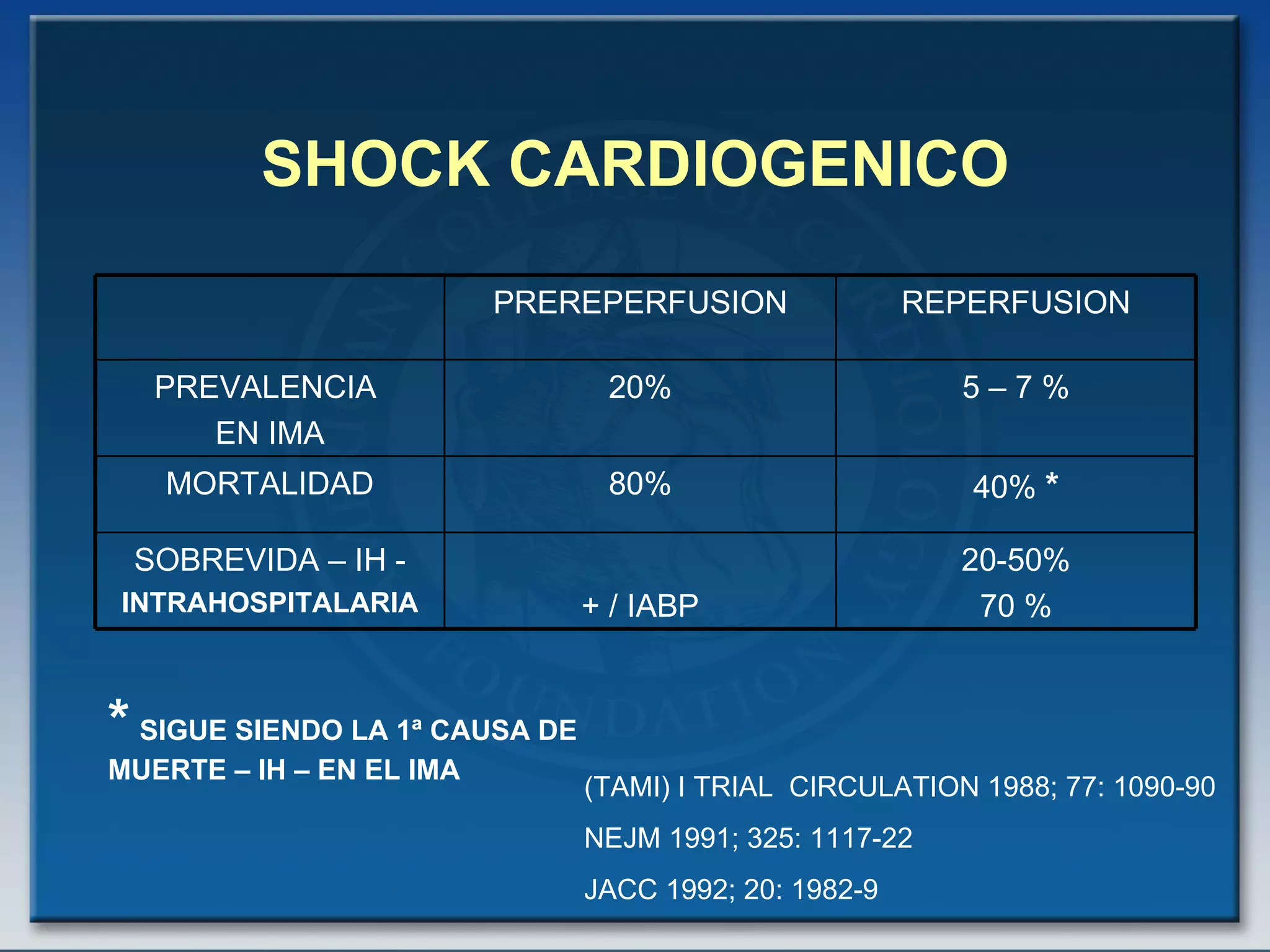
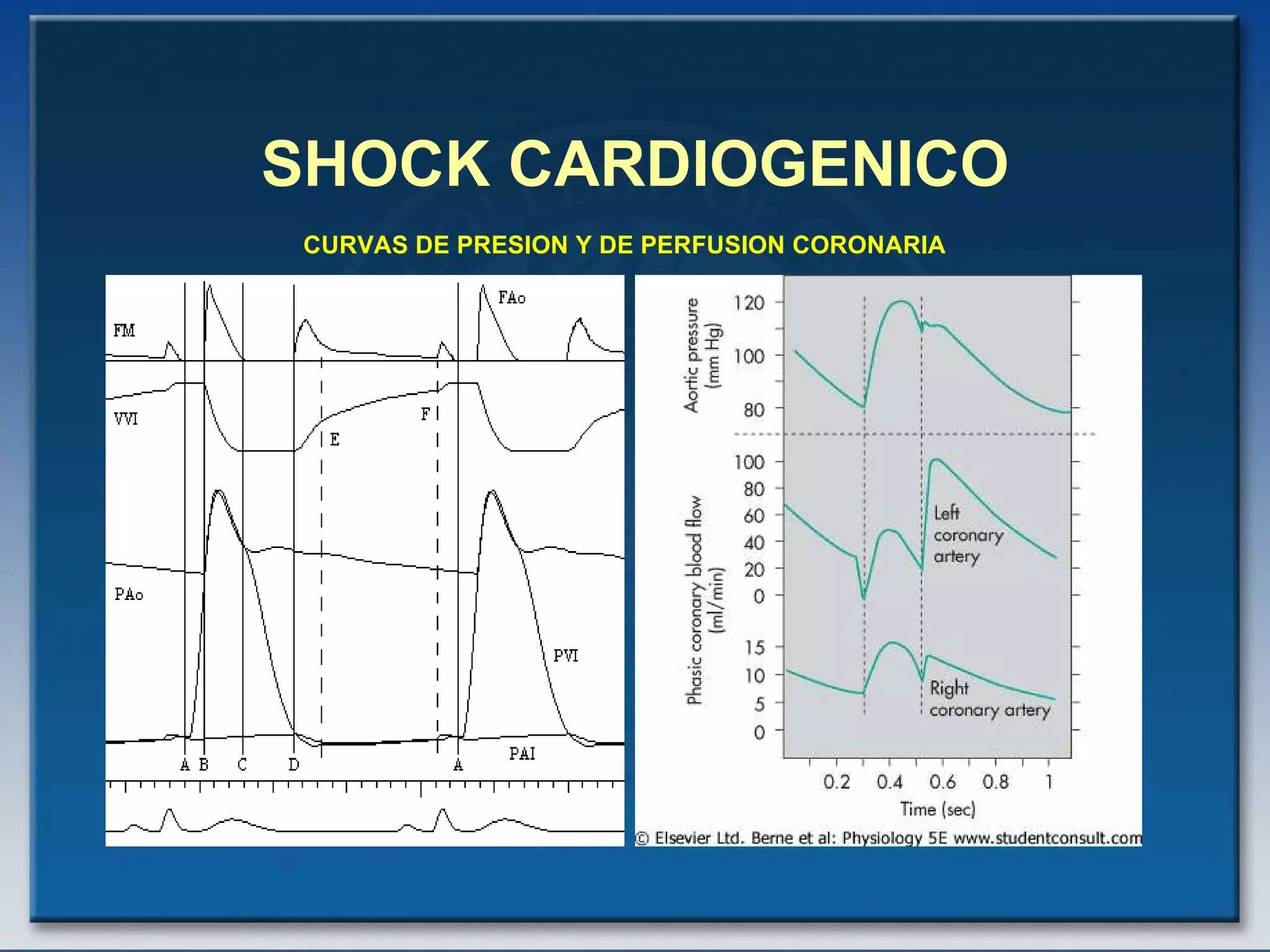
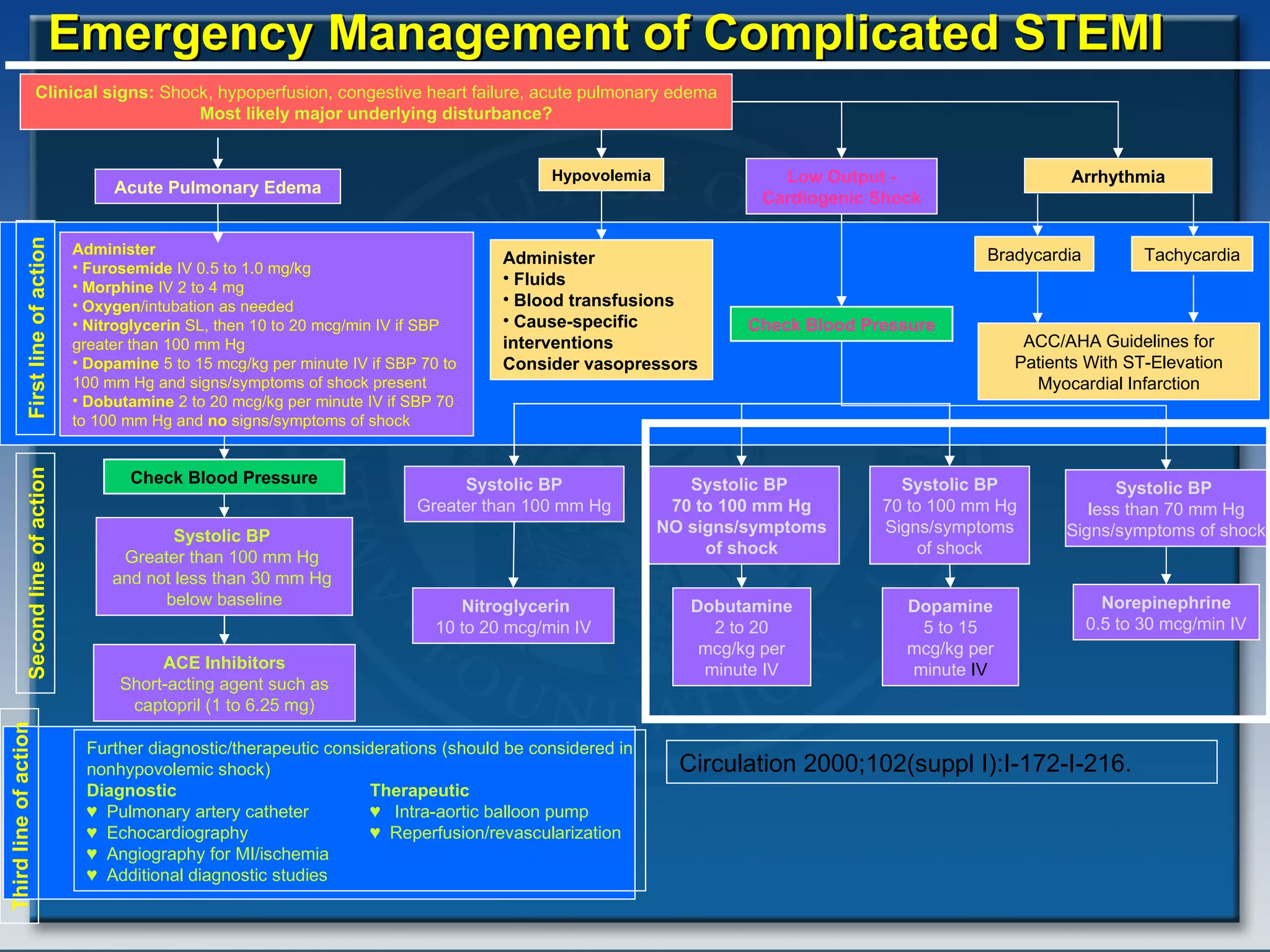
- The document discusses