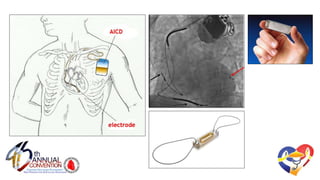
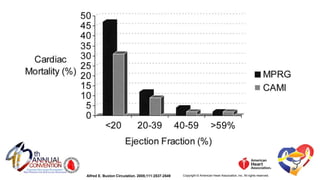
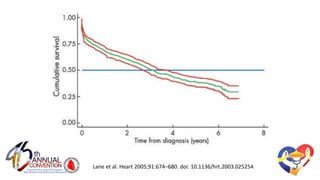
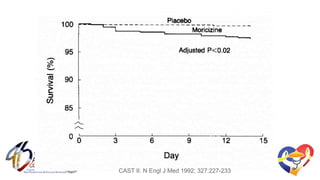
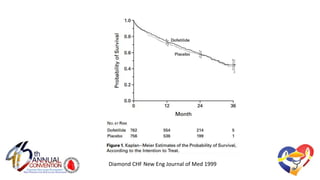
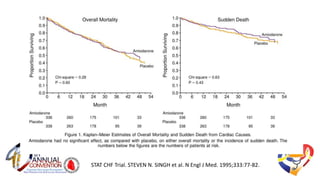
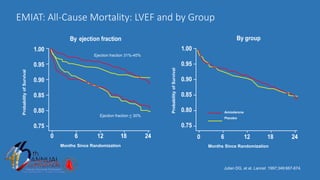
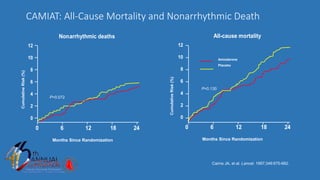
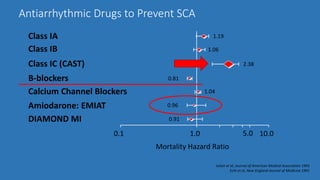
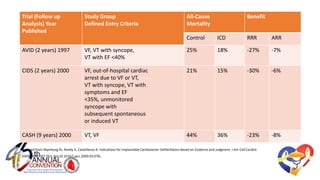
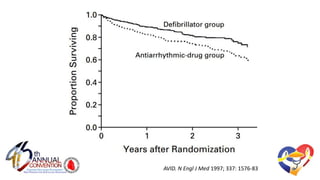
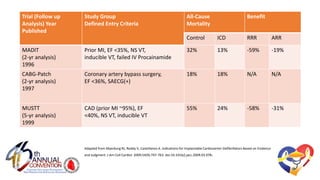
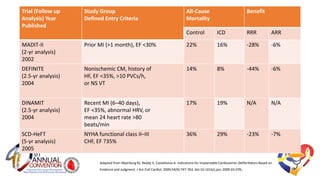
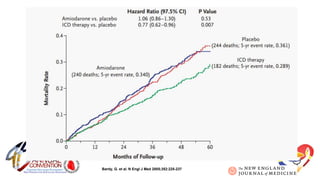
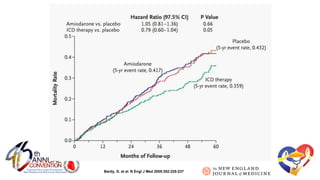
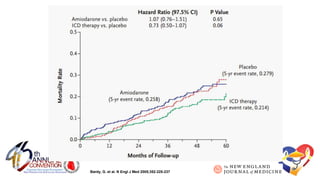
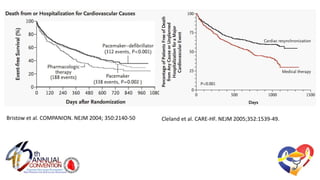
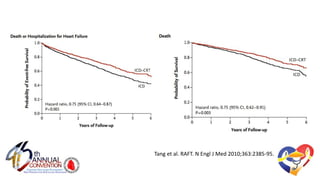
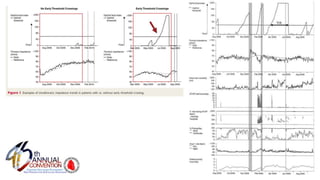
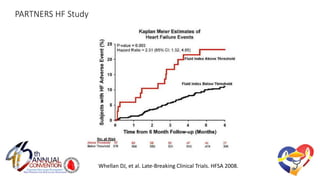
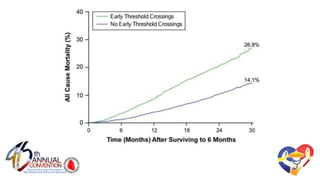
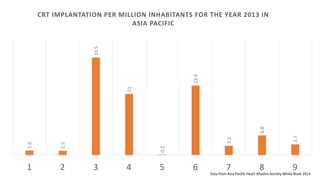
The document presents a comprehensive overview of studies related to heart failure treatment, focusing on the efficacy of various antiarrhythmic drugs and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs). It discusses mortality rates and survival probabilities among heart failure patients treated with amiodarone, ICDs, and other therapies, highlighting significant findings across multiple trials. The evidence suggests that ICDs may be more effective than amiodarone in reducing all-cause mortality in various patient populations.