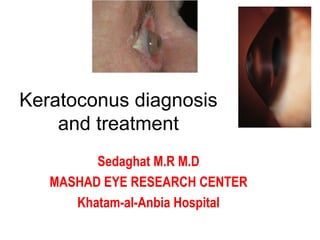
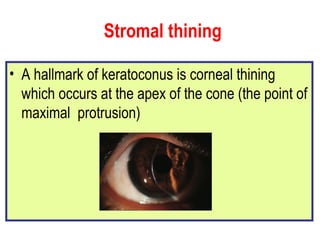
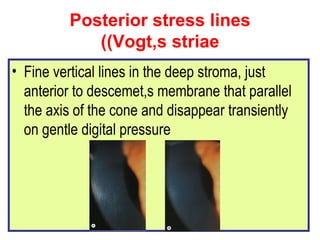
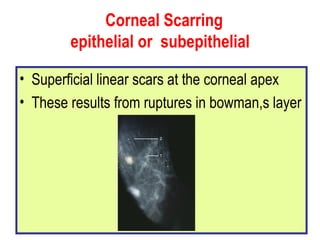
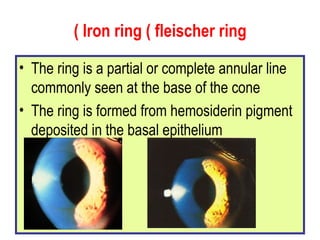
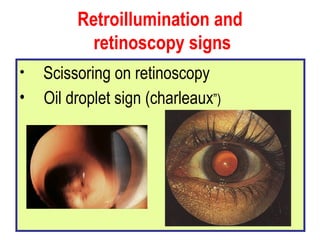
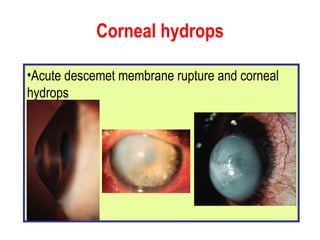
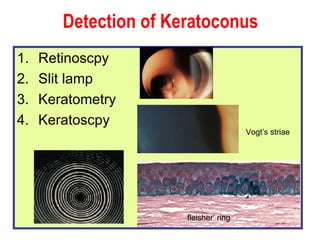
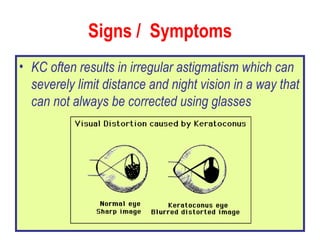
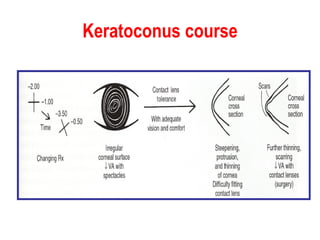
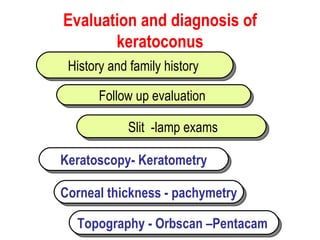
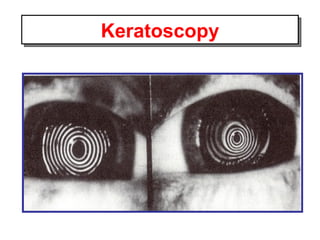
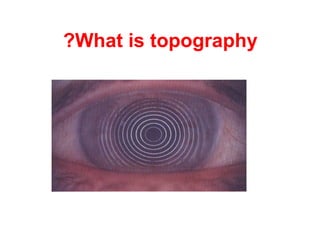
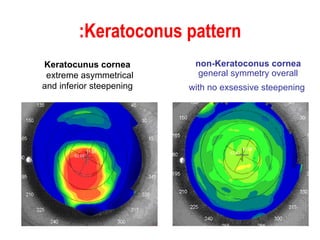
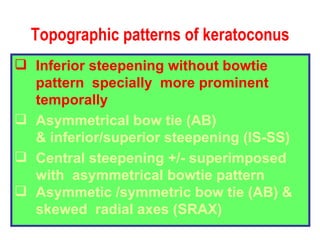
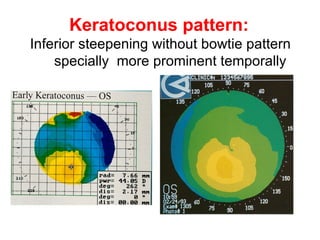
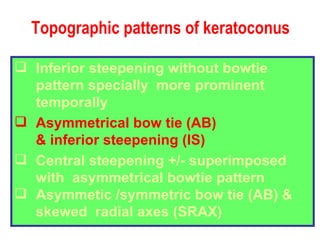
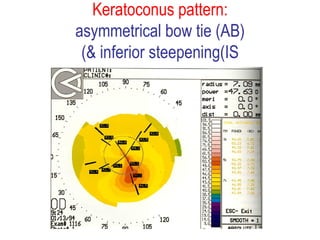
