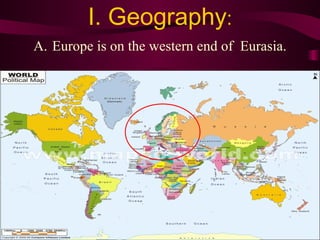
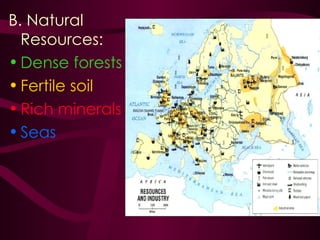
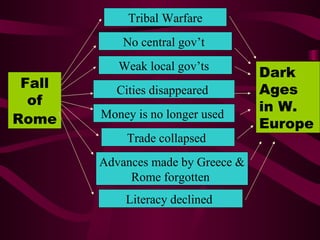
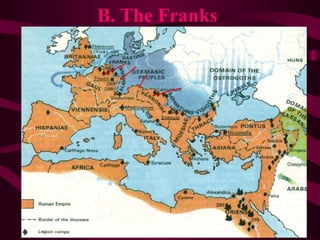
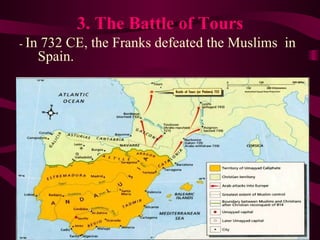
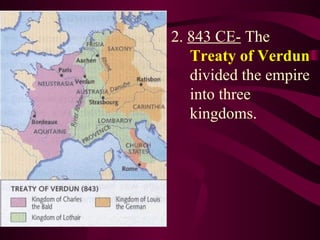
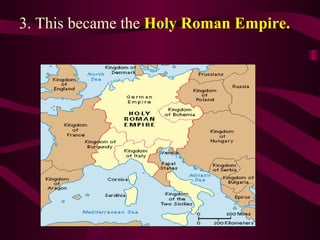
Medieval Europe spanned from 500 to 1500 CE following the fall of Rome. It was characterized by weak local governments and a decline in cities, trade, and literacy. Germanic tribes divided the region into small kingdoms. The Franks, led by Clovis, established the Merovingian dynasty and converted to Christianity. Charlemagne further united Europe under the Carolingian Empire in 800 CE and promoted education. After his death, the empire fragmented and was vulnerable to attacks from Muslims, Magyars, and Vikings. Feudalism developed as a political and economic system defined by the exchange of land for military service between lords and vassals.