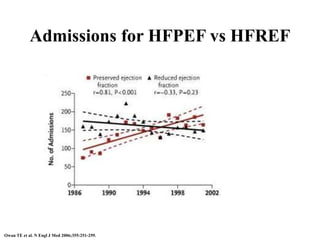
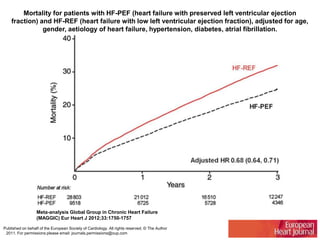
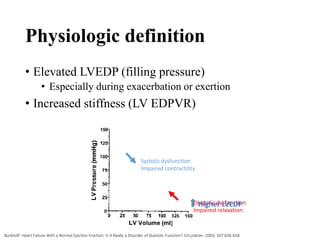
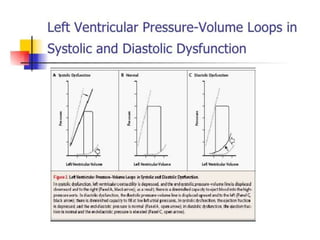
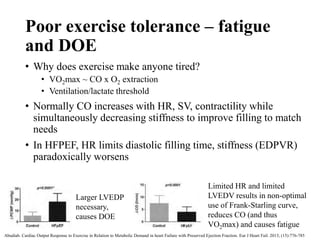
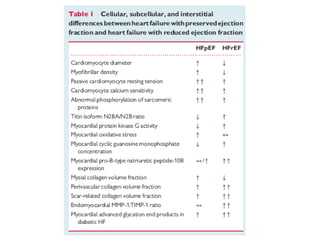
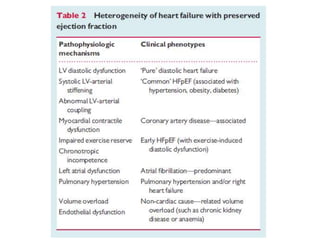
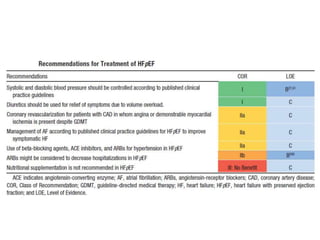
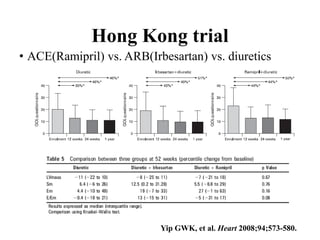
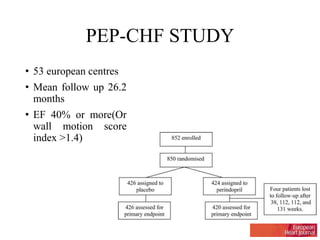
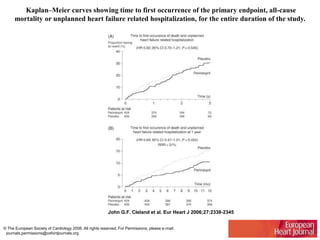
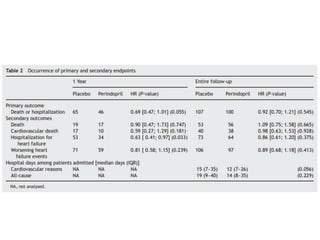
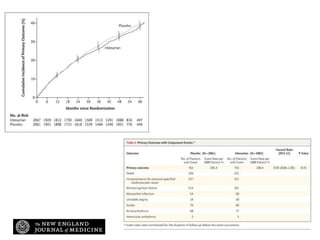
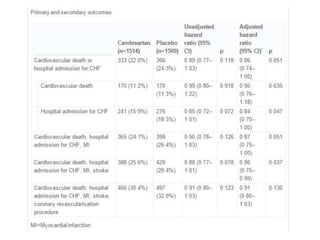
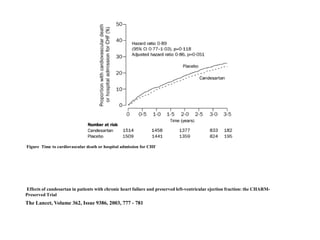
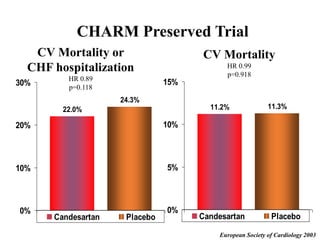
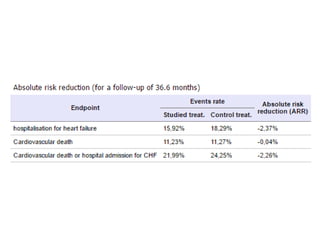
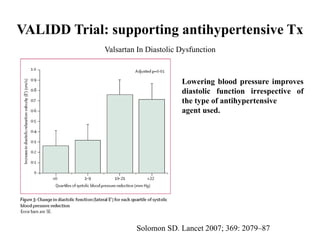
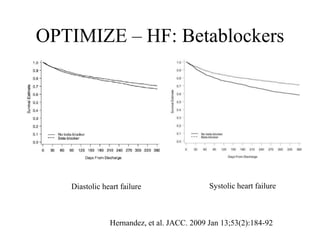
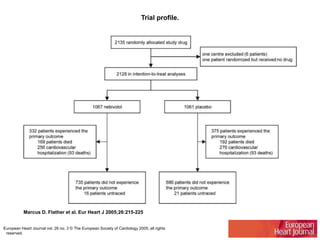
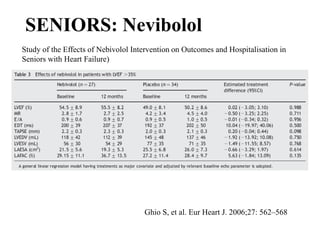
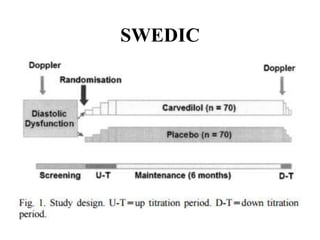
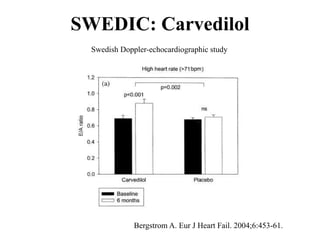
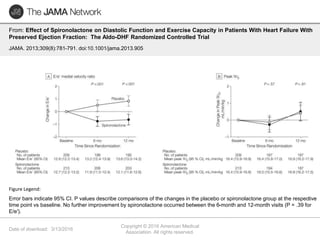
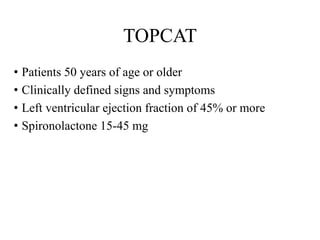
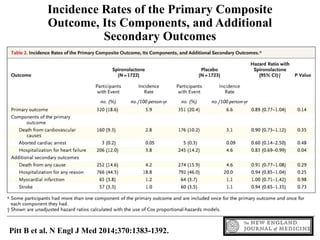
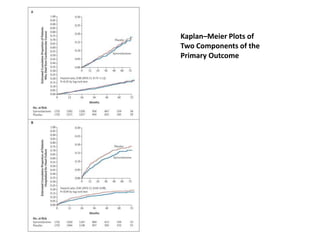
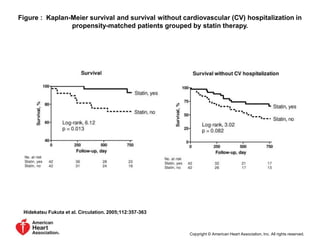
