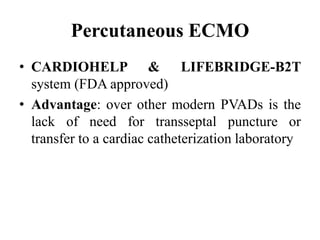
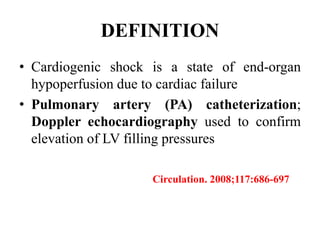
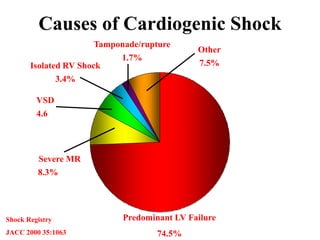
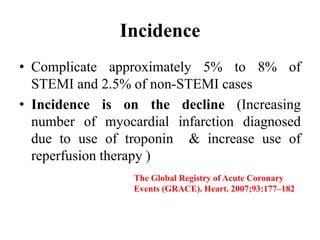
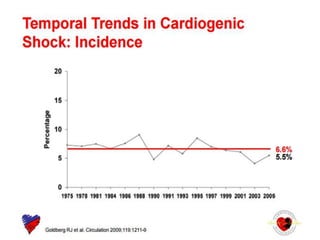
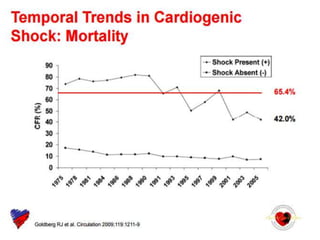
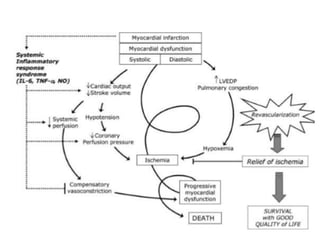
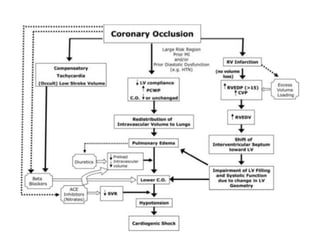
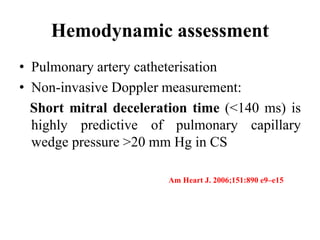
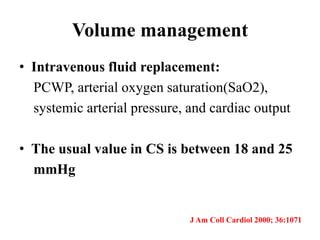
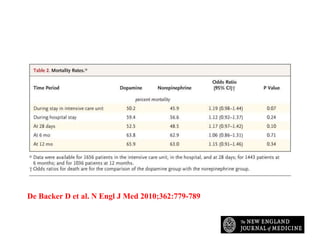
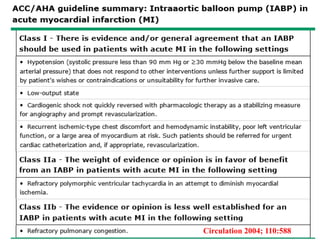
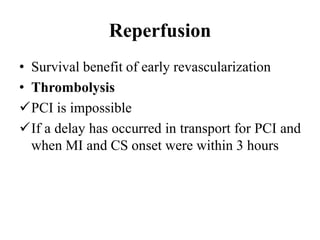
This document discusses the current management of cardiogenic shock. It defines cardiogenic shock and describes its causes, predictors of mortality, and pathophysiology. Treatment involves hemodynamic support, volume management, inotropic drugs, and early revascularization, which significantly reduces mortality. Mechanical circulatory support devices like IABP, Tandem Heart, Impella, and ECMO can further improve hemodynamics and outcomes when used as adjuncts to optimal medical therapy. Timing of revascularization is critical, with survival benefits seen for up to 48 hours after myocardial infarction onset. Special considerations are discussed for managing shock in the elderly, from mechanical causes, and with specific device therapies.

