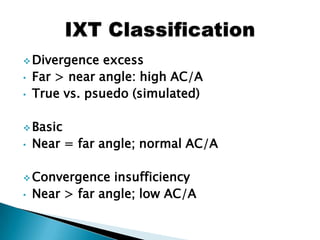
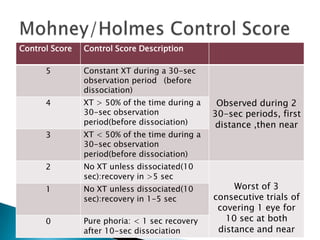
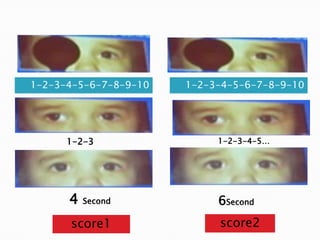
This document discusses intermittent exotropia, providing details on its clinical characteristics, diagnostic evaluation, and treatment approaches. It notes that IXT is the most common type of exotropia, typically onset in early childhood. Control is assessed using a 5-point scale by observing the eye alignment over 30 seconds before and after dissociation. Control can vary throughout the day. Treatment may include optical correction, occlusion, vision therapy to improve fusion and reduce suppression, and in severe cases, surgery.