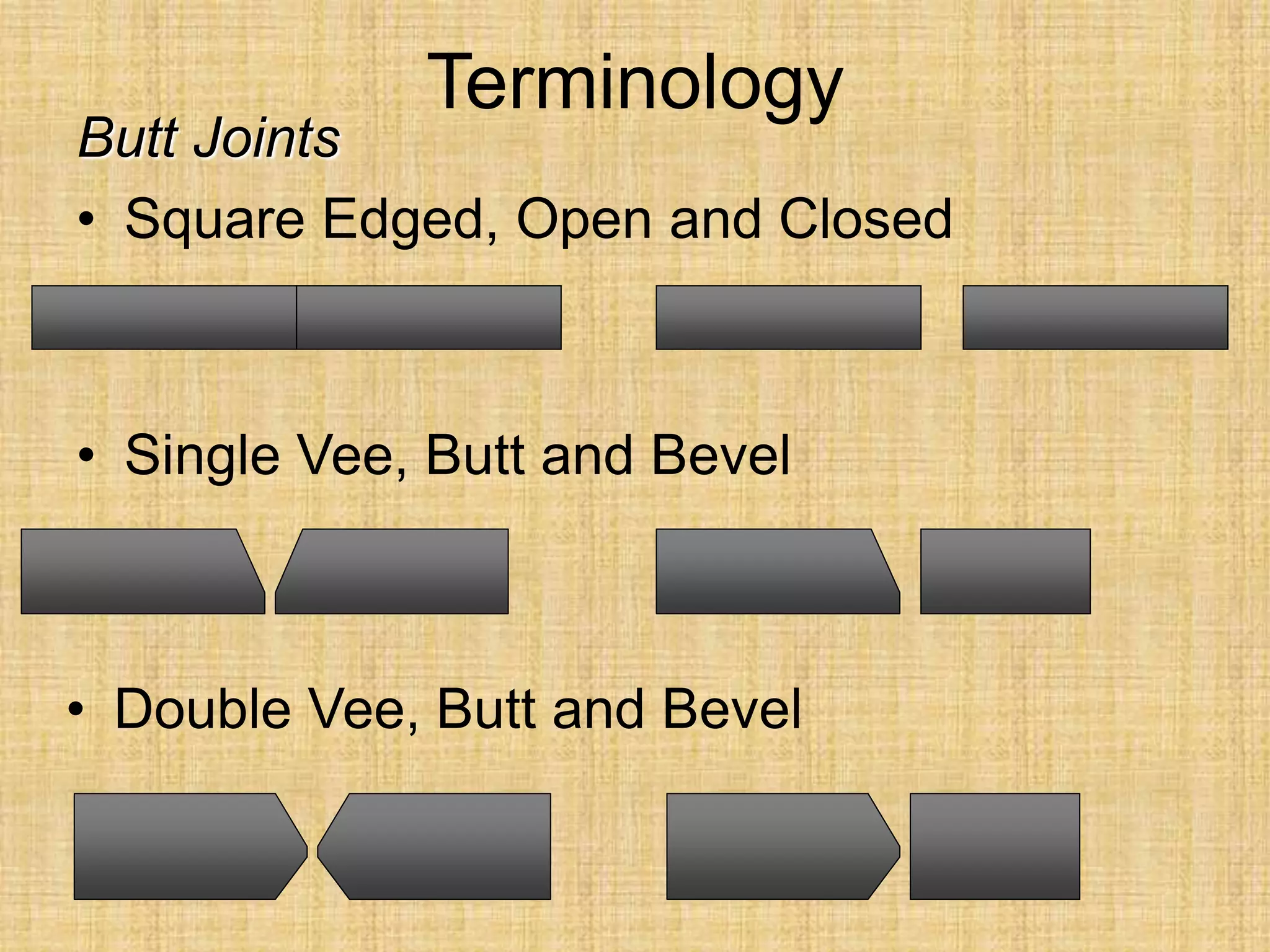
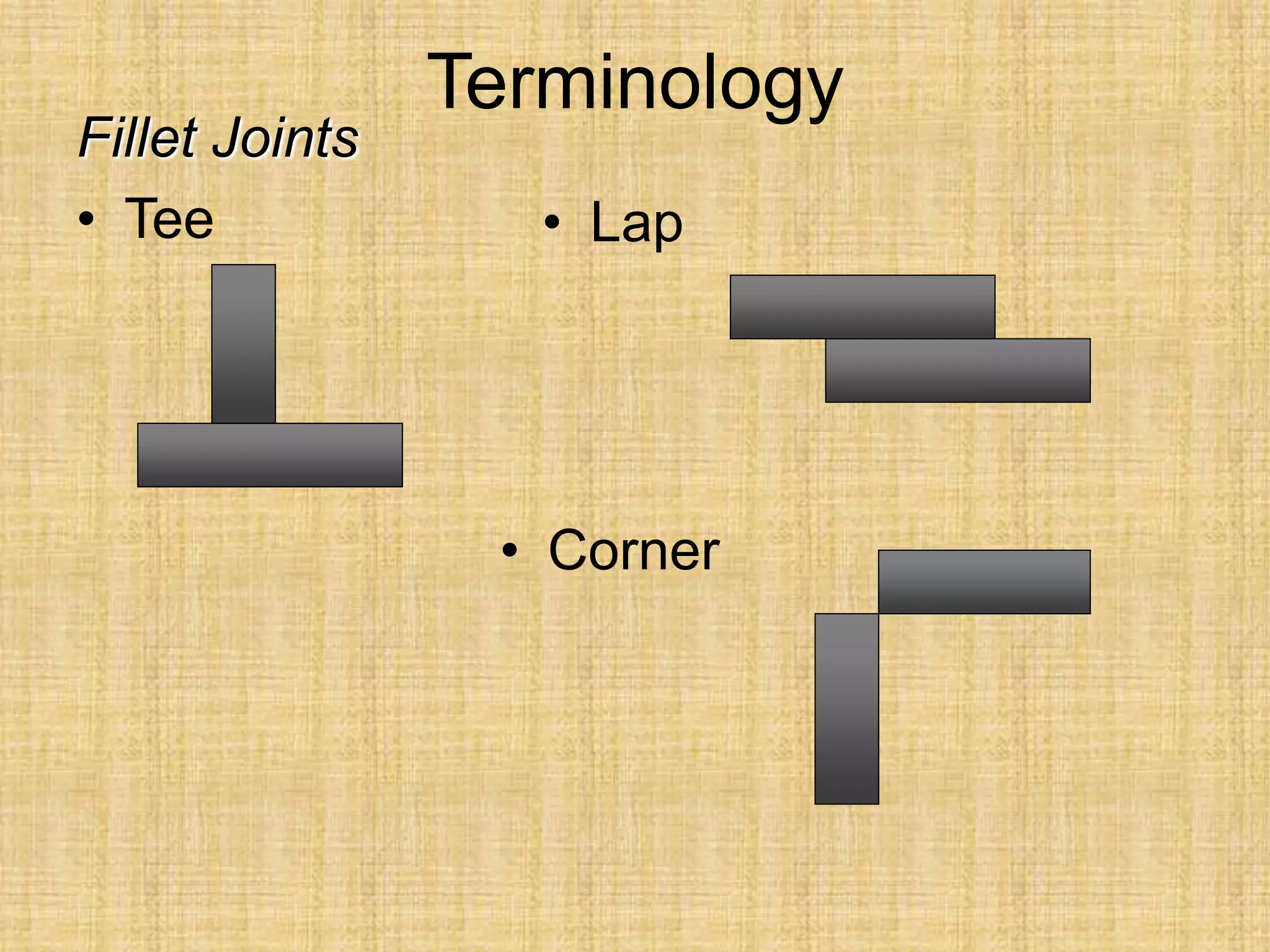
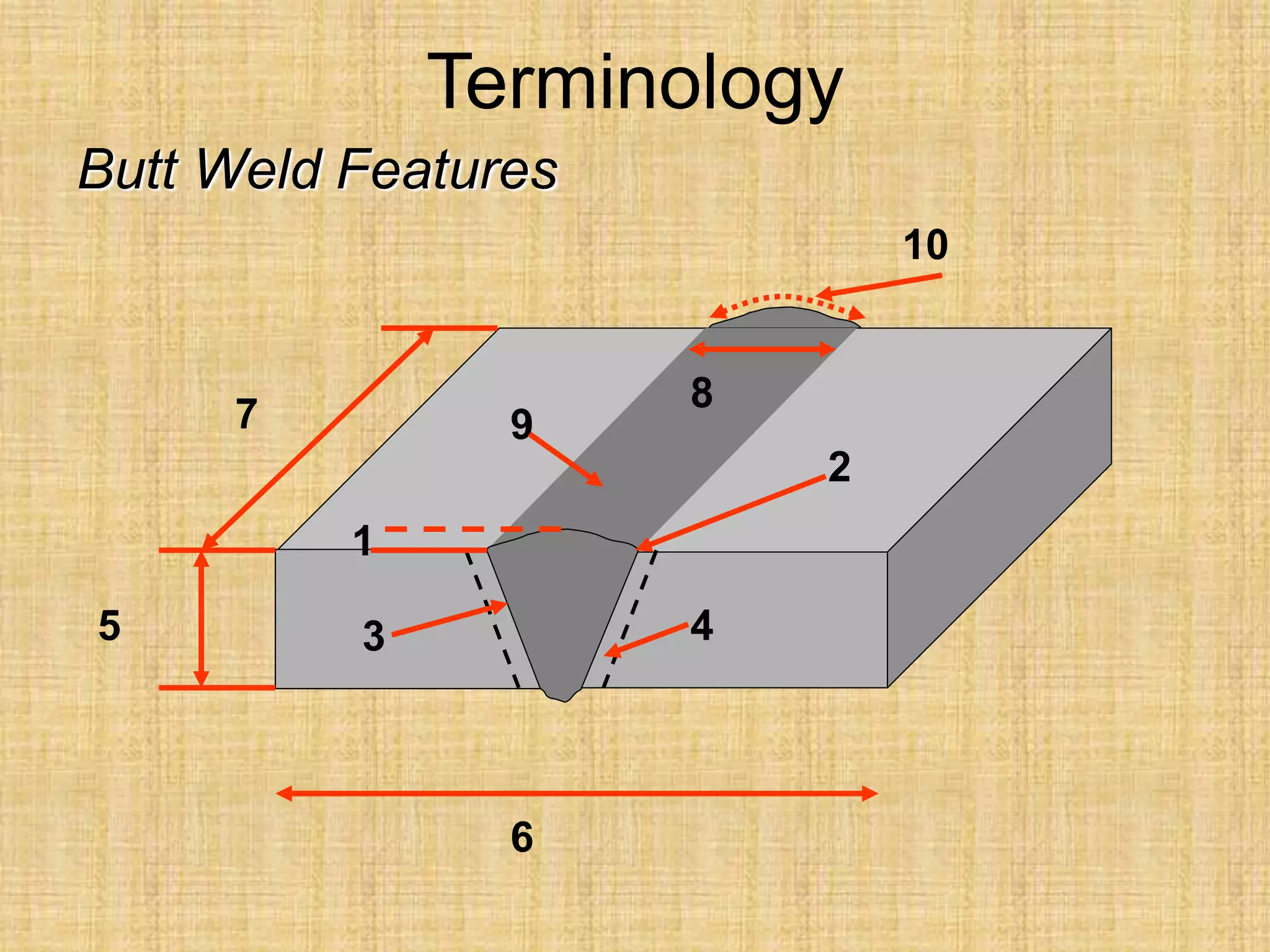
