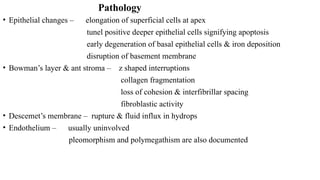
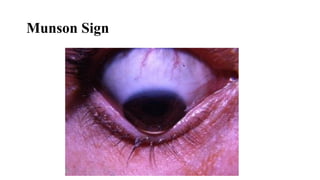
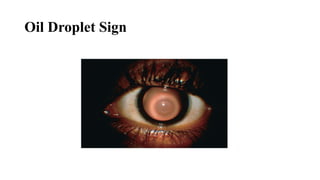
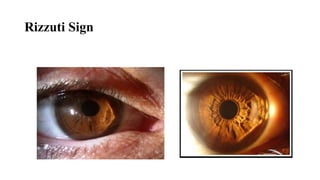
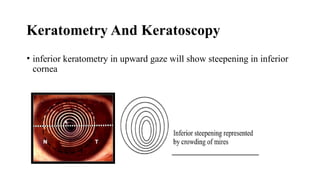
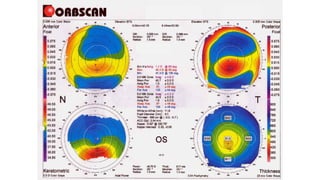
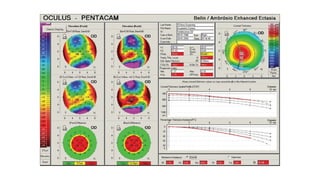
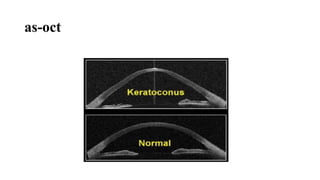
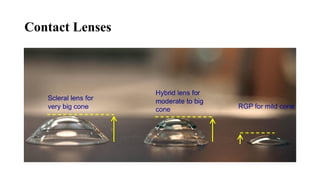
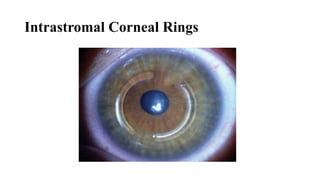
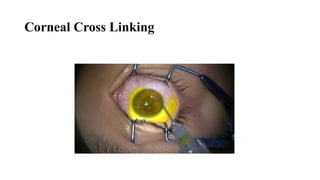
Keratoconus is a non-inflammatory condition characterized by the conical shaping and thinning of the cornea, often leading to visual impairment, particularly prevalent in Asians and individuals from the Middle East. The condition is usually bilateral, has a gradual onset during puberty, and can be influenced by various systemic and ocular disorders. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluations and specialized imaging, while treatment options include spectacle correction, contact lenses, intrastromal ring segments, corneal cross-linking, and keratoplasty.