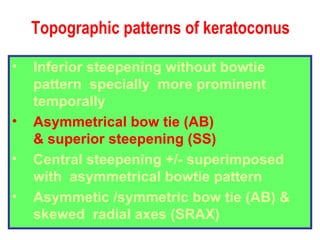
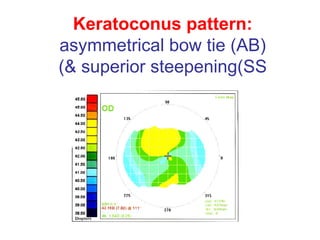
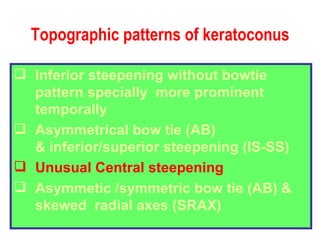
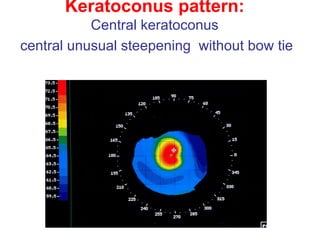
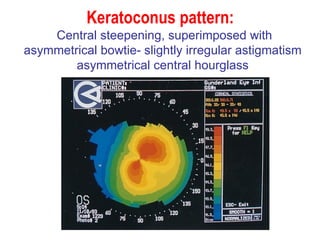
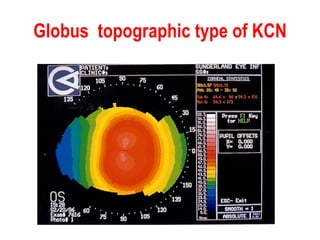
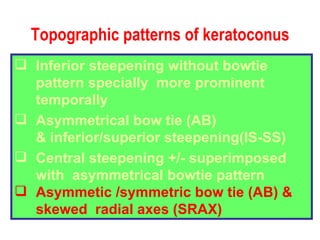
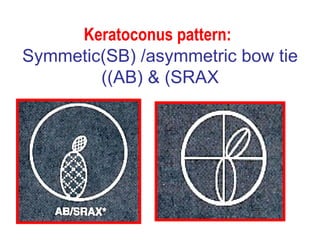
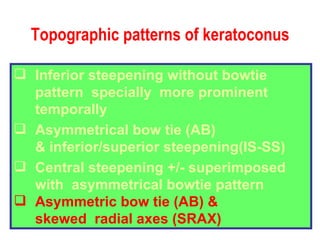
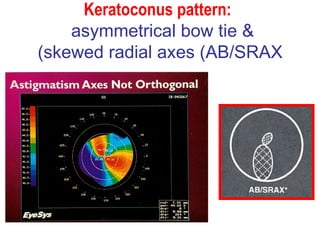
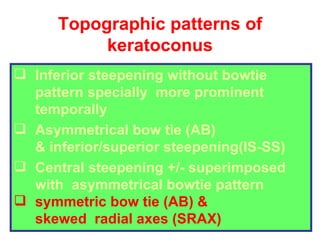
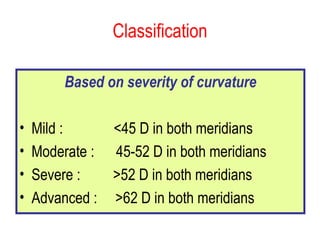
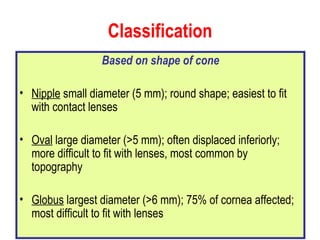
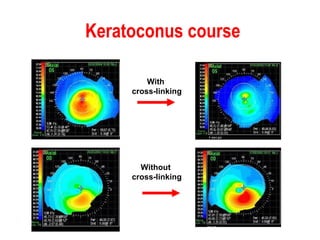
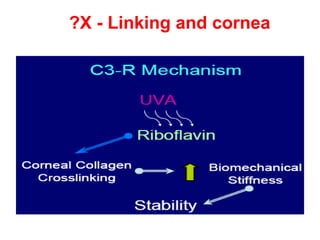
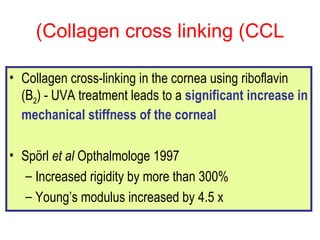
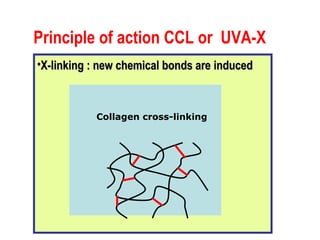
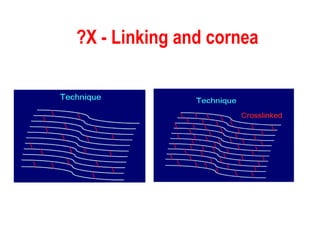
