Embed presentation
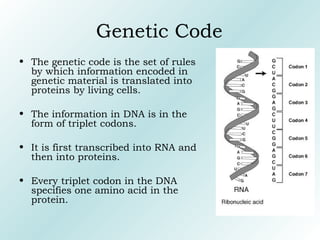

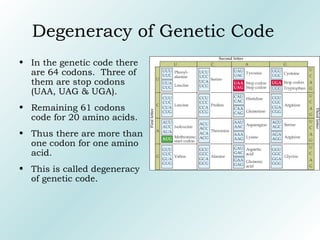

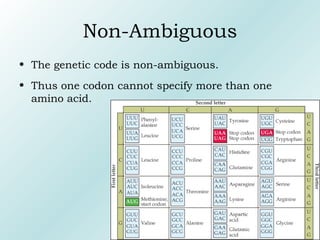
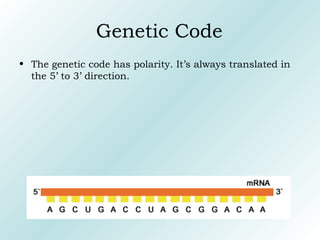
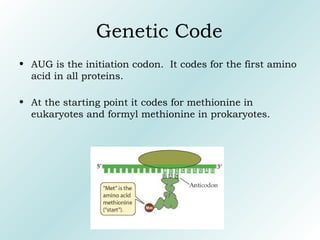
The genetic code contains rules for translating genetic information in DNA into proteins. It uses triplet codons where each codon specifies a single amino acid. The code is degenerate, with more than one codon coding for an amino acid. It is non-overlapping and non-ambiguous, with each codon corresponding to only one amino acid. Translation proceeds continuously in a 5' to 3' direction, with AUG always initiating protein synthesis and specifying methionine.






