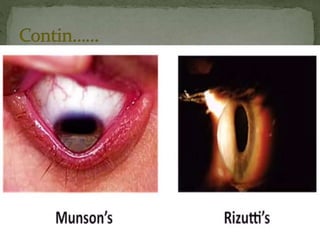
Keratoconus is a non-inflammatory thinning of the cornea that causes it to assume a conical shape, impairing vision. It is usually bilateral and centered below the visual axis. Other similar conditions include pellucid marginal degeneration, keratoglobus, and post-keratoconus. Keratoconus is associated with genetic disorders and eye diseases and can be diagnosed using signs like Munson's sign, Rizzuti's sign, and scissoring on retinoscopy. As it progresses, the cornea develops thinning, Fleischer's ring, Vogt's striae, and scarring. In severe cases, the cornea can rupture causing hydrops.