered social structures, challenged established authorities, and led to increased social mobility and economic changes. The analysis emphasizes the impact of the church, the rise of the middle class, and the evolution of political power during this transformative period.