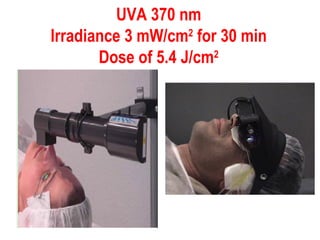
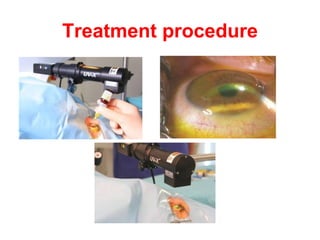
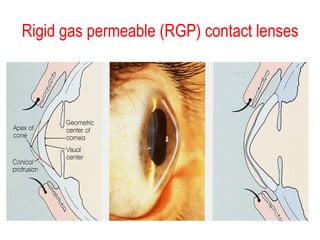
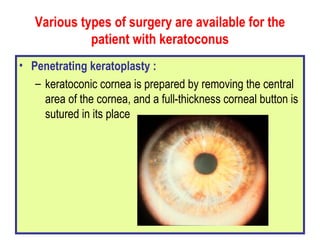
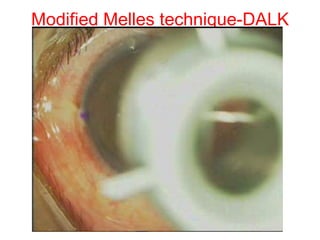
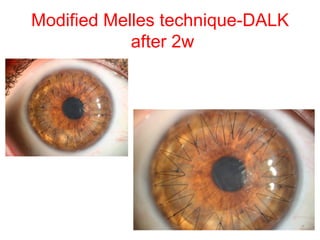
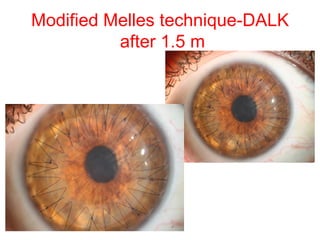
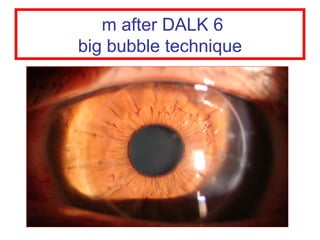
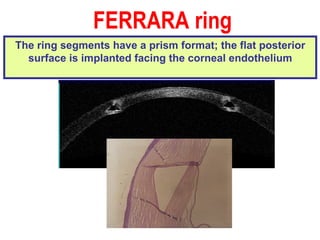
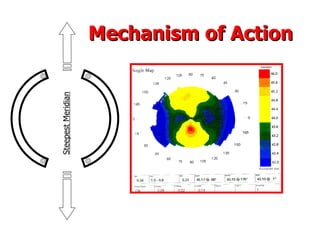
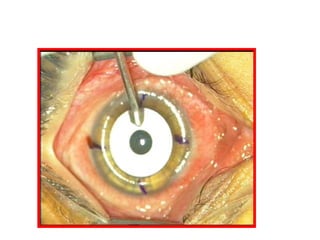
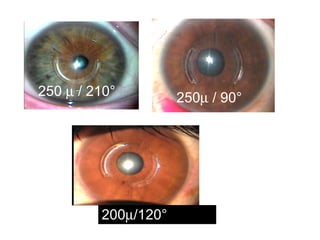
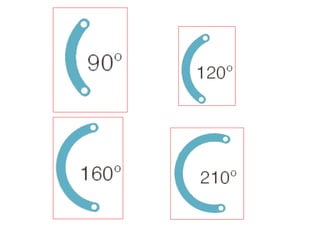
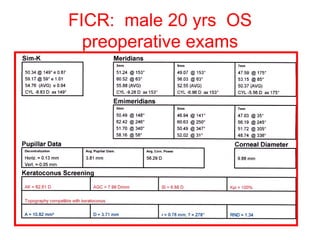
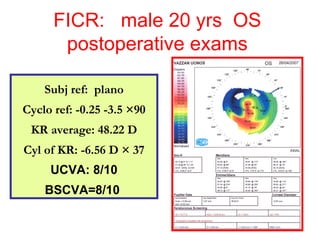
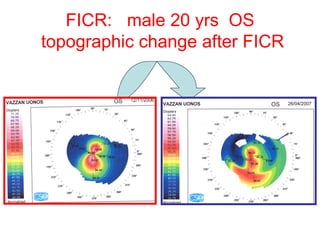
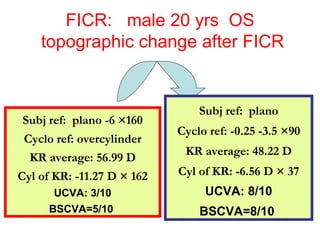