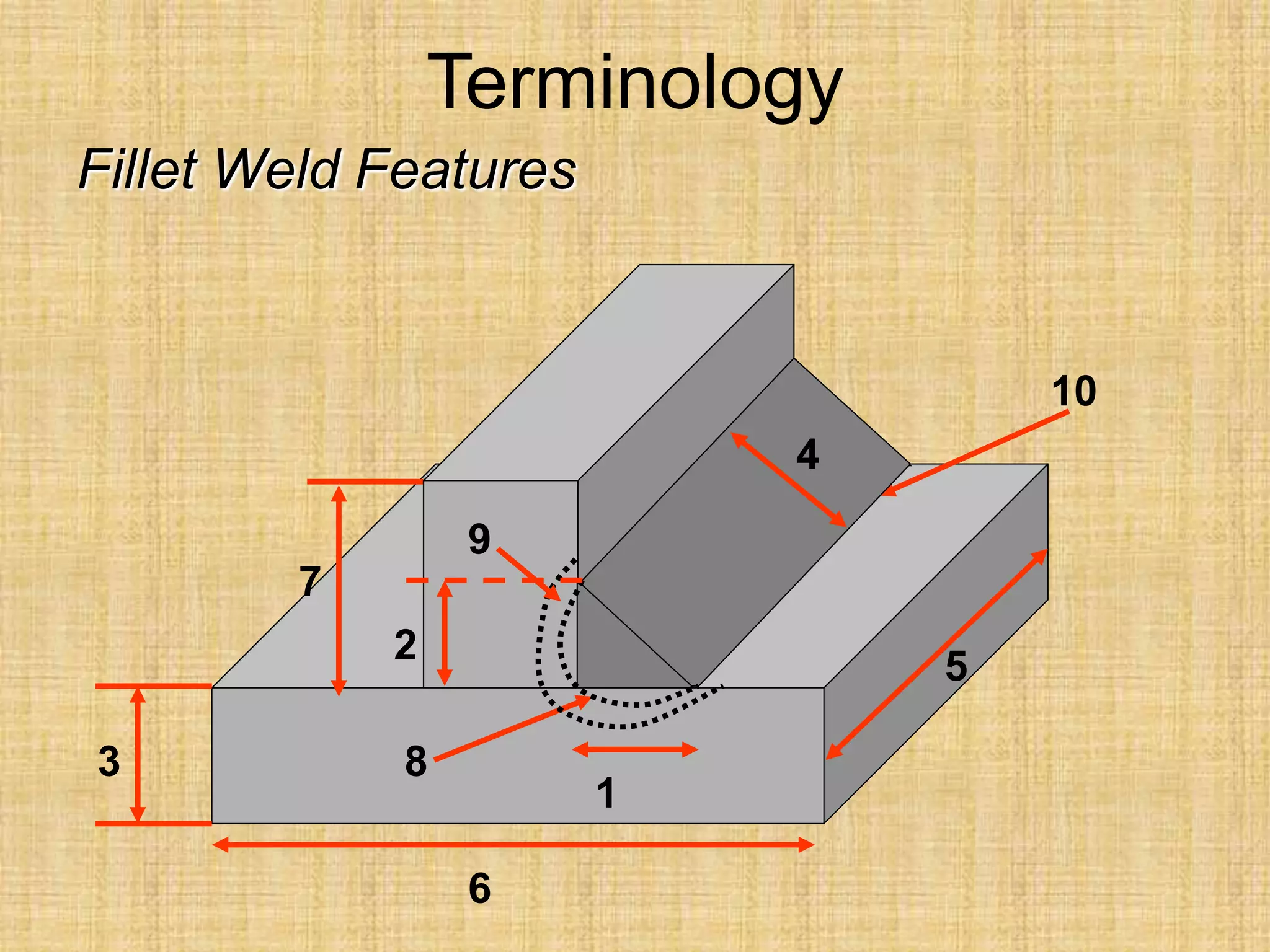
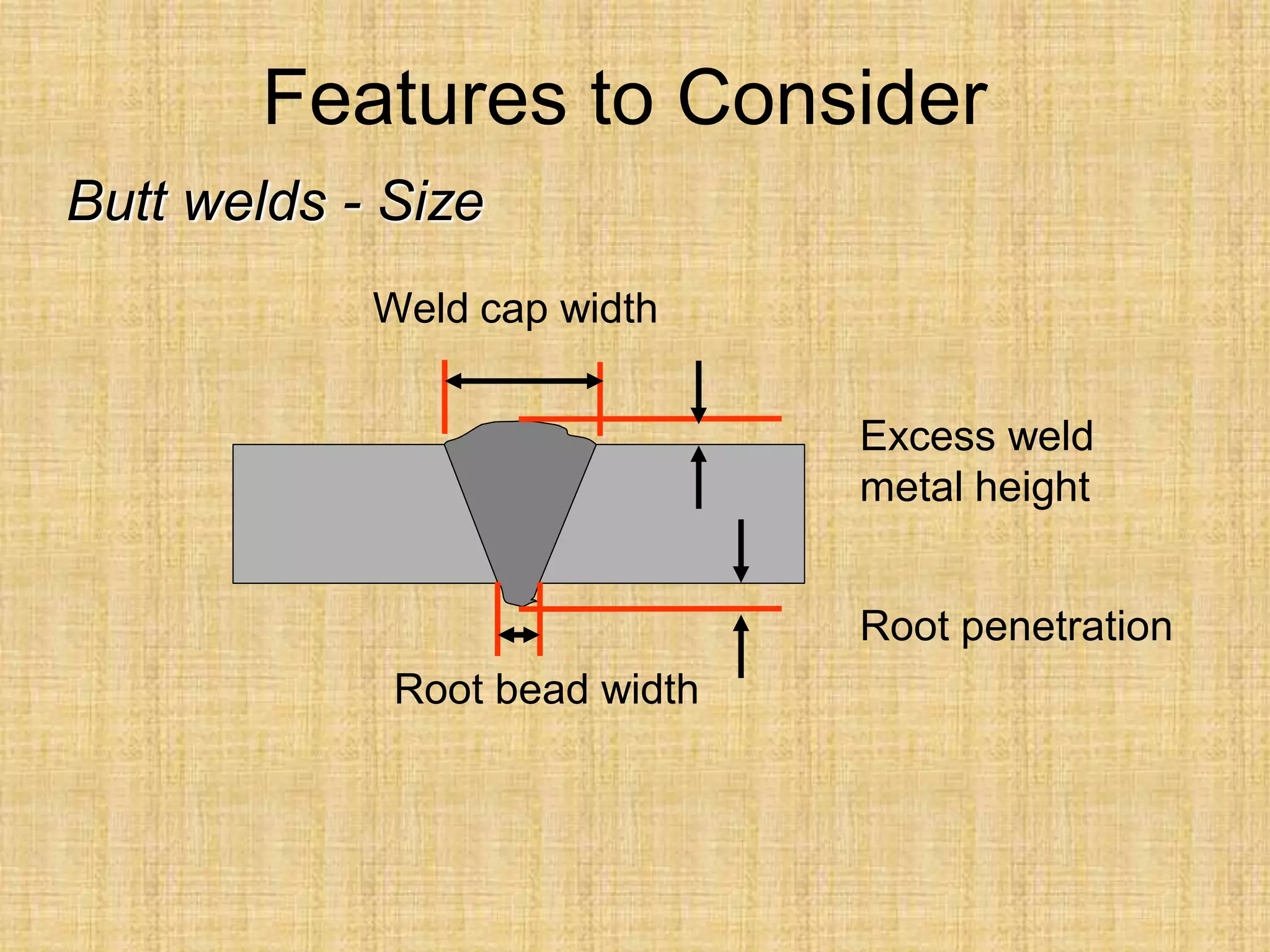