cardiogenic shock, which is a clinical condition defined by hypotension and signs of hypoperfusion due to impaired cardiac function, usually caused by acute myocardial infarction.
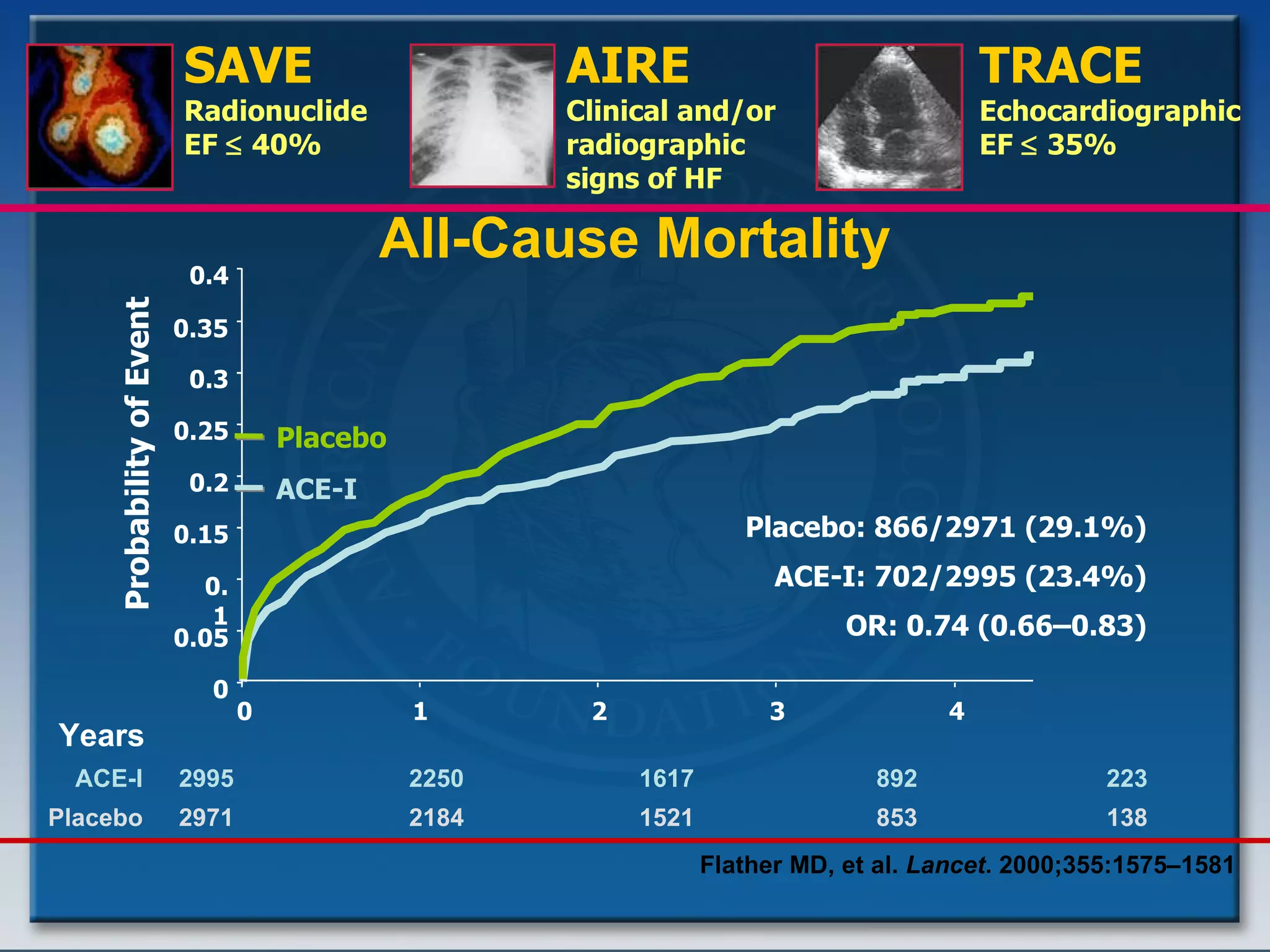
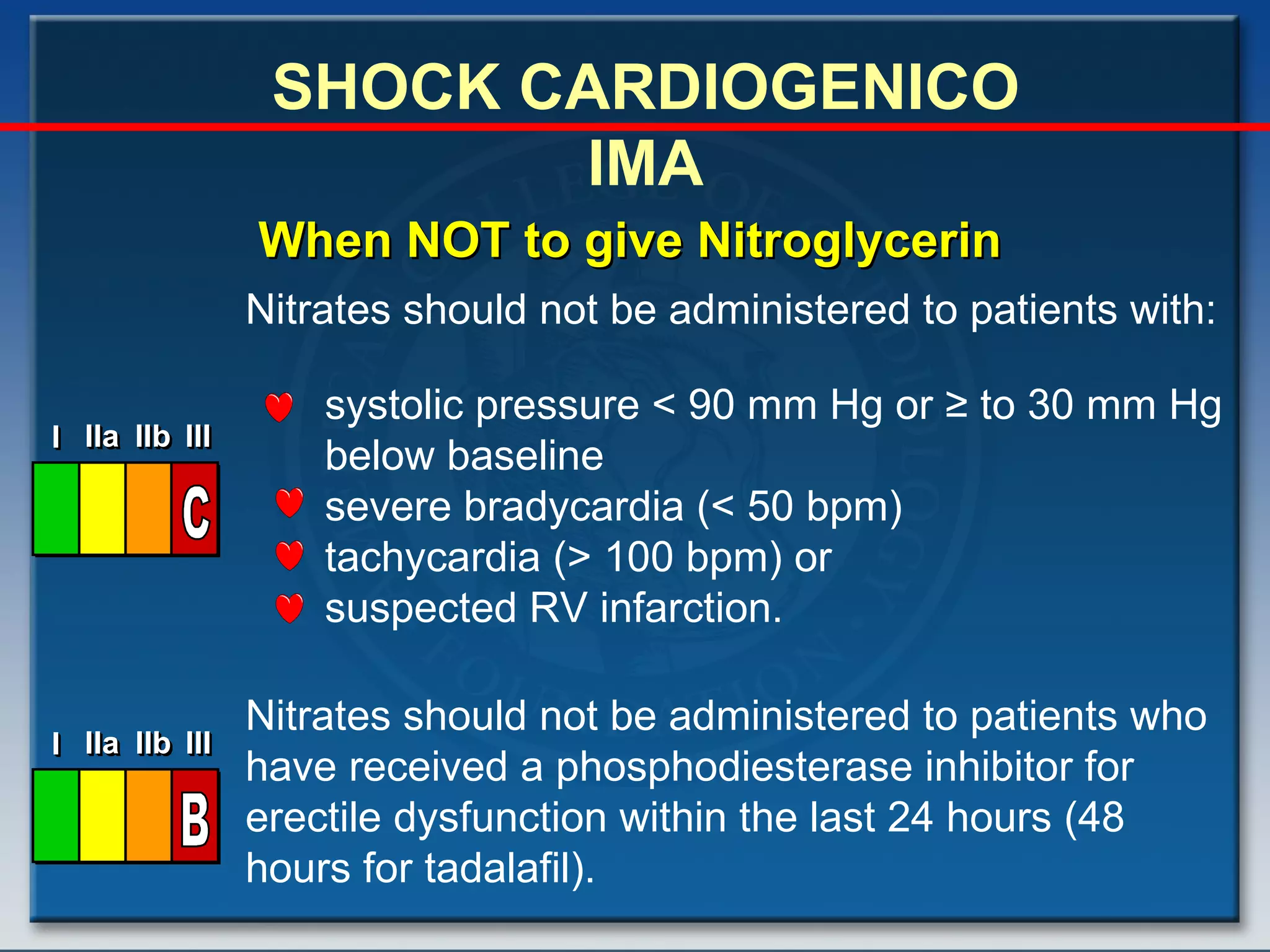
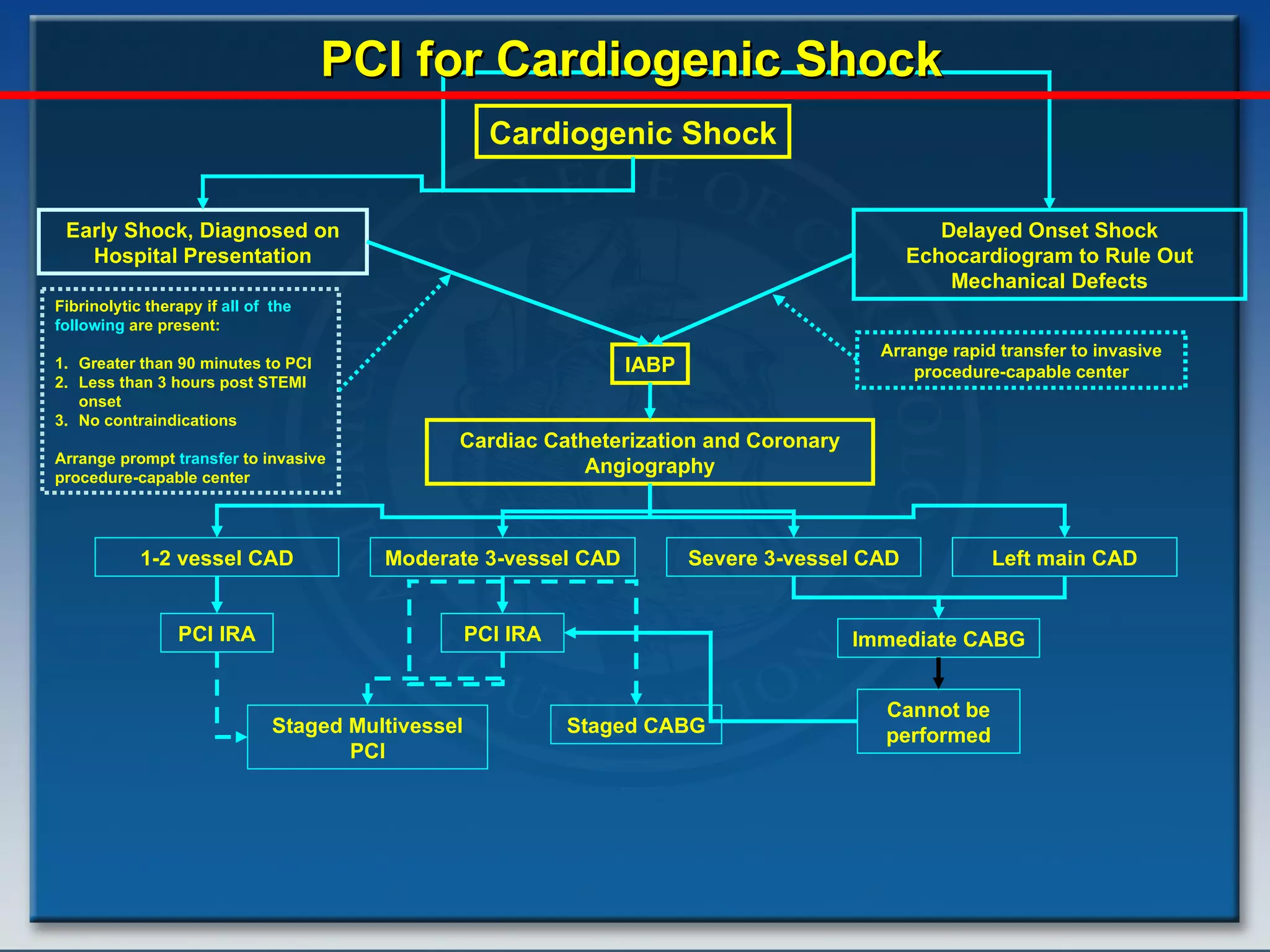
