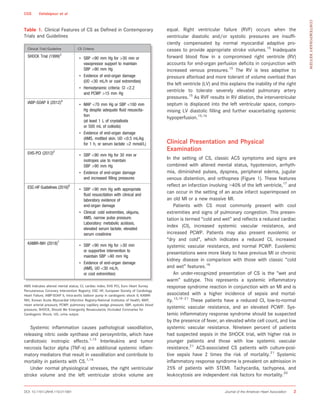
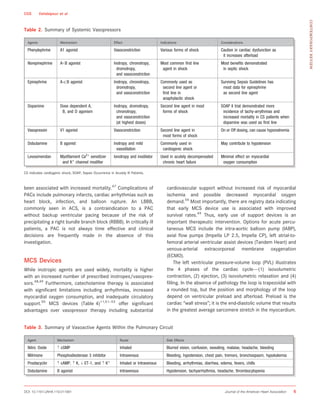
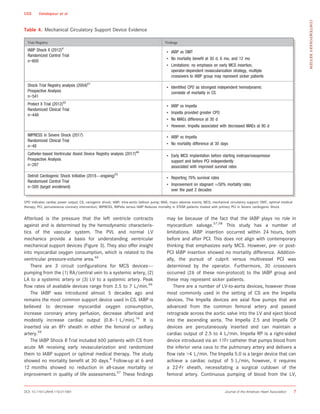
Cardiogenic shock is caused by severe impairment of myocardial function leading to low cardiac output and organ hypoperfusion. It commonly results from acute myocardial infarction and presents as hypotension refractory to fluids with signs of poor organ perfusion. Definitions of cardiogenic shock require hypotension, evidence of end-organ damage, and suspected cardiac dysfunction. Treatment involves revascularization, inotropes, vasopressors, and mechanical circulatory support.