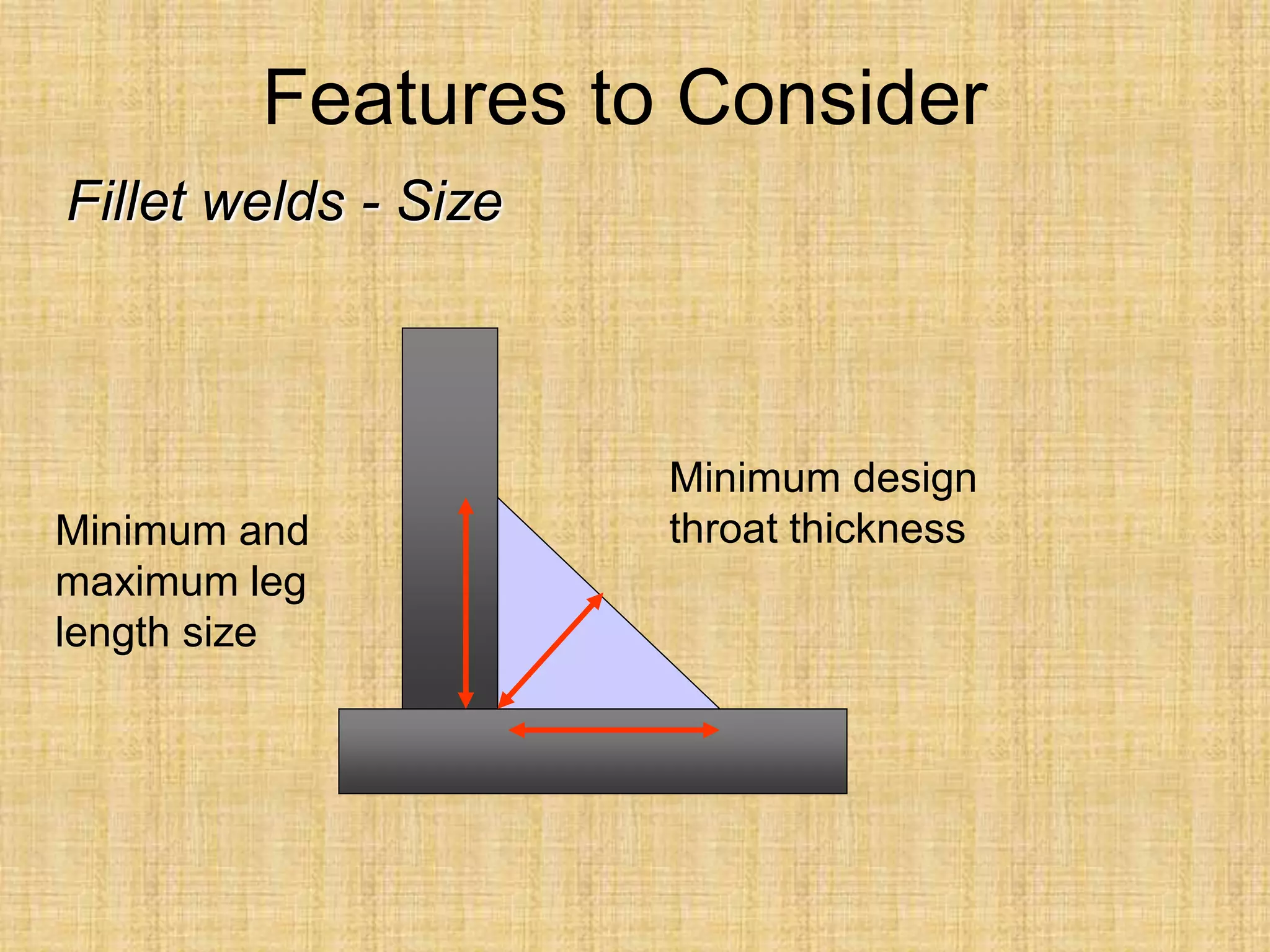
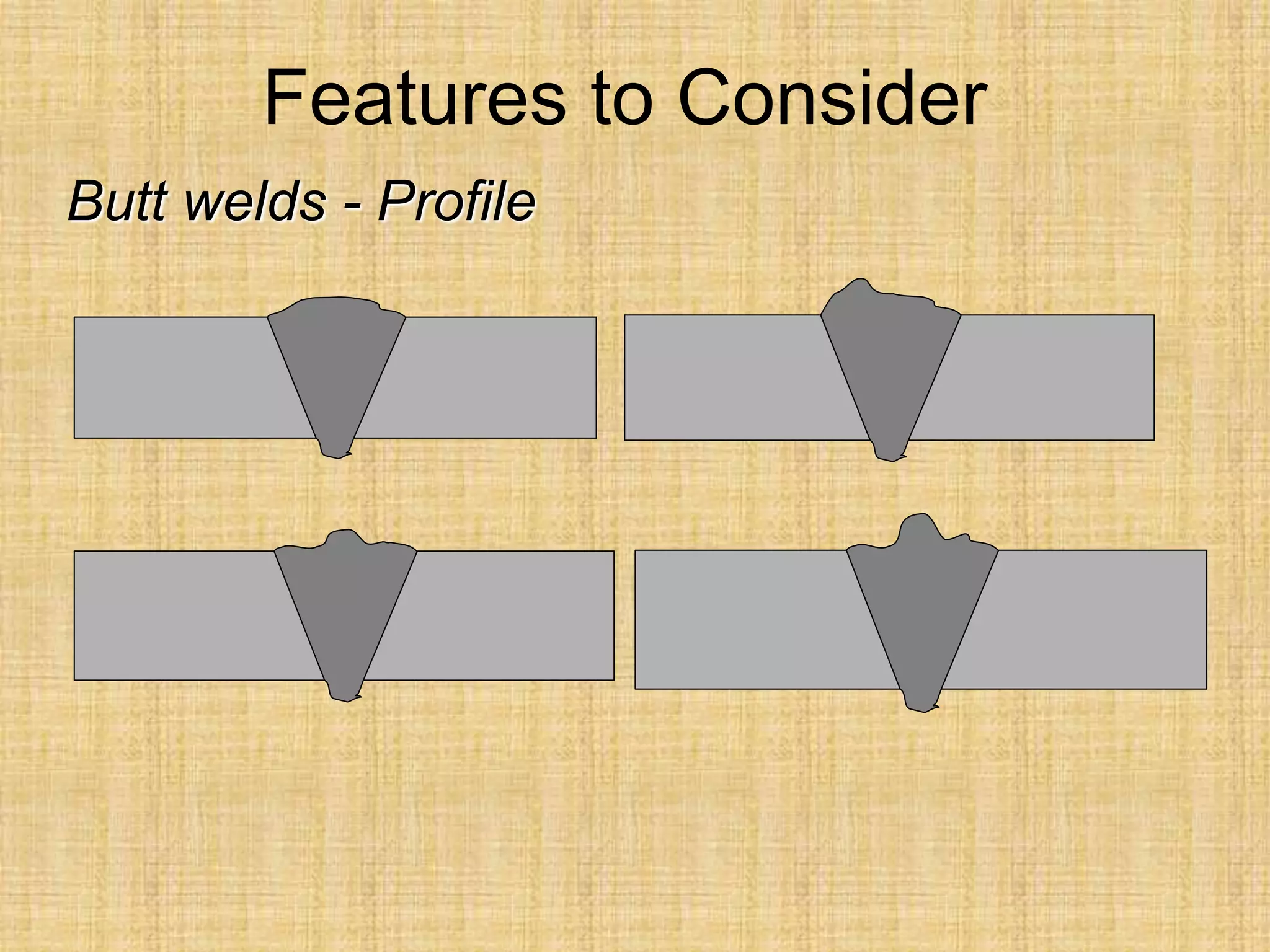
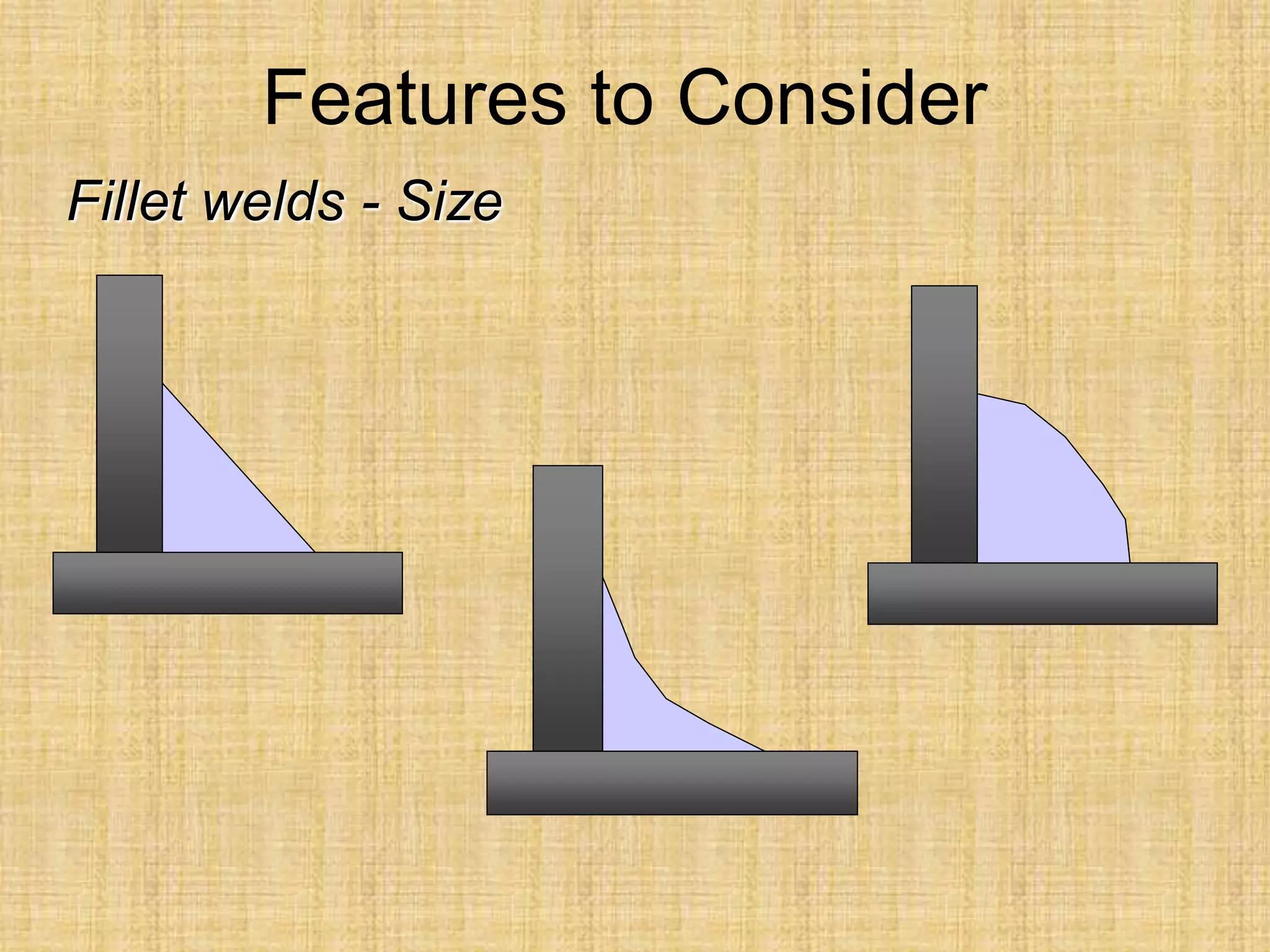