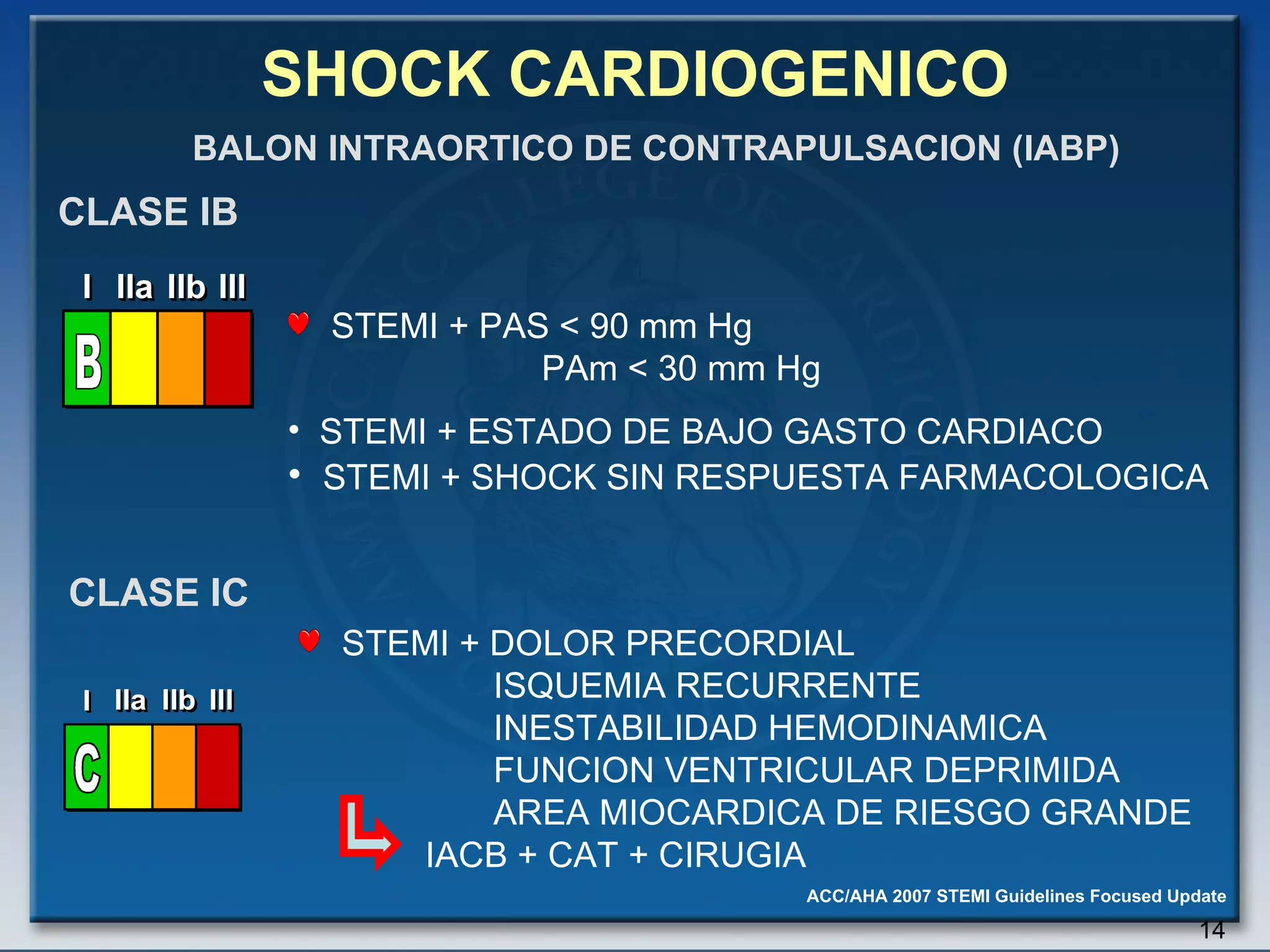
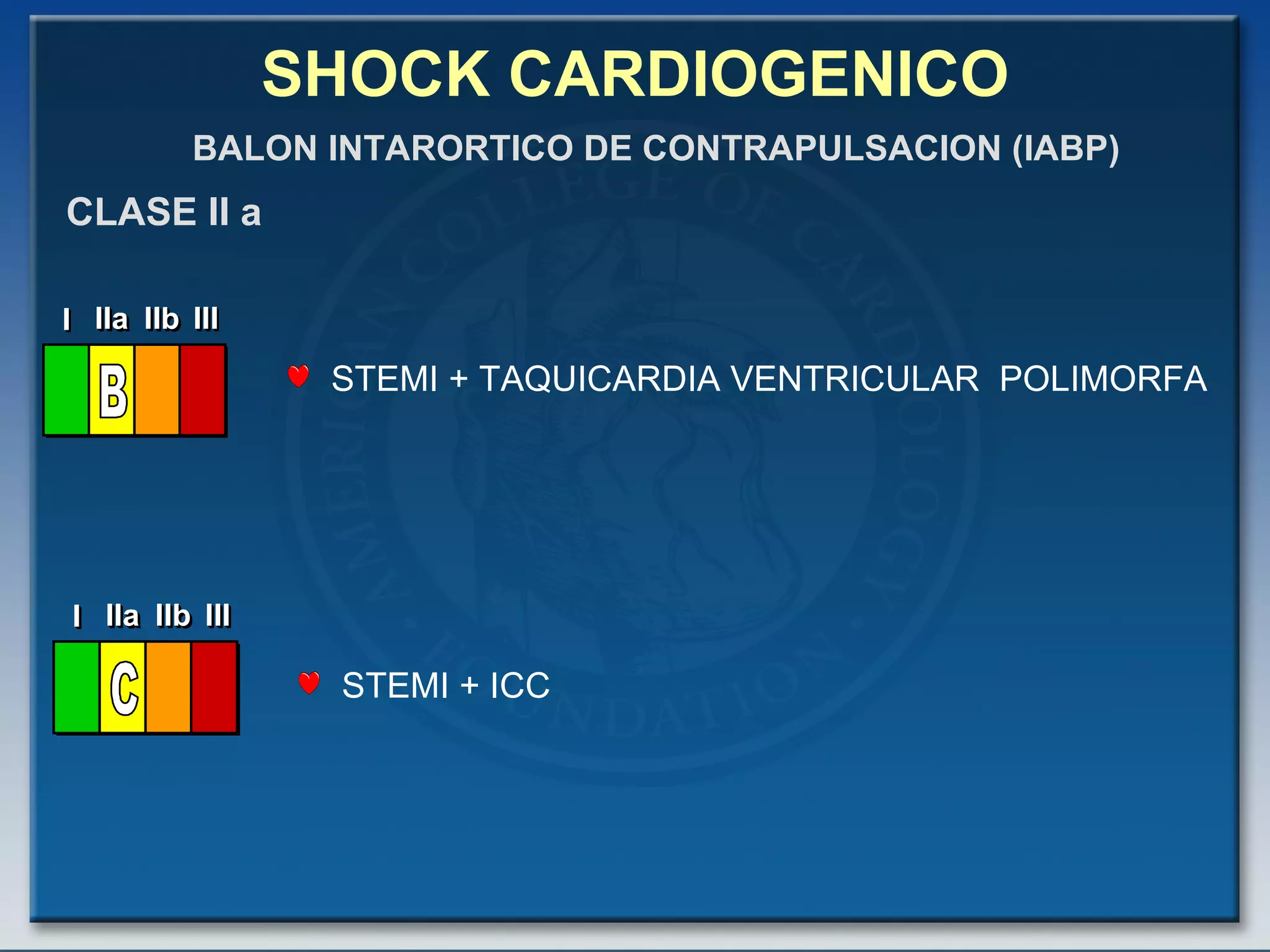
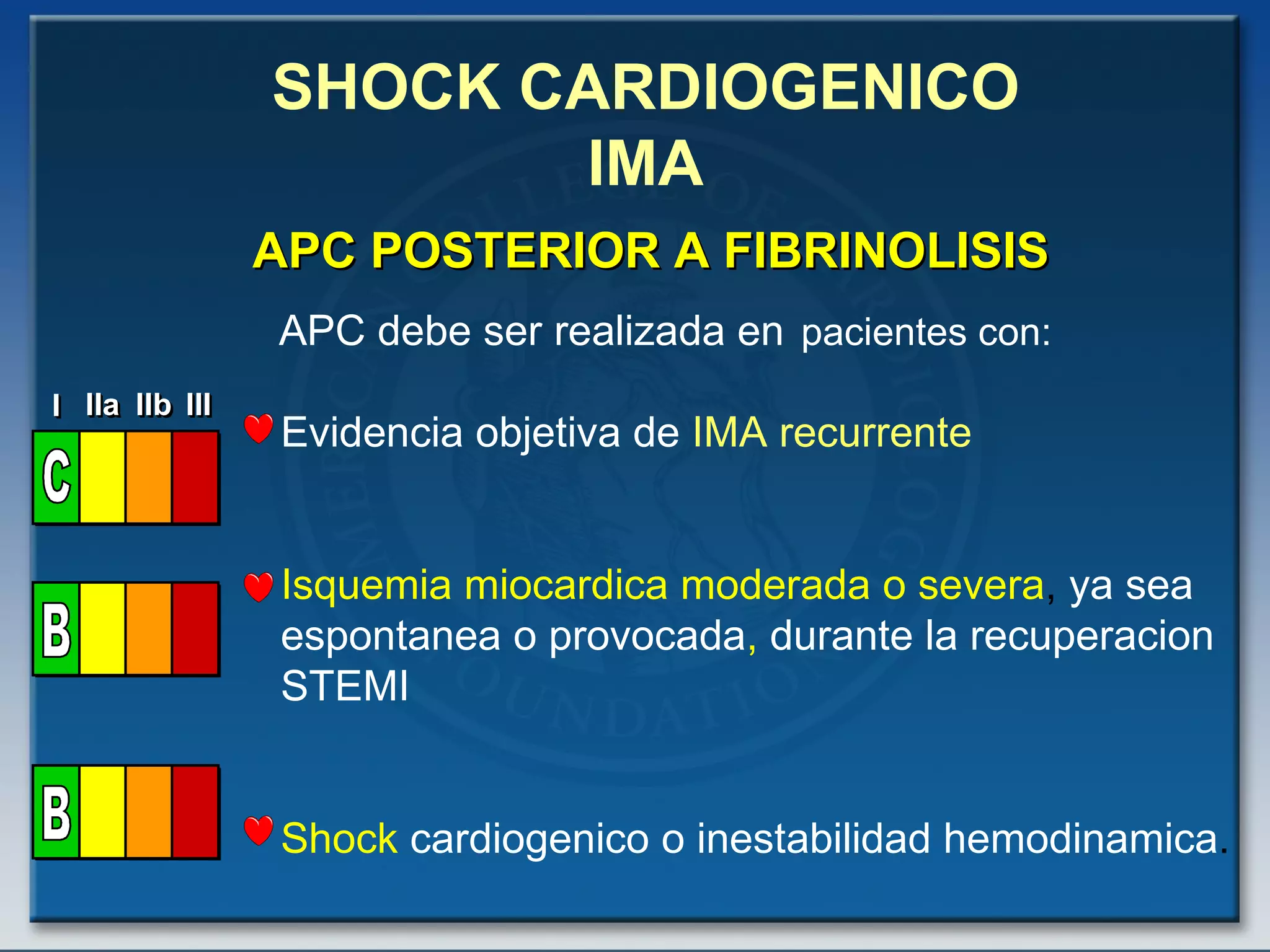
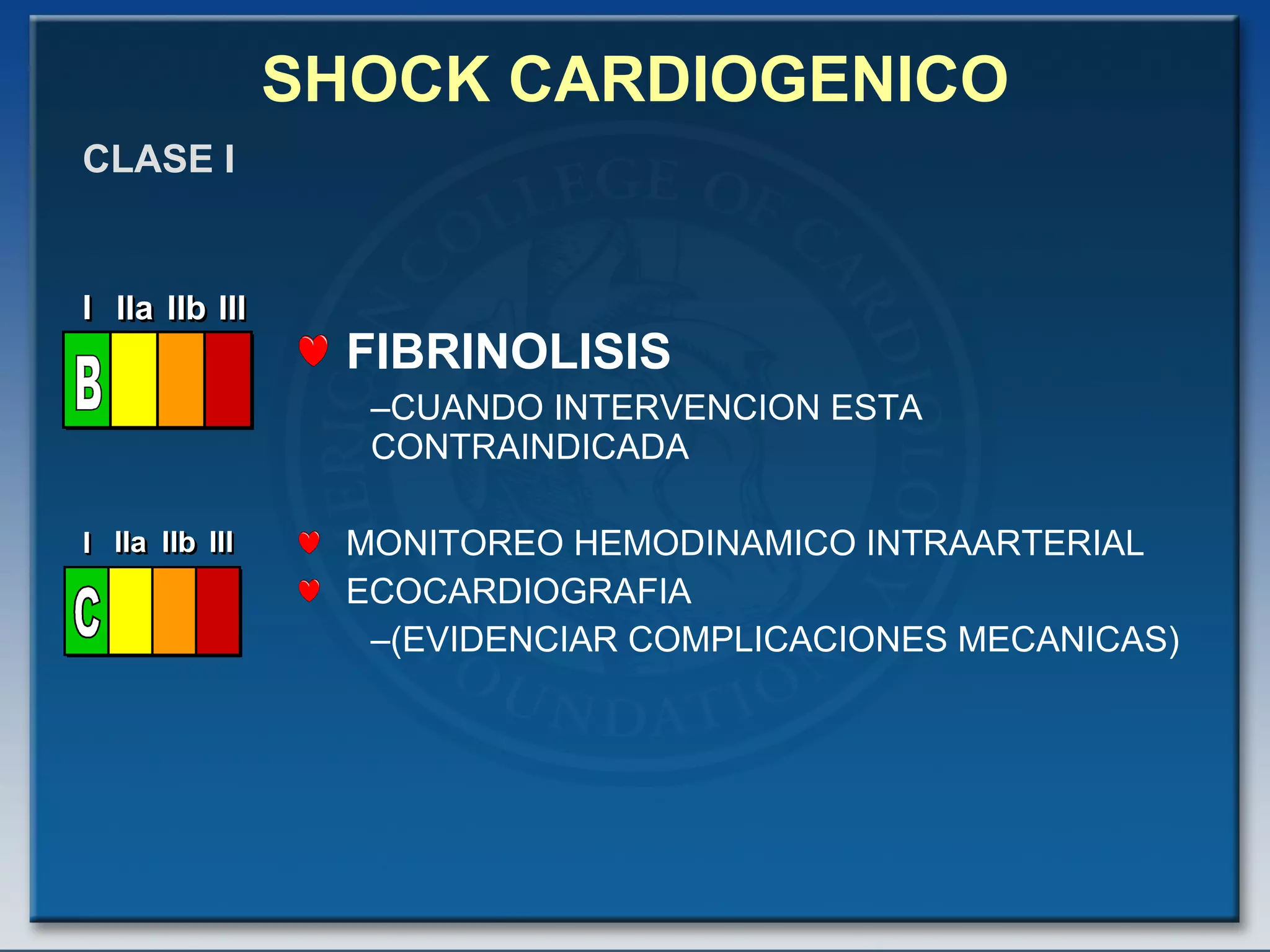