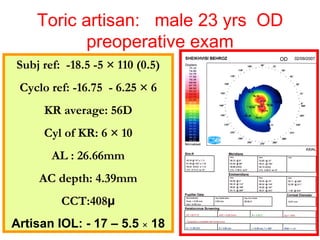
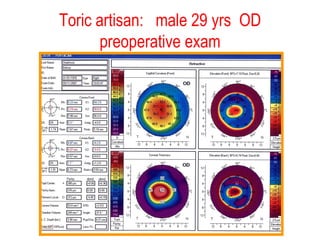
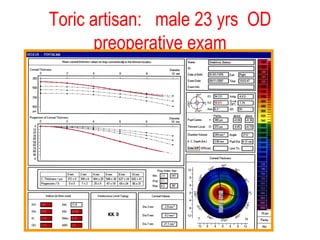
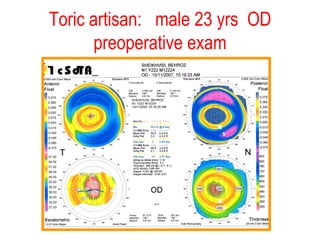
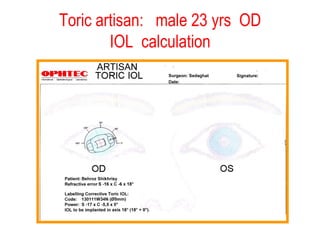
This document summarizes keratoconus diagnosis and treatment. It discusses the prevalence of keratoconus, signs and symptoms, clinical classification, evaluation methods including topography, and classification based on severity. Keratoconus is typically diagnosed based on topographic patterns showing asymmetric steepening, such as inferior steepening, asymmetric or symmetric bowties, or skewed radial axes. Evaluation involves history, slit lamp exams, keratometry, pachymetry, and topography to detect patterns indicative of keratoconus.