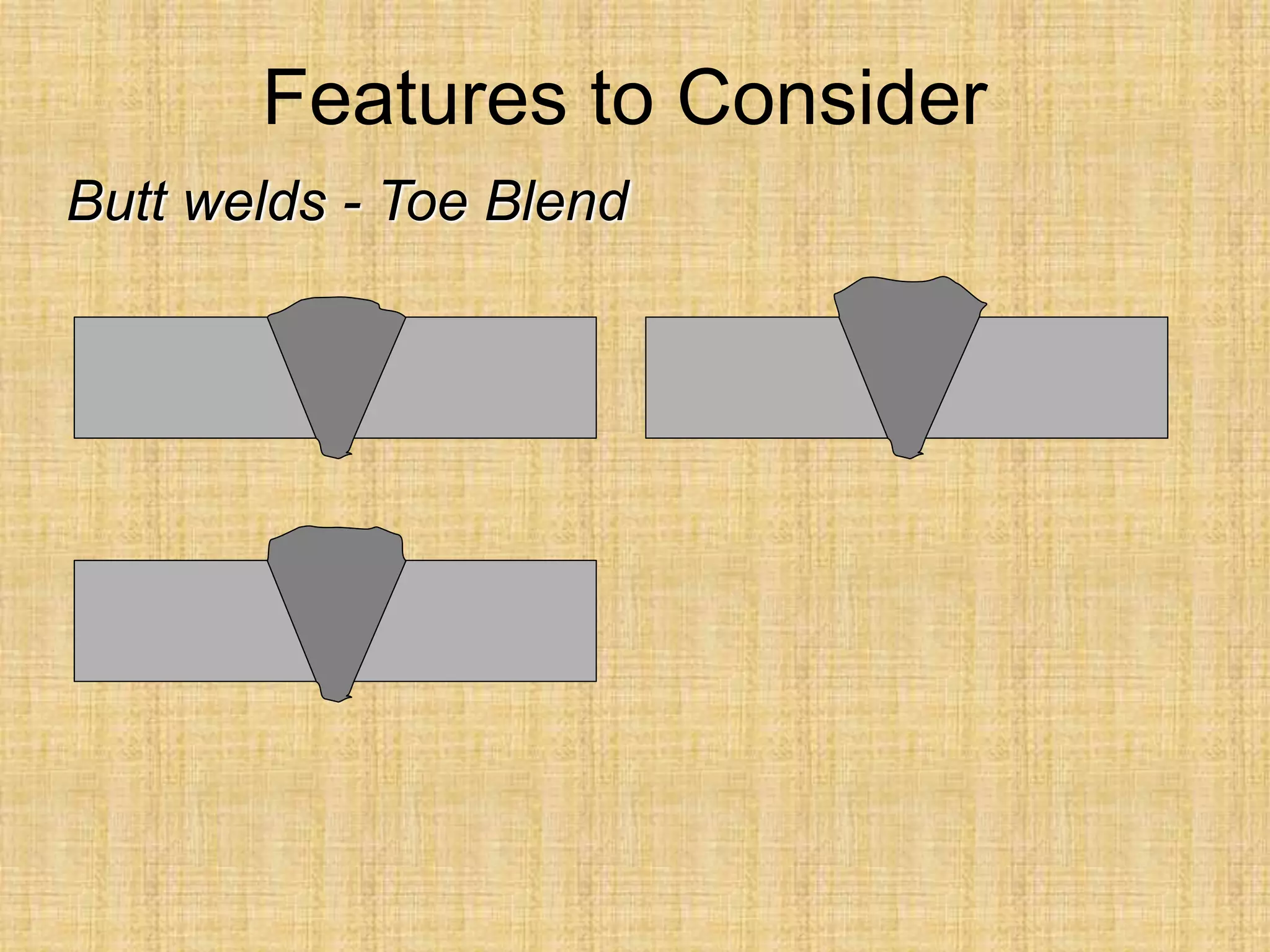
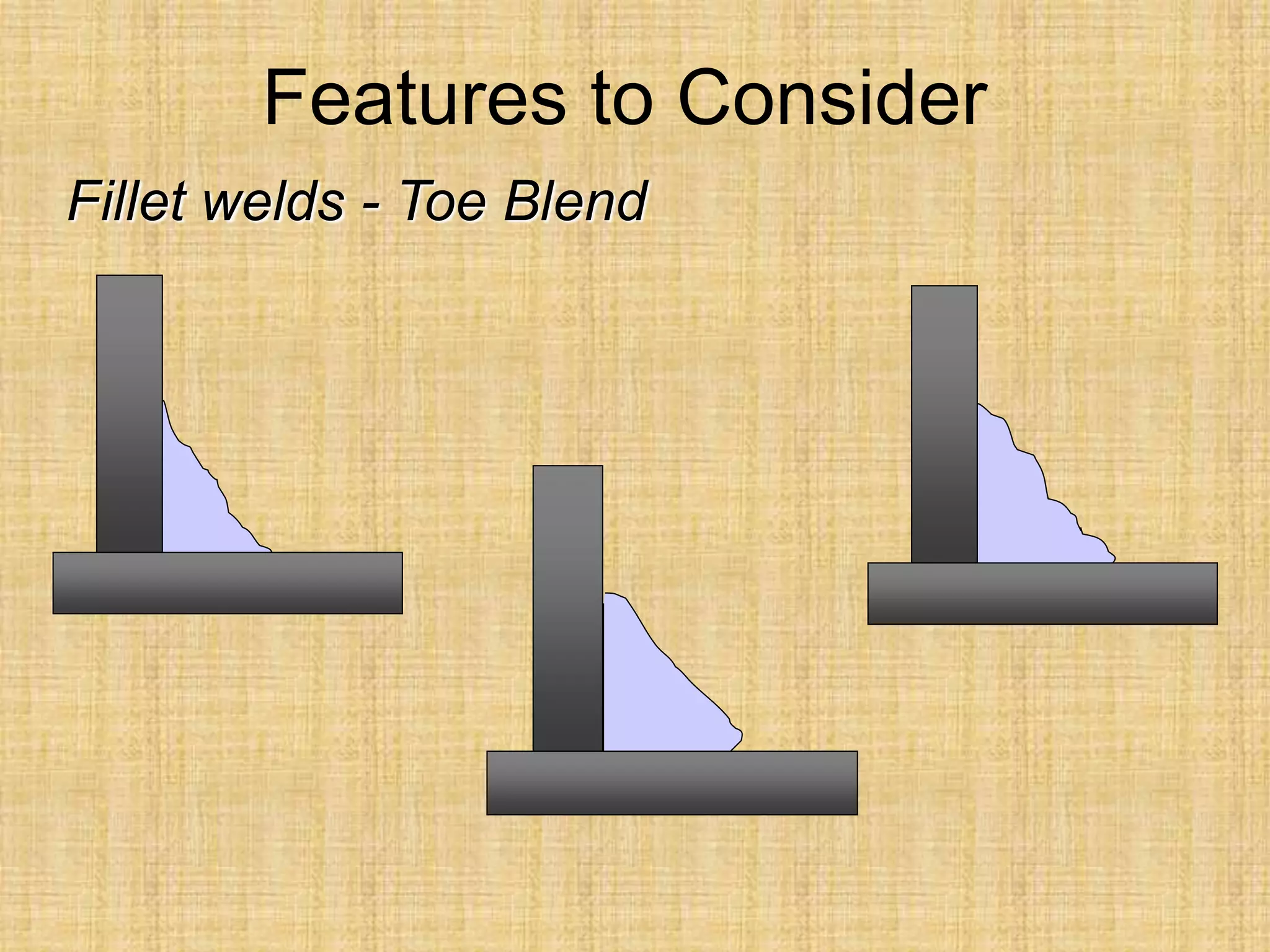