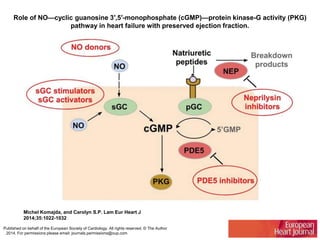
This document discusses heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), formerly known as diastolic heart failure. It provides background on HFpEF versus systolic heart failure and explores the pathophysiology and management of HFpEF. Key points include:
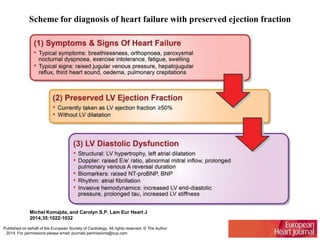
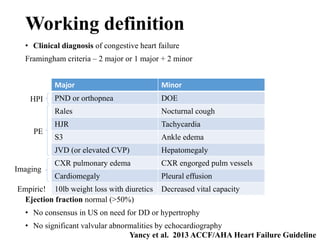
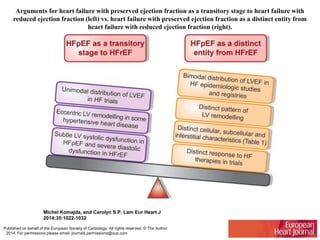
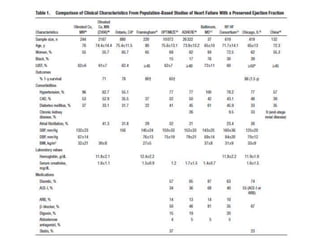
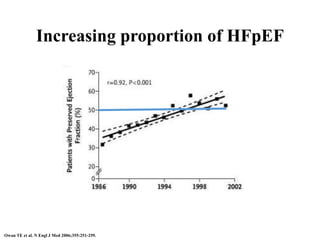
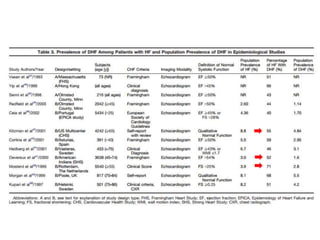
1) HFpEF is a distinct clinical syndrome from heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), with normal ejection fraction but evidence of diastolic dysfunction.
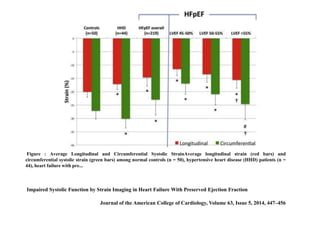
2) Impaired systolic function can be detected in HFpEF patients using strain imaging, despite preserved global ejection fraction.
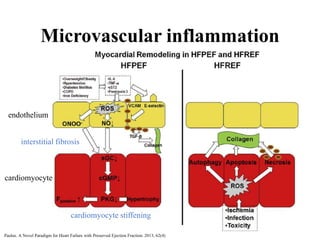
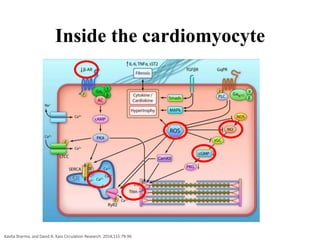
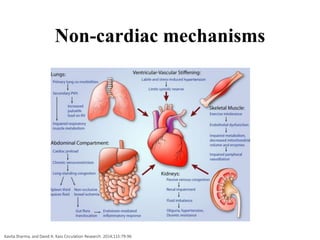
3) The pathophysiology of HFpEF is complex and multifactorial, involving microvascular inflammation, cardiomyocyte stiff