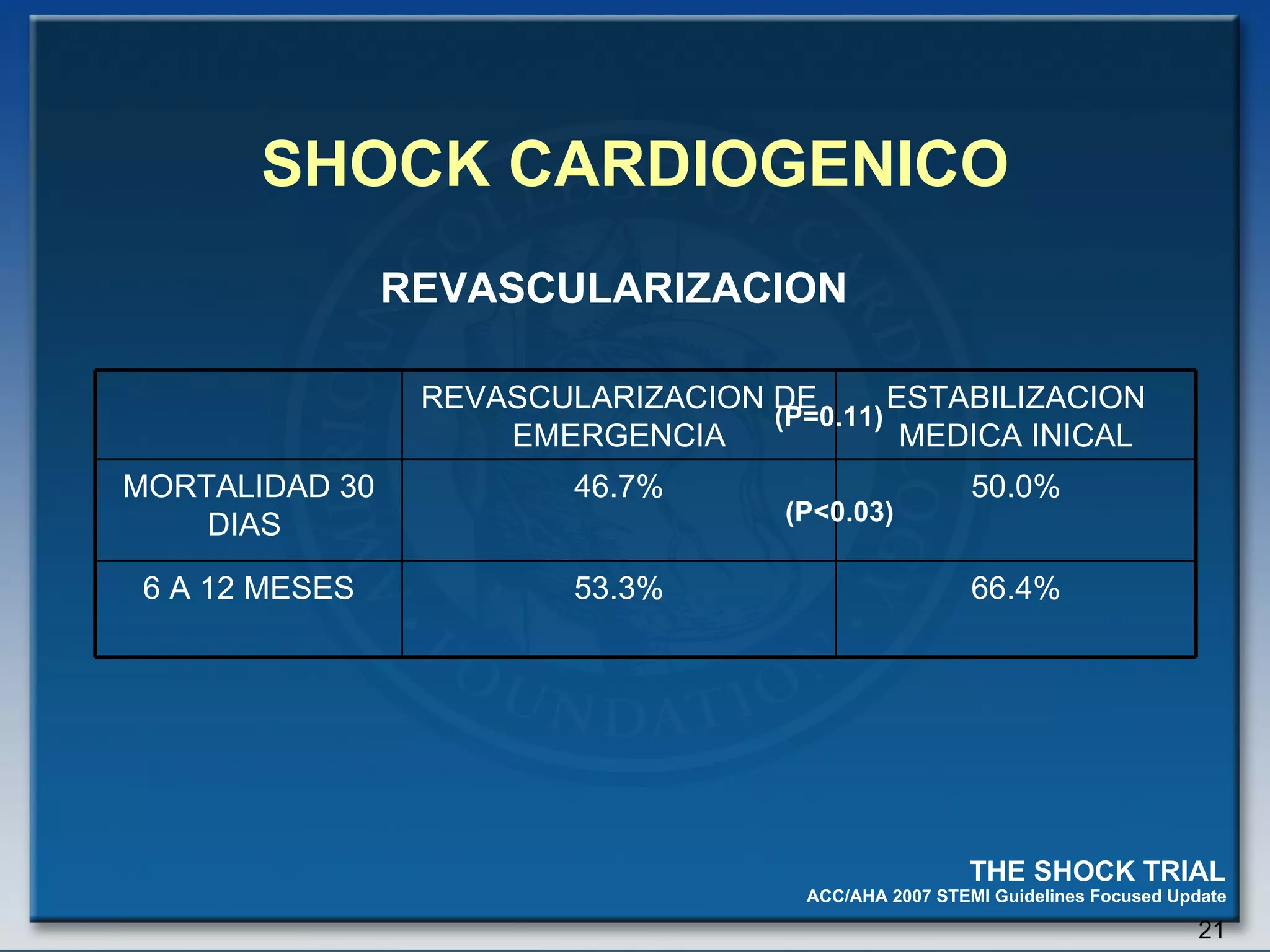
- Key treatments discussed for cardiogenic shock include early revascularization (within 18 hours) for younger patients, use of an intra-aortic balloon pump, and inotropic support. Fibrinolysis may be considered when intervention is contraindicated.
