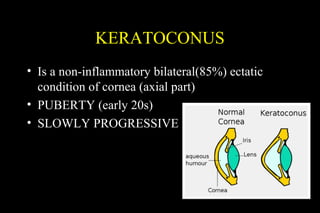
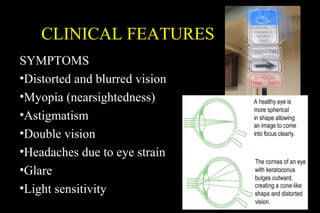
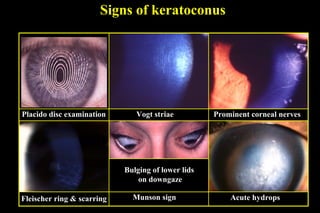
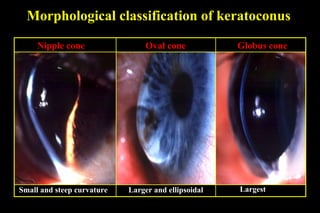
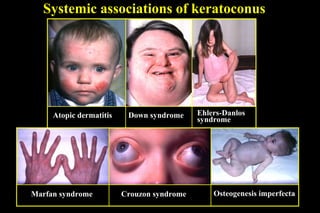
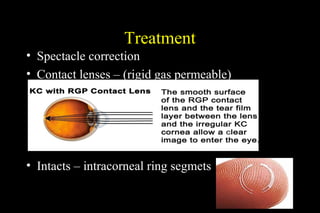
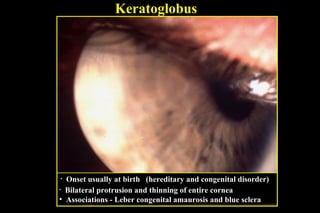
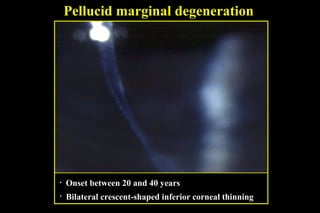
This document discusses ectatic conditions of the cornea, focusing on keratoconus. It defines keratoconus as a non-inflammatory, bilateral ectatic condition of the cornea's axial part, usually emerging in early 20s. While the etiology is unclear, theories include a developmental or degenerative condition. Symptoms include blurred and distorted vision, myopia, astigmatism, and light sensitivity. Signs include corneal thinning, scarring, and bulging of lower lids on downgaze. Treatment progresses from spectacle correction to rigid contact lenses to corneal collagen crosslinking or keratoplasty depending on severity. Keratoglobus emerges at birth as bilateral protrusion and thinning of the entire cor