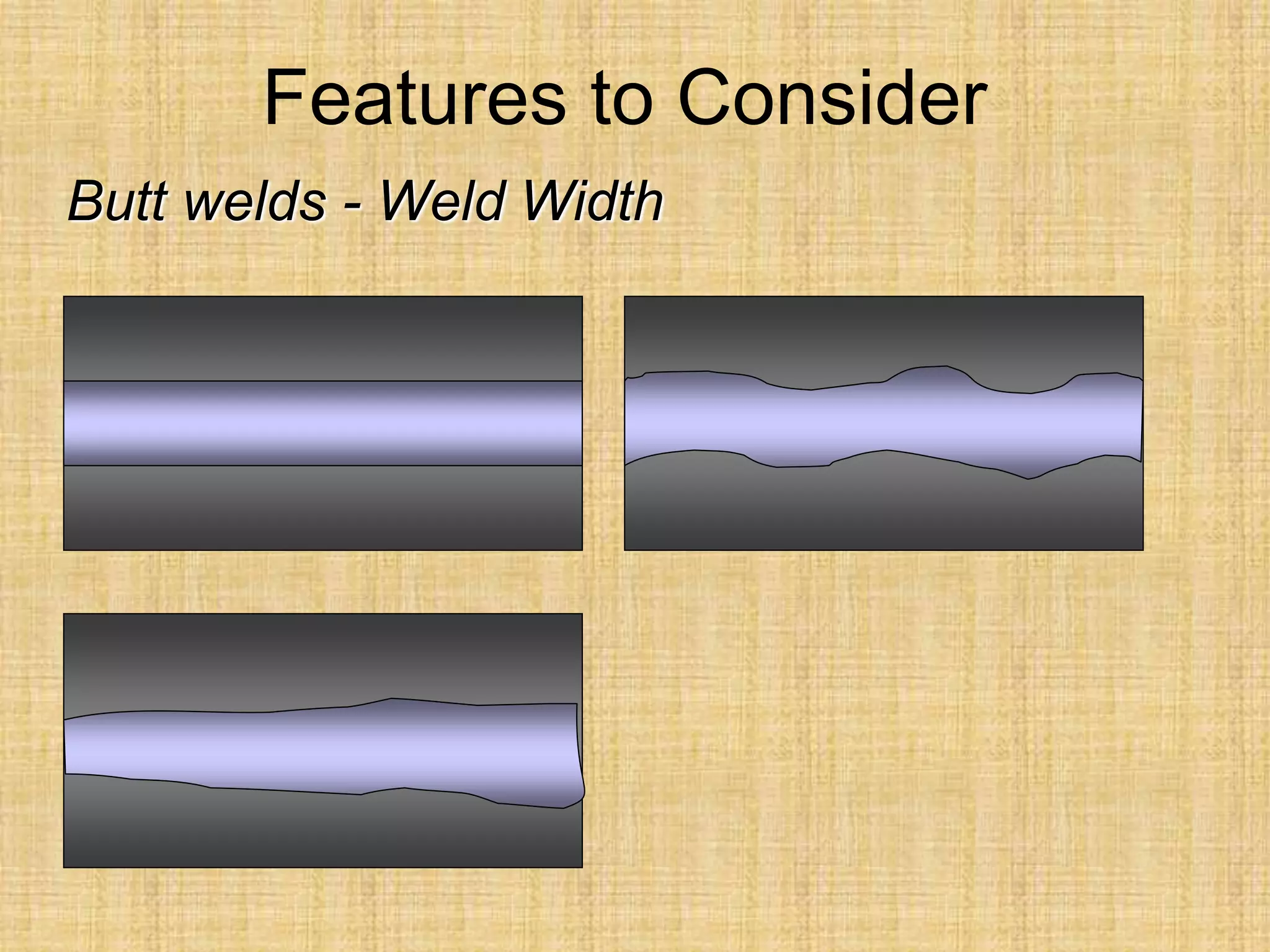
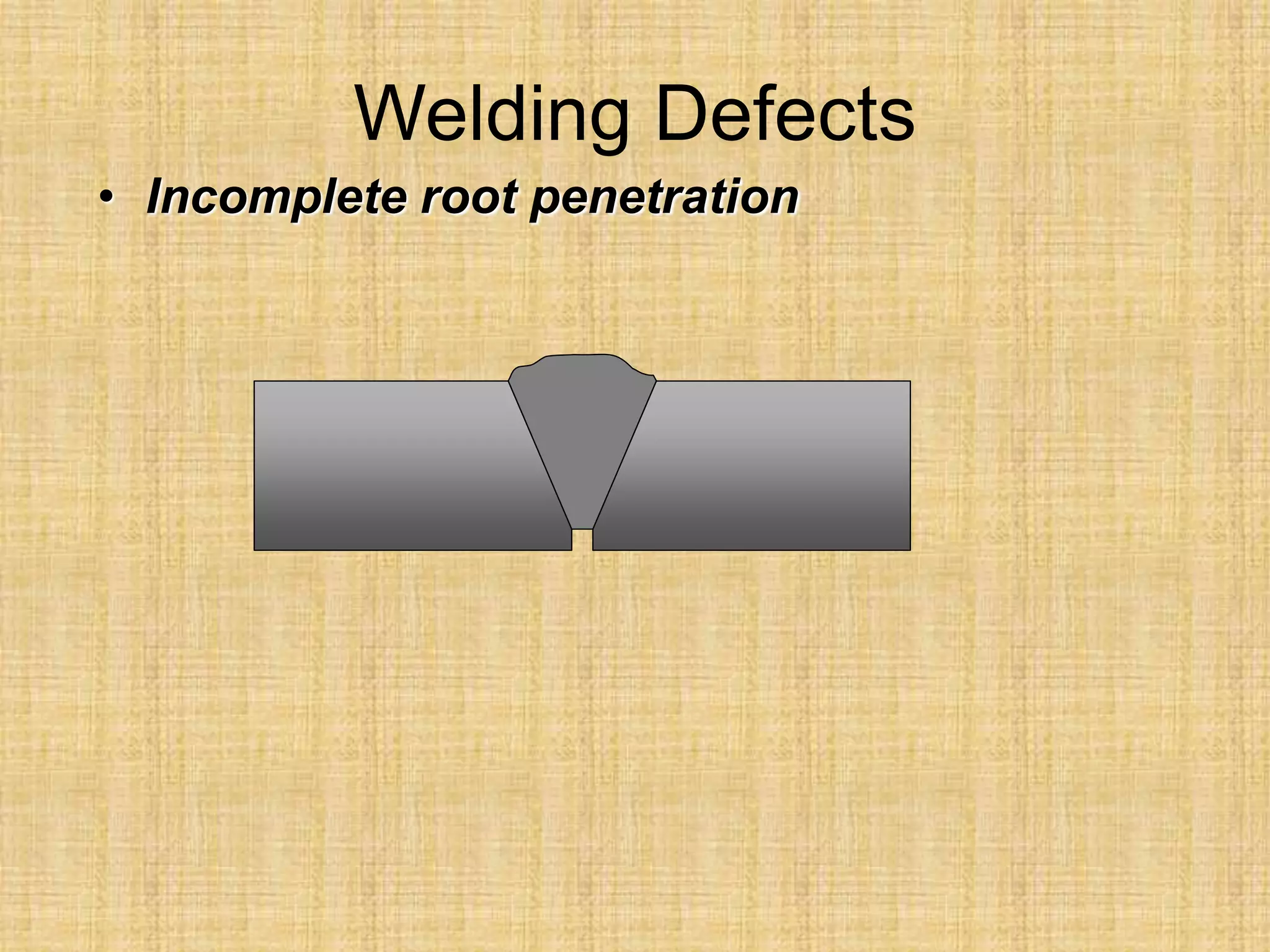
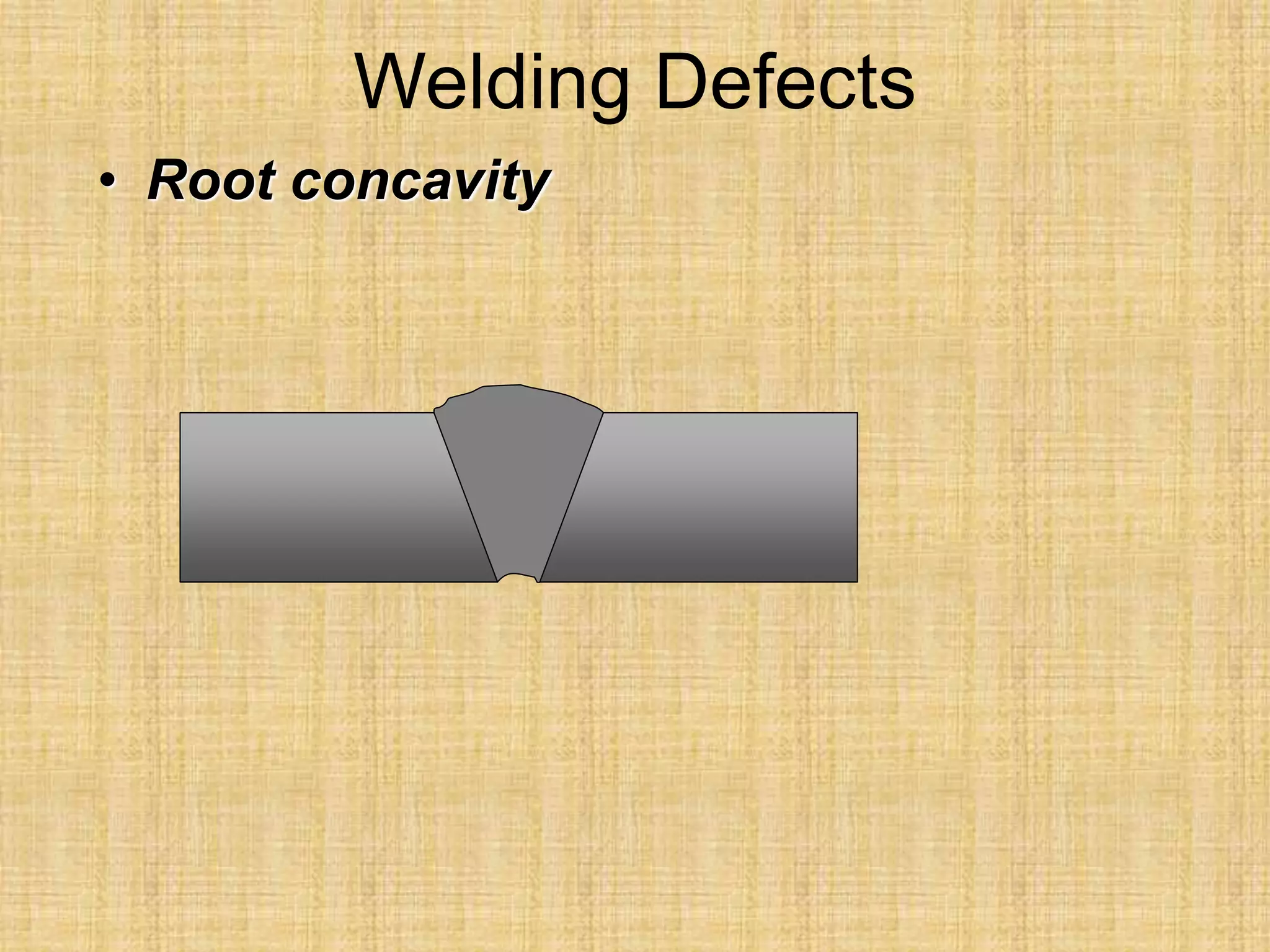
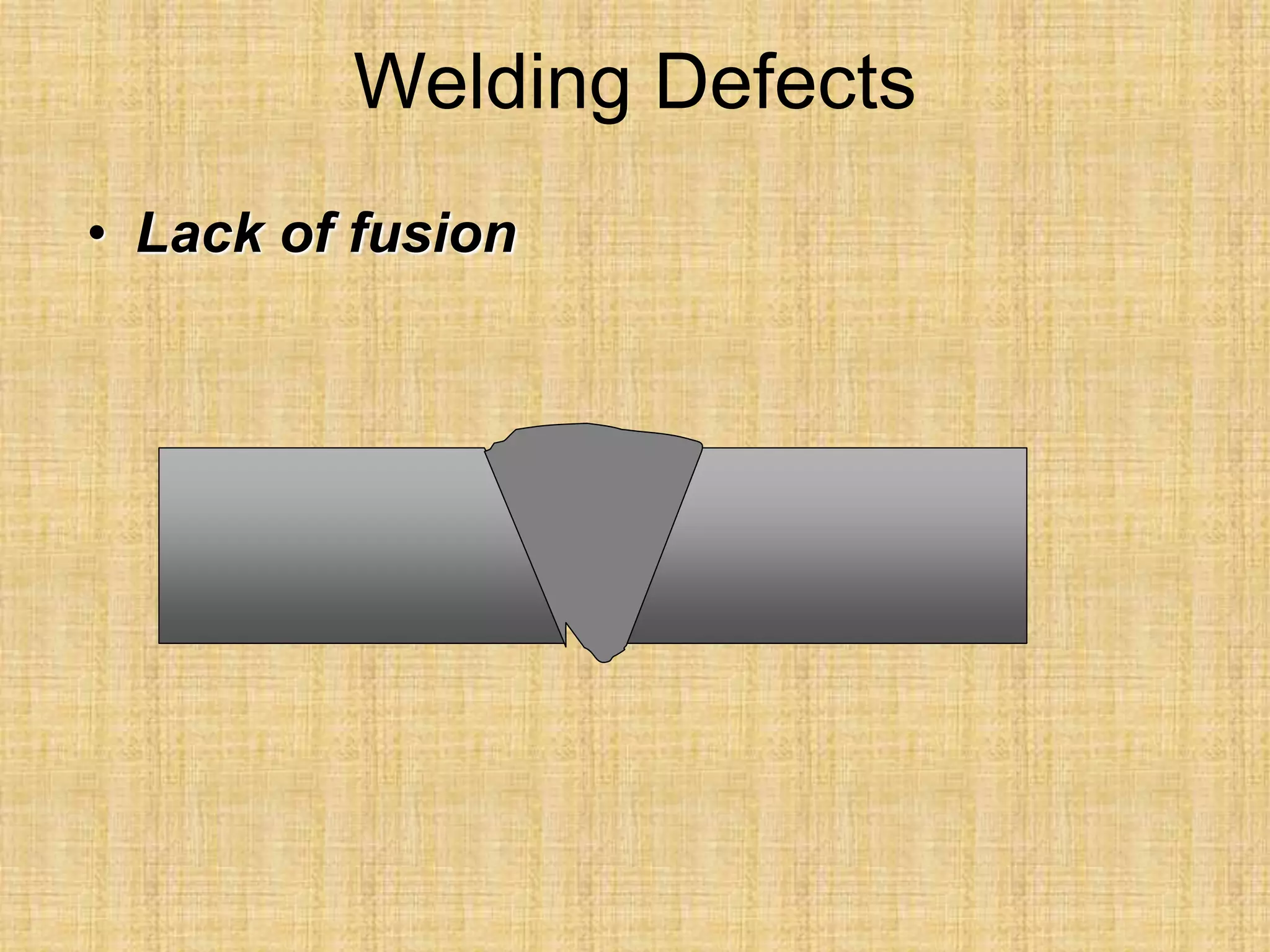
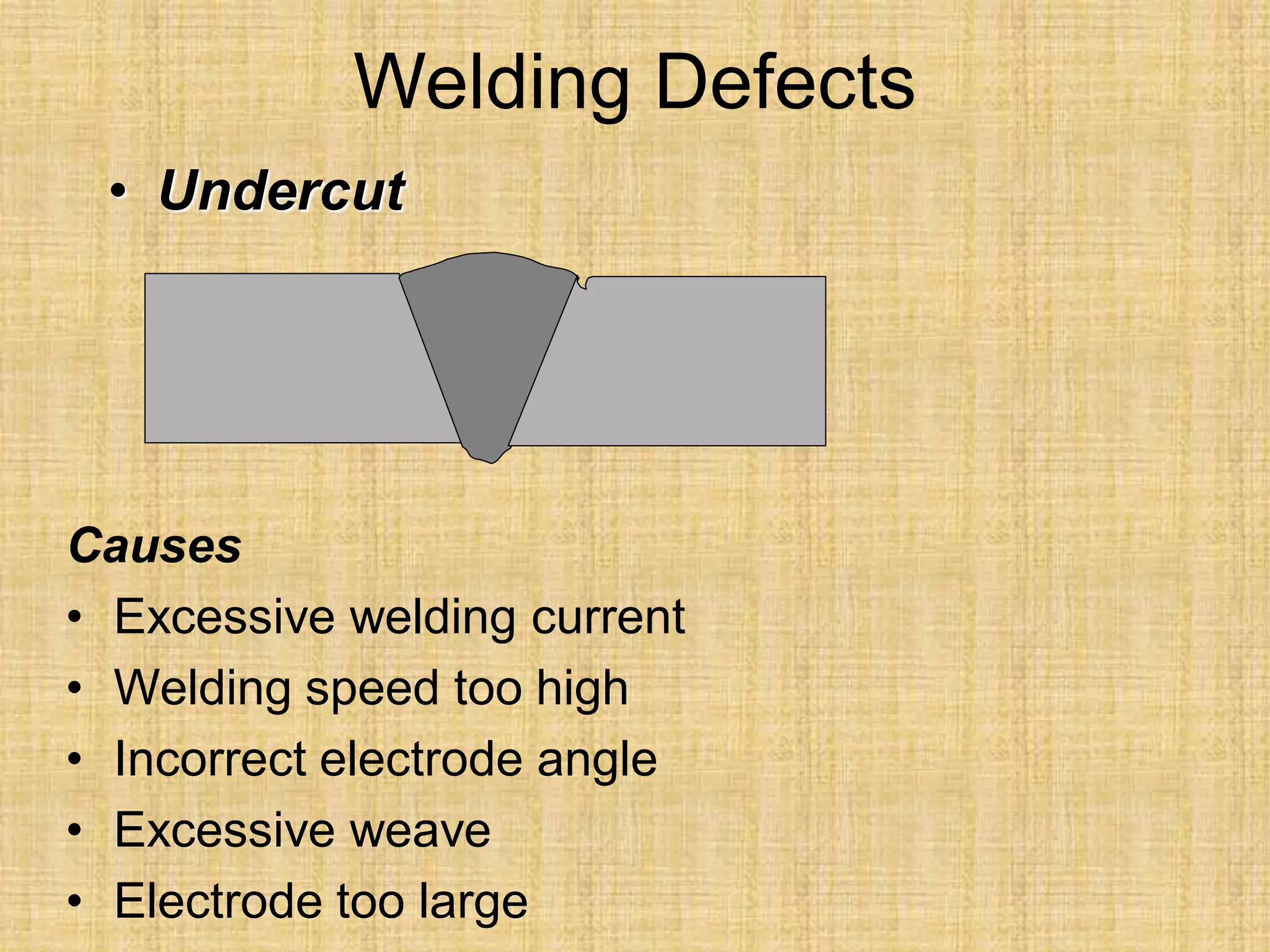
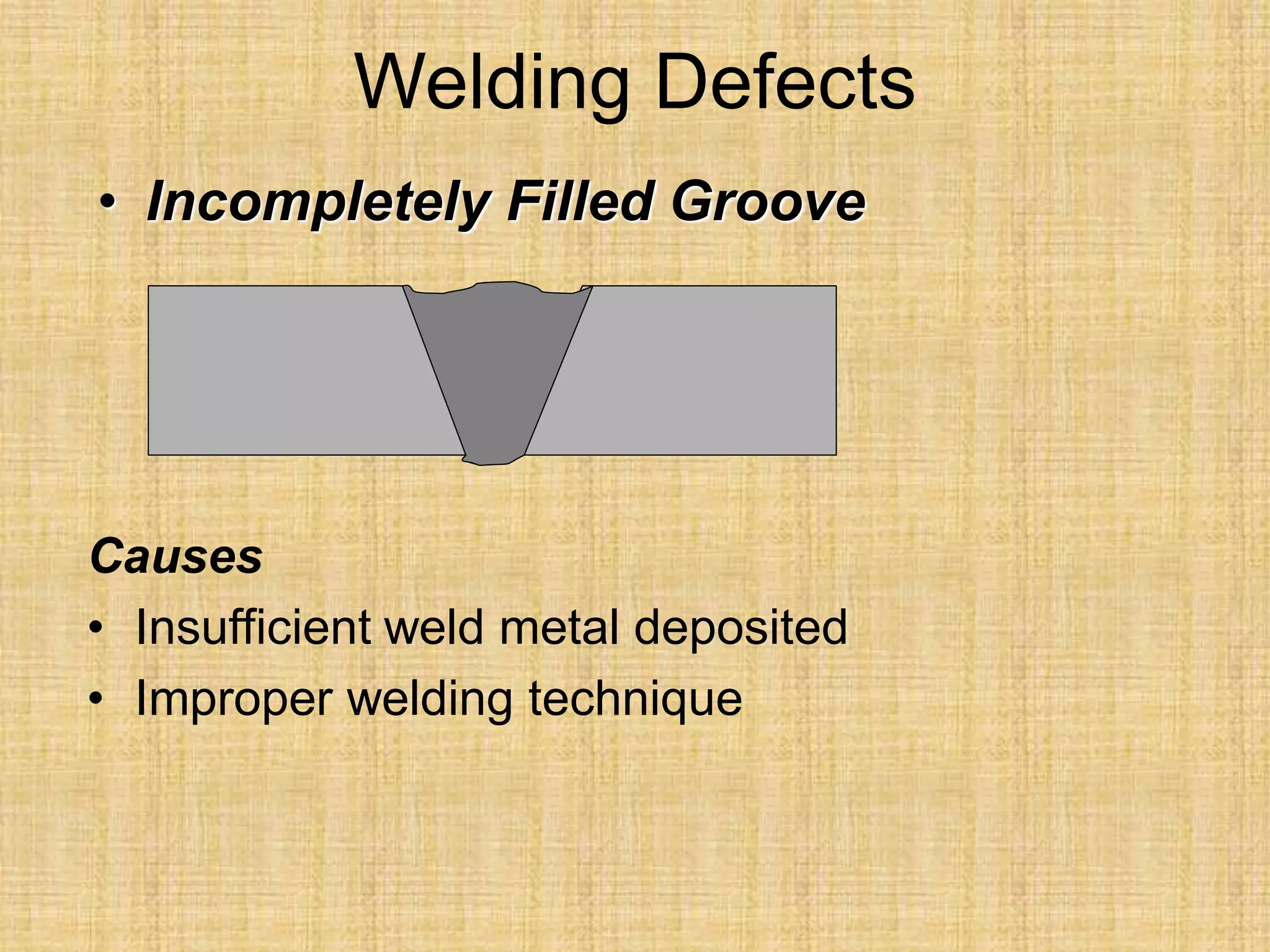
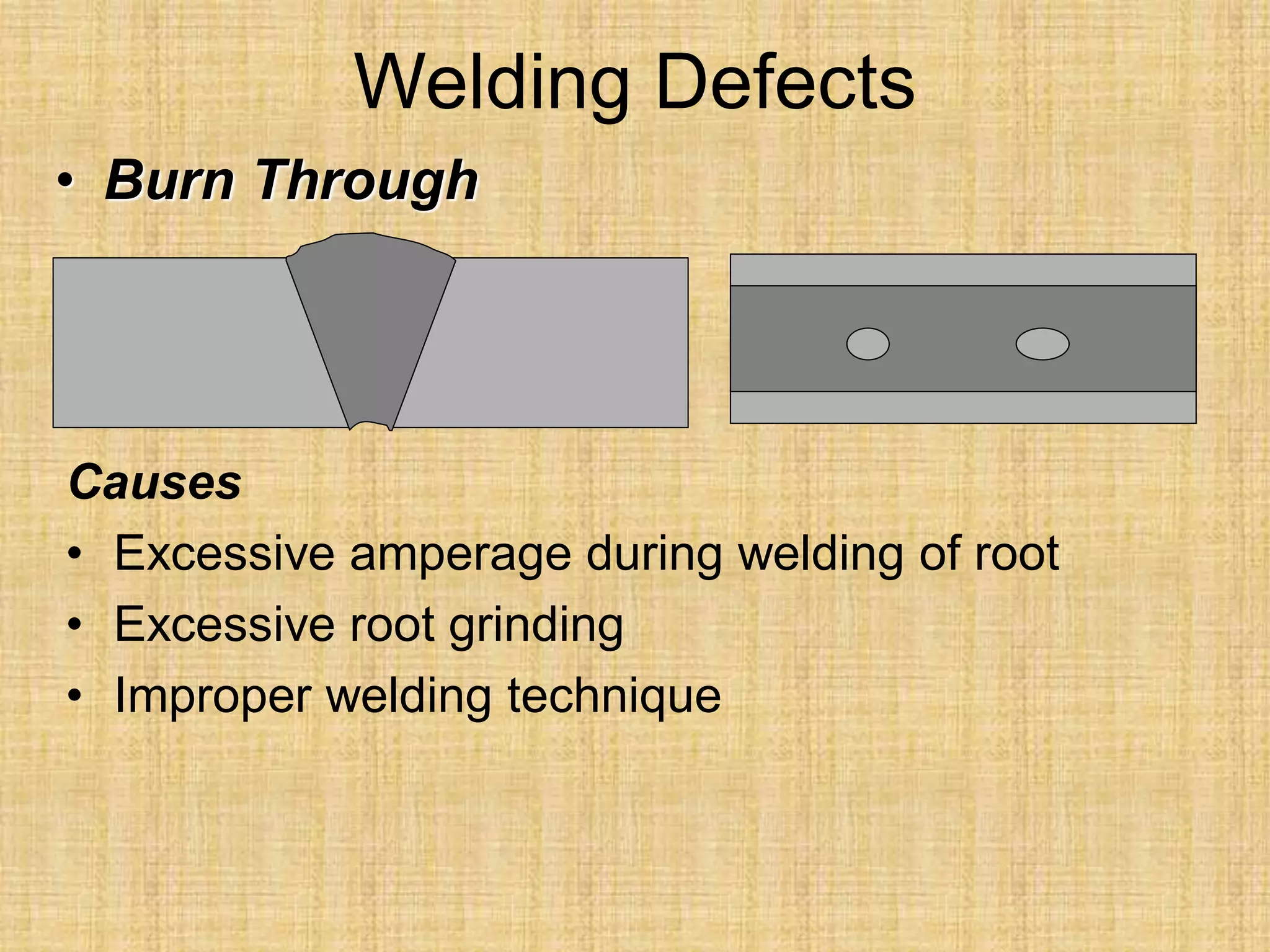
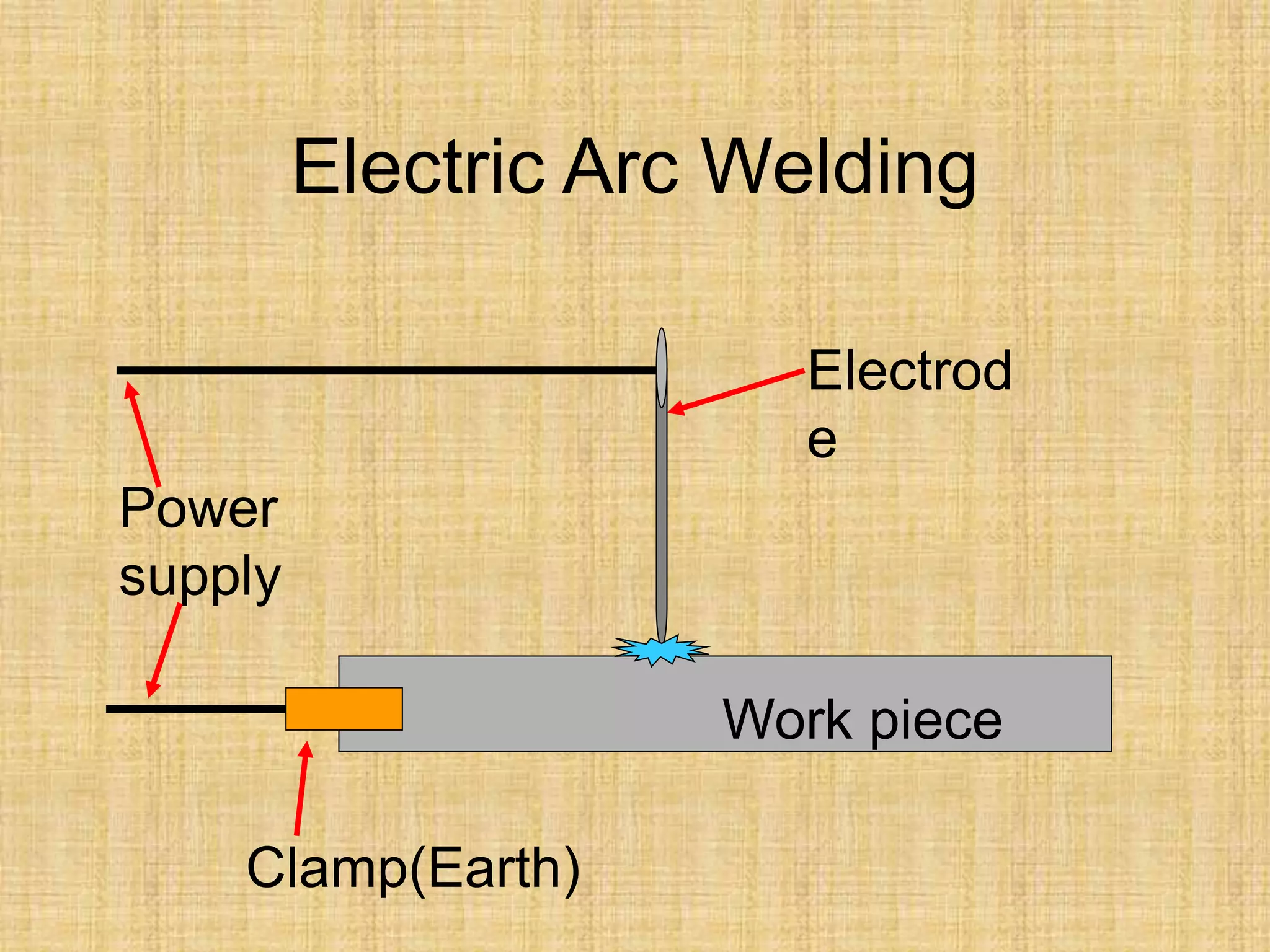
