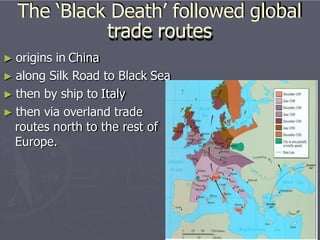
The 14th century in Europe was defined by catastrophic events like the Little Ice Age, the Hundred Years' War, the Black Death plague, and the Great Schism in the Catholic Church. These events had wide-ranging social, economic, and political impacts. The Black Death alone killed 30-60% of Europe's population, weakening the feudal system and strengthening the power of kings over nobles and the Church. Cities grew as survivors fled the countryside, and new social classes like craftsmen rose up. The devastation of the 14th century set the stage for revolutionary changes in the early modern period.









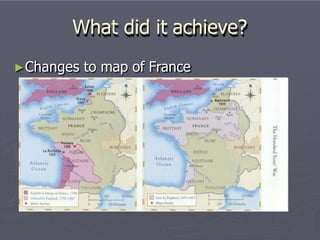
![Changes to the power of the kings
France
Kings become more powerful
-civil war between nobles
ends
- uses the taille [tax] to
increase his treasury
support of the king
England
Rise of French nationalism in Kings become less powerful
- 1341 law states that
Parliament (a council of nobles)
has to approve all taxes
Nobles become more powerful->
leads to civil war- War of the
Roses (ended 1485 by Henry
VII)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calamitous14thcentury2-151027151517-lva1-app6892/85/Calamitous-14th-century-2-11-320.jpg)


![The Black Death (overview)
► 1346-1352
► Spread from Asia to Europe
► Killed 1/3 to 1/2 of the
population (50 - 75 million)
► Up to 50% of some cities
and entire towns and villages
ESPN Effects
►E: manorial/agricultural base
begins to shift to cities and
craftsmen due to loss of serfs
►S: Serfdom ends, the Catholic
Church loses power
►P: kings gain power over noble
and the Church
►N: urban centers [cities] rise,
less dependency on the land](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calamitous14thcentury2-151027151517-lva1-app6892/85/Calamitous-14th-century-2-14-320.jpg)




![The Great Schism [split]
(1378- 1417)
► Began as an argument between the King of France
and the Pope- Who has more power and authority?
► 1305- old pope dies, new one is French-> moves
from Rome to Avignon, France where the Popes
stay until 1377…advantage France
► 1377- Pope Urban VI is elected in Rome –
advantage the Catholic Church
► French Cardinals refuse to recognize Urban VI and
elect their own Pope
• Now there are 2 Popes!!! (one in Rome, one in Avignon)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calamitous14thcentury2-151027151517-lva1-app6892/85/Calamitous-14th-century-2-20-320.jpg)
![► 1408 Kings call a Council to elect a new Pope.
However, both old Popes refuse to step down, now
there are three popes!!!!!
► 1417 a Council removes all three popes and selected
Pope Martin V which ends the Great Schism.
► The Pope would never again be able to successfully
challenge the power of the kings in Europe.
The Great Schism Continues
► The two Popes excommunicated each other along
with the people who followed them. Now all
Catholic Christians [throughout Europe] were going
to Hell….Advantage: other power structures - kings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calamitous14thcentury2-151027151517-lva1-app6892/85/Calamitous-14th-century-2-21-320.jpg)
![14th Century Economic Effects
Peasants:
Smaller labor supply: as farm
workers decreased, wages
increased
Per capita income increased:
there were fewer people
[Black Death].
Cost of food decreased due to
decreased demand
Serfs left land -,went to cities
and craftsmen [artisans]
Wages soared
Nobles:
land is worth less
serfs leave land reducing
the workforce
fewer crops to harvest
and sales were at low
prices – less income
rising prices for newly
manufactured goods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calamitous14thcentury2-151027151517-lva1-app6892/85/Calamitous-14th-century-2-22-320.jpg)