![• Persistent hypotension (systolic blood pressure <80 to 90 mm
Hg or mean arterial pressure 30 mm Hg lower than baseline)
• Severe reduction in cardiac index (<1.8 L / min/m2
without support or <2.0 to 2.2 L/ min/m 2 with support)
• Adequate or elevated filling pressure (eg, left
ventricular [LV] end-diastolic pressure >18 mm Hg or right ventricular [RV] end-
diastolic pressure >10 to 15 mm Hg)
• Clinically by cool extremities, decreased urine output, and/or alteration in
mental status.
Circulation. 2008;117:686-697](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation-151015182524-lva1-app6891/85/Cardiogenic-shock-3-320.jpg)









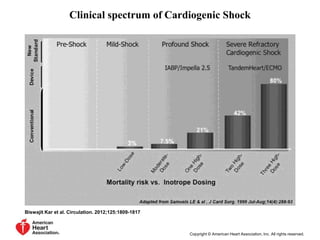
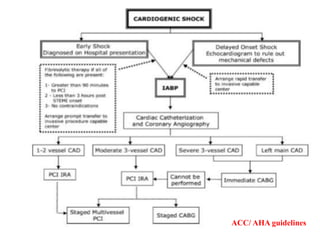
![Timing of PCI
• Presentation 0 to 6 hours after symptom onset
was associated with the lowest mortality
[ ALKK registry(German). door-to-angiography times were <90 minutes in
approximately three fourths of patients. ]
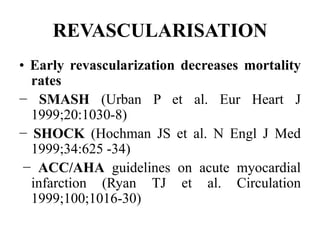
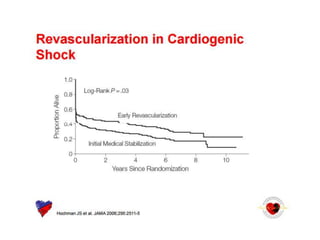
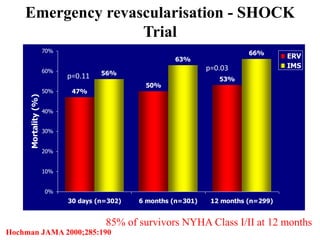
• SHOCK trial: increasing long-term mortality
as time to revascularization increased from 0
to 8 hours
• Survival benefit as long as 48 hours after MI
and 18 hours after shock onset](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation-151015182524-lva1-app6891/85/Cardiogenic-shock-39-320.jpg)

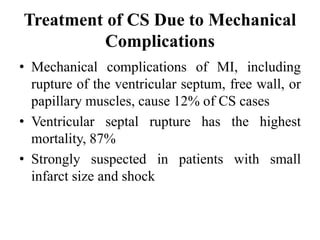
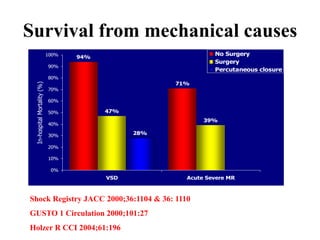

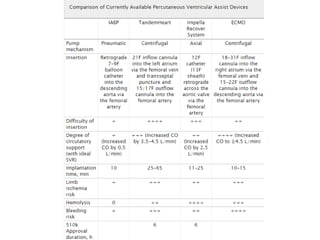
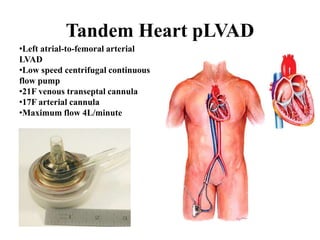
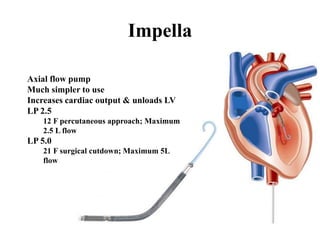
![Other mechanical devices
• Left ventricular and biventricular assist device
: surgically placed, bridge to therapy & bridge to
transplantation
• Percutaneous left atrialto-
femoral arterial ventricular assist device(Tand
em heart)
• ECMO
• Percutaneous transvalvular left ventricular ass
ist device (LVAD)[Impella]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation-151015182524-lva1-app6891/85/Cardiogenic-shock-45-320.jpg)