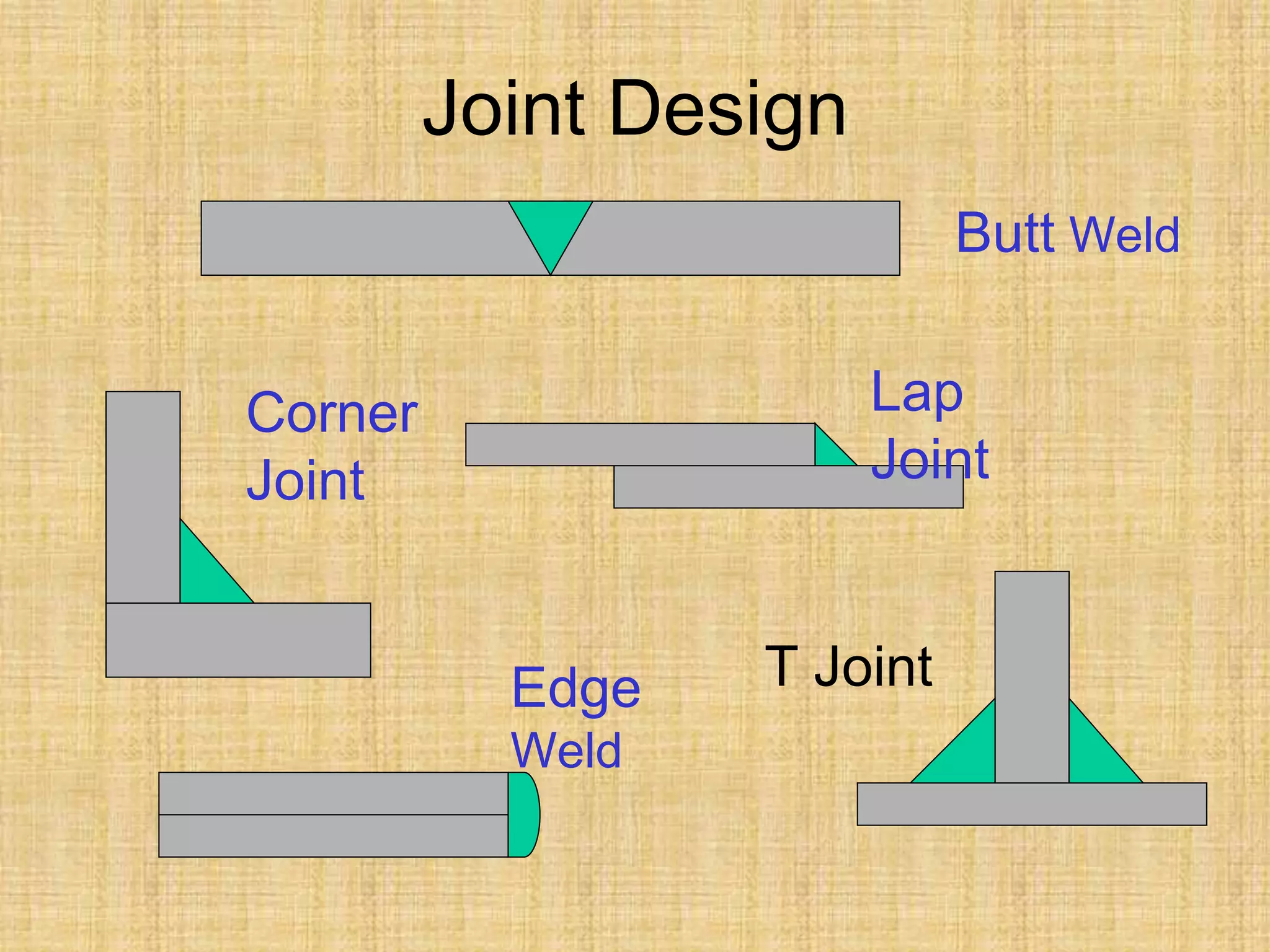
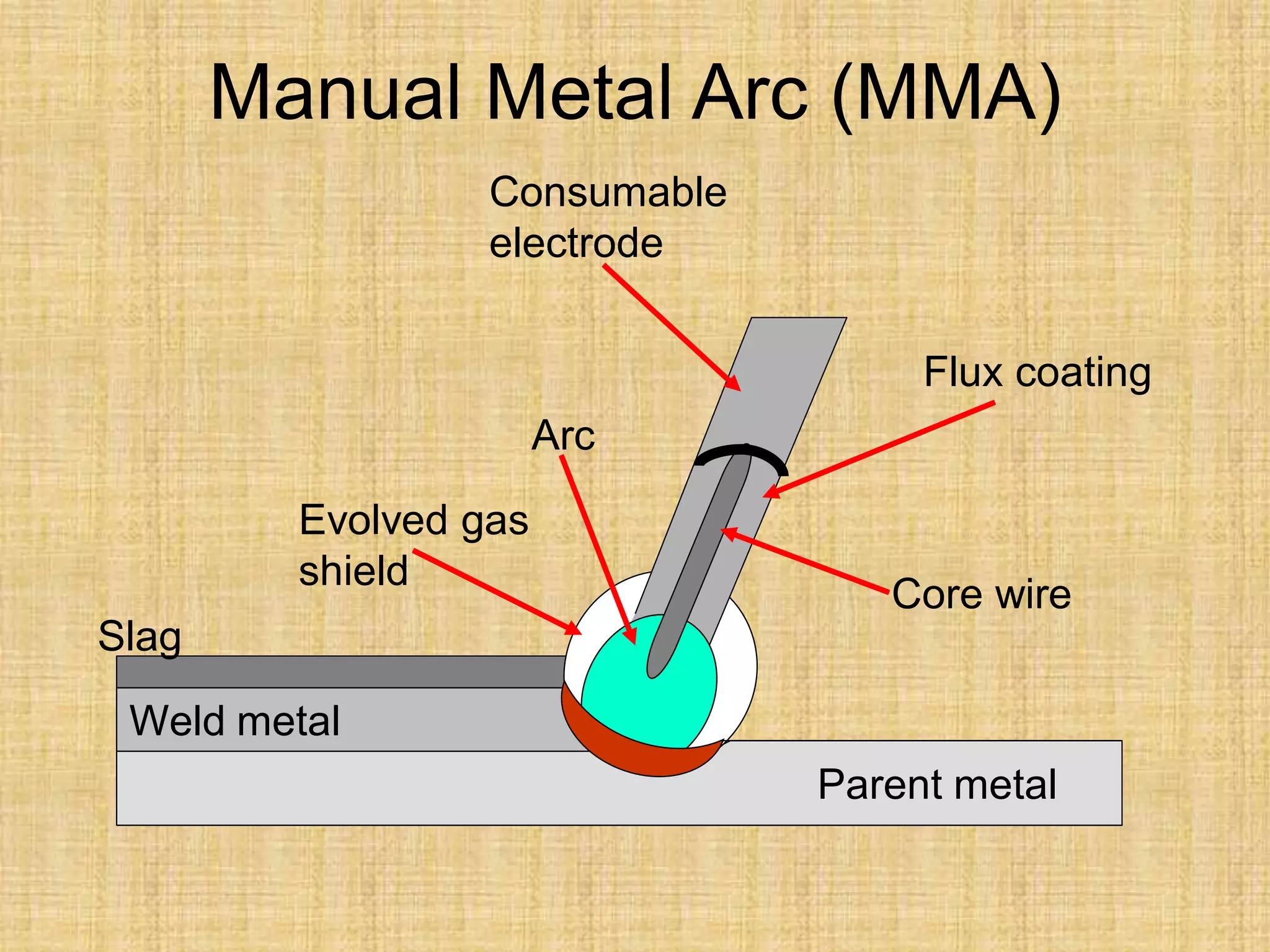
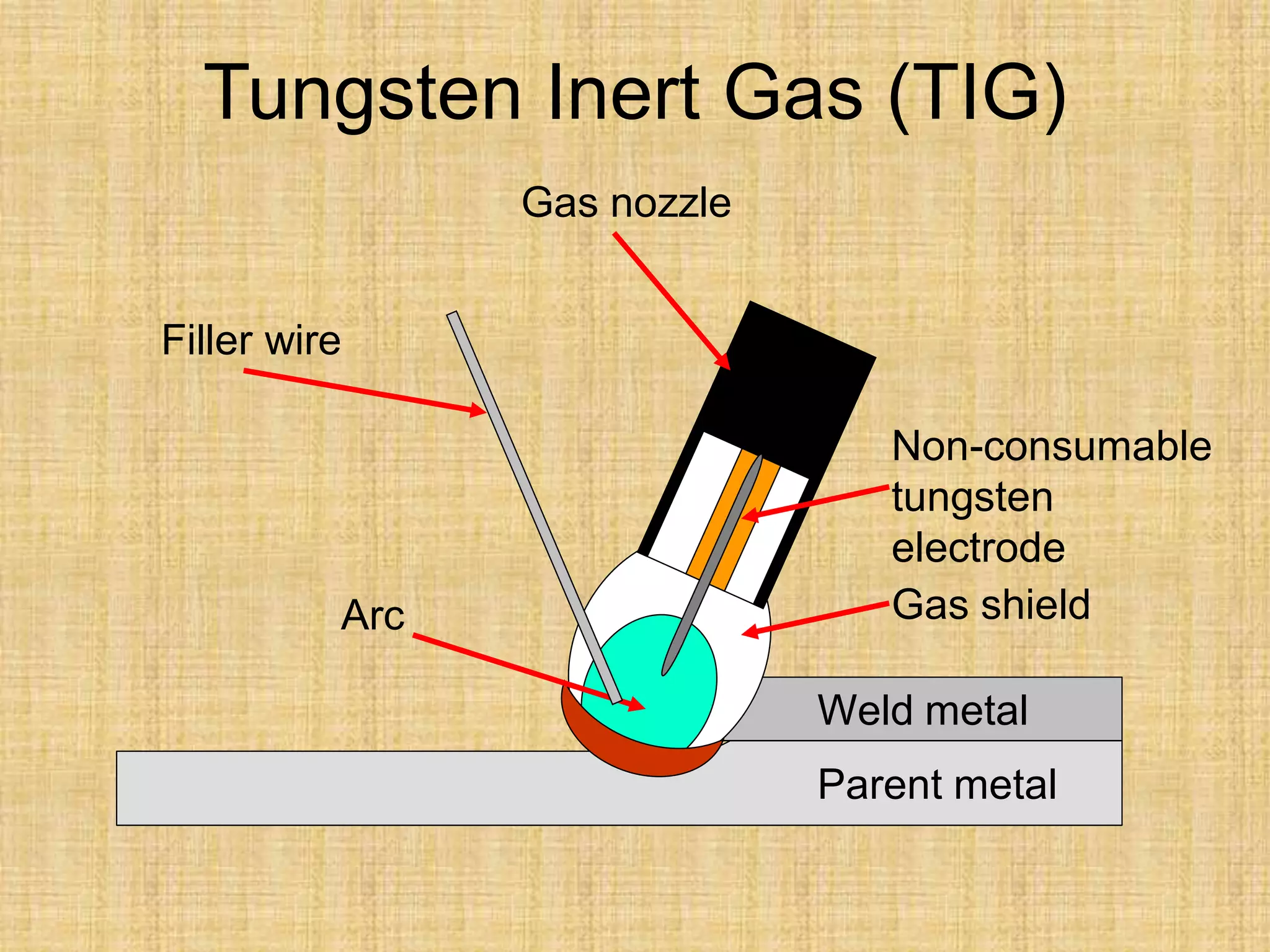