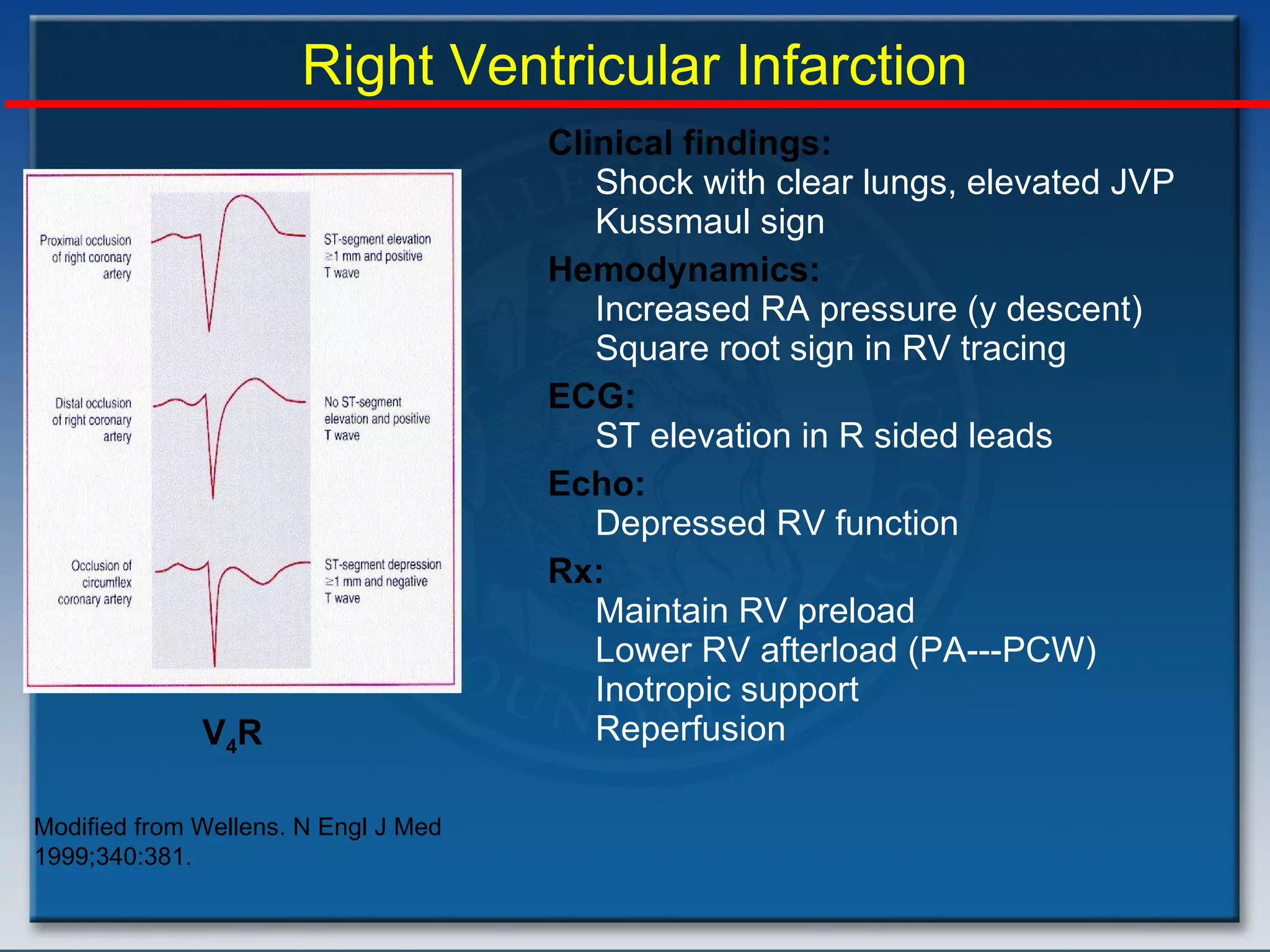
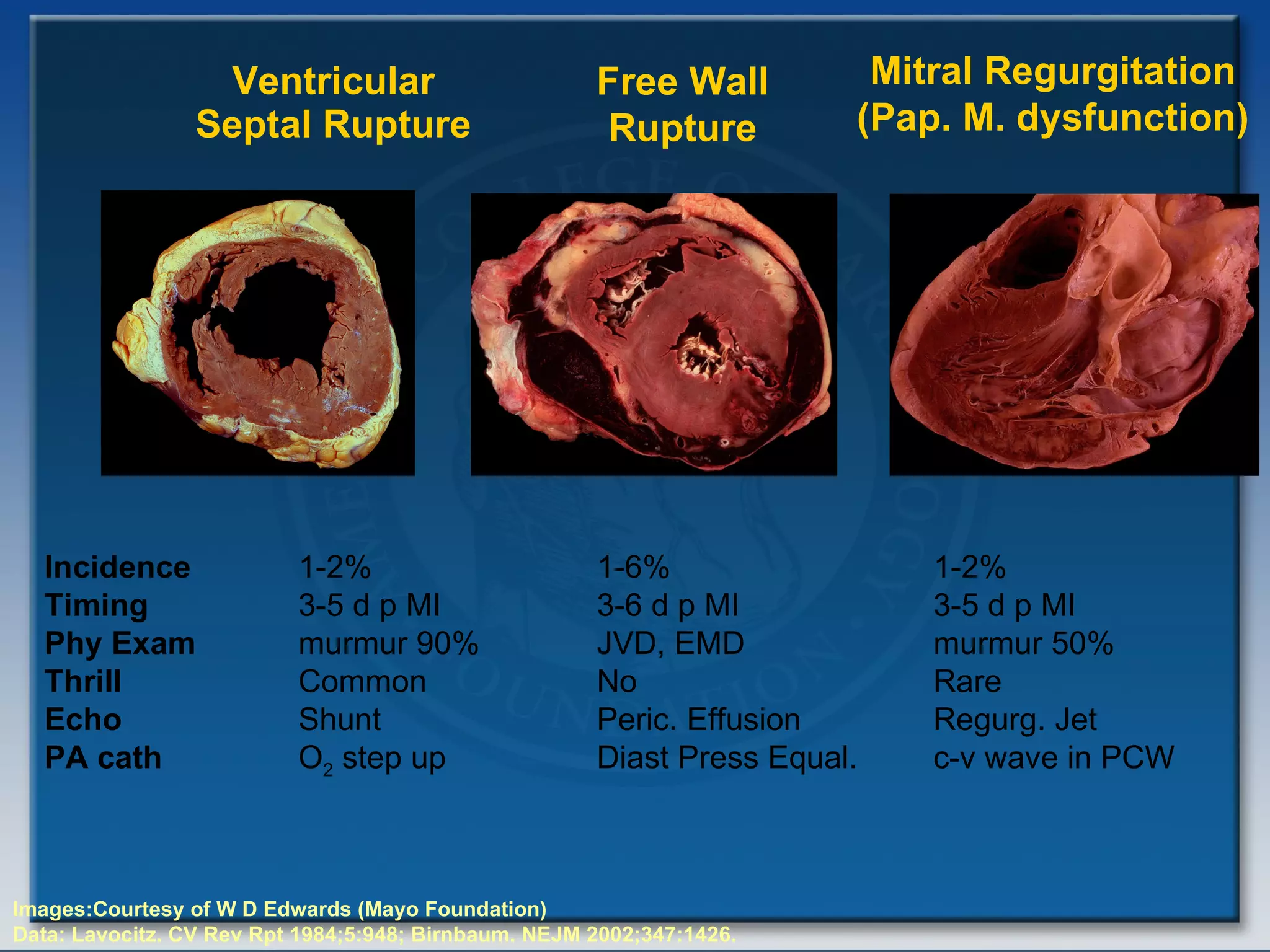
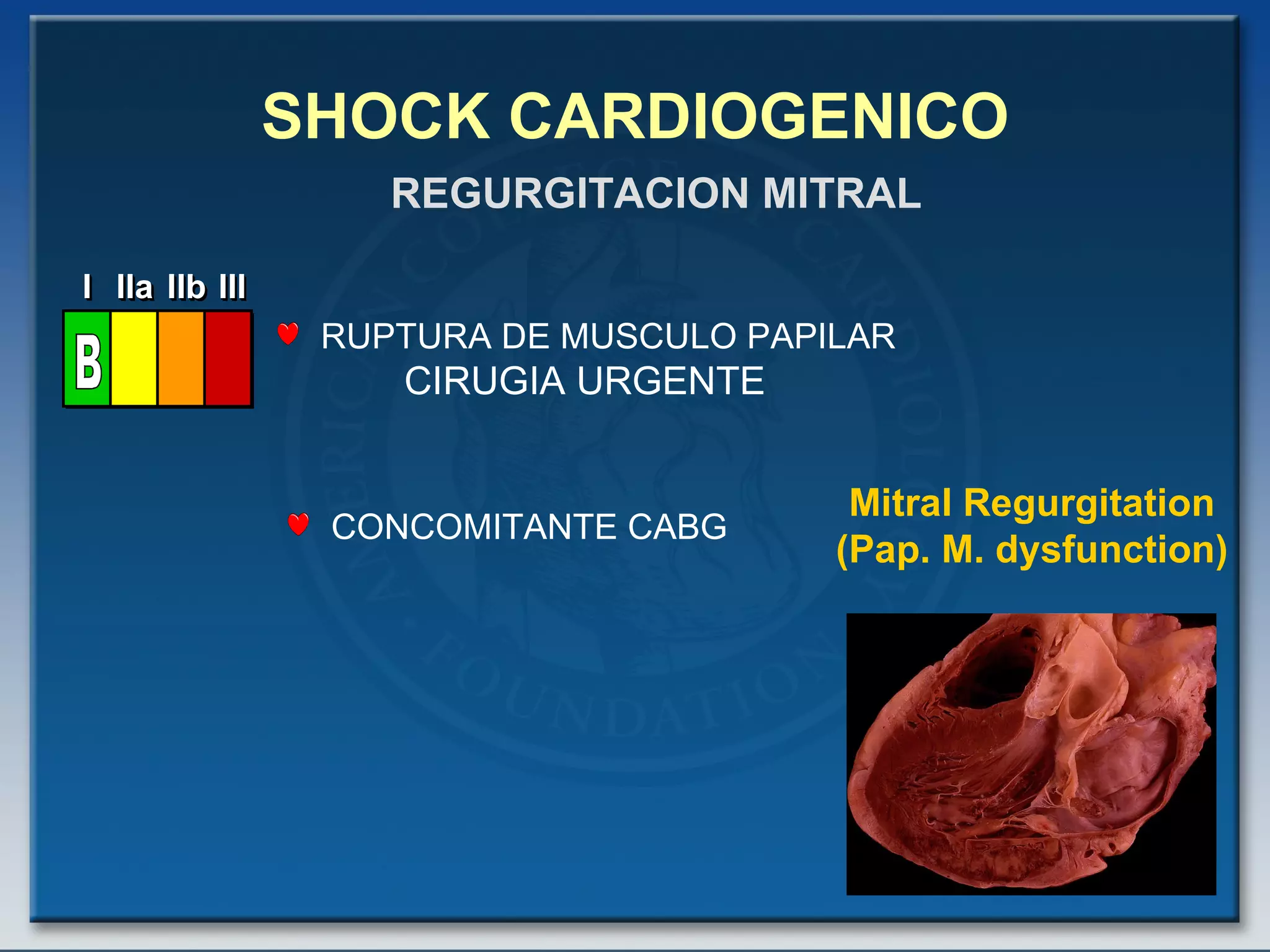
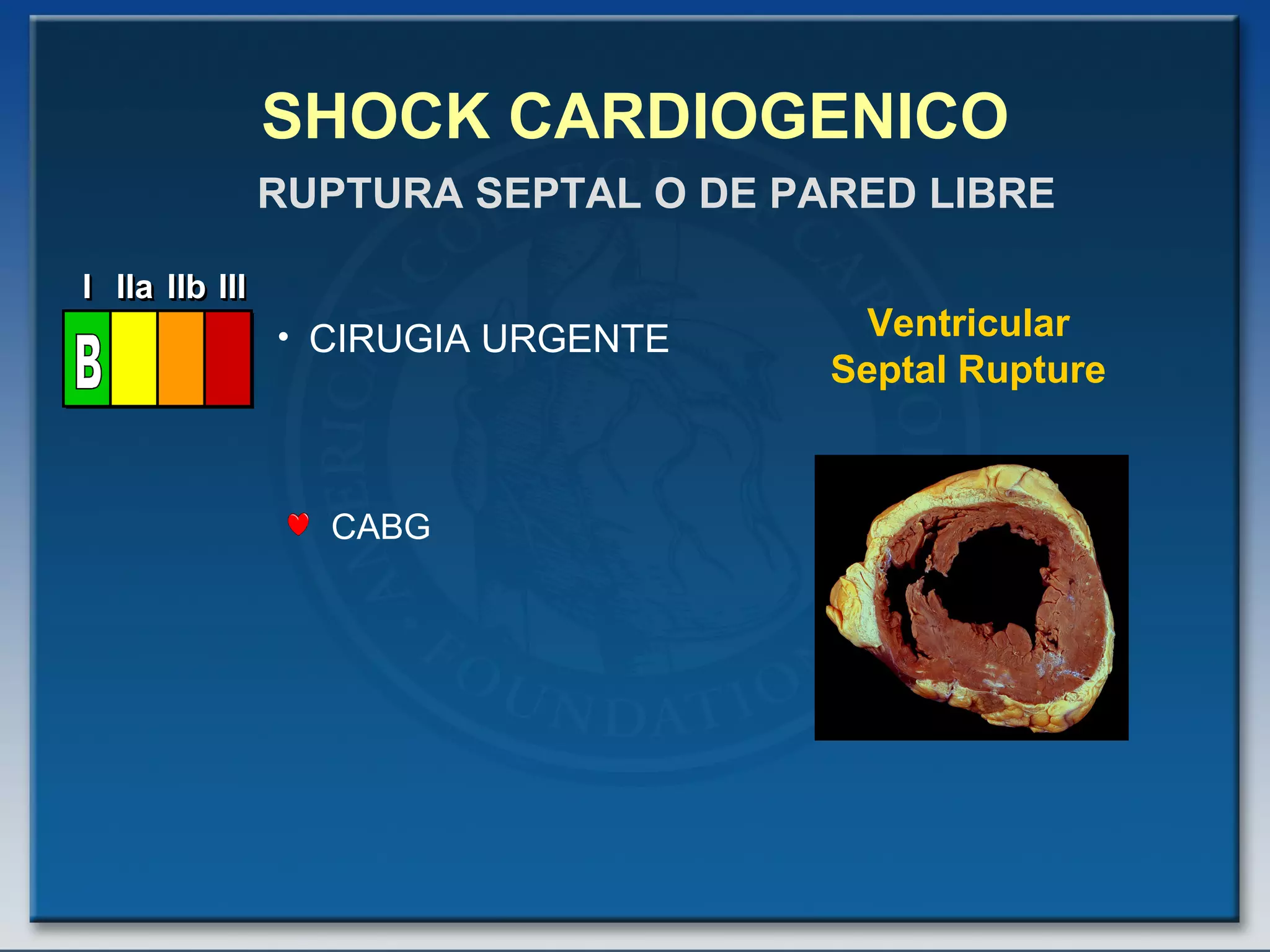
- Factors such as right ventricular infarction, arrhythmias, and mechanical complications also warrant consideration in management of cardiogenic shock. Early reperfusion and hemodynamic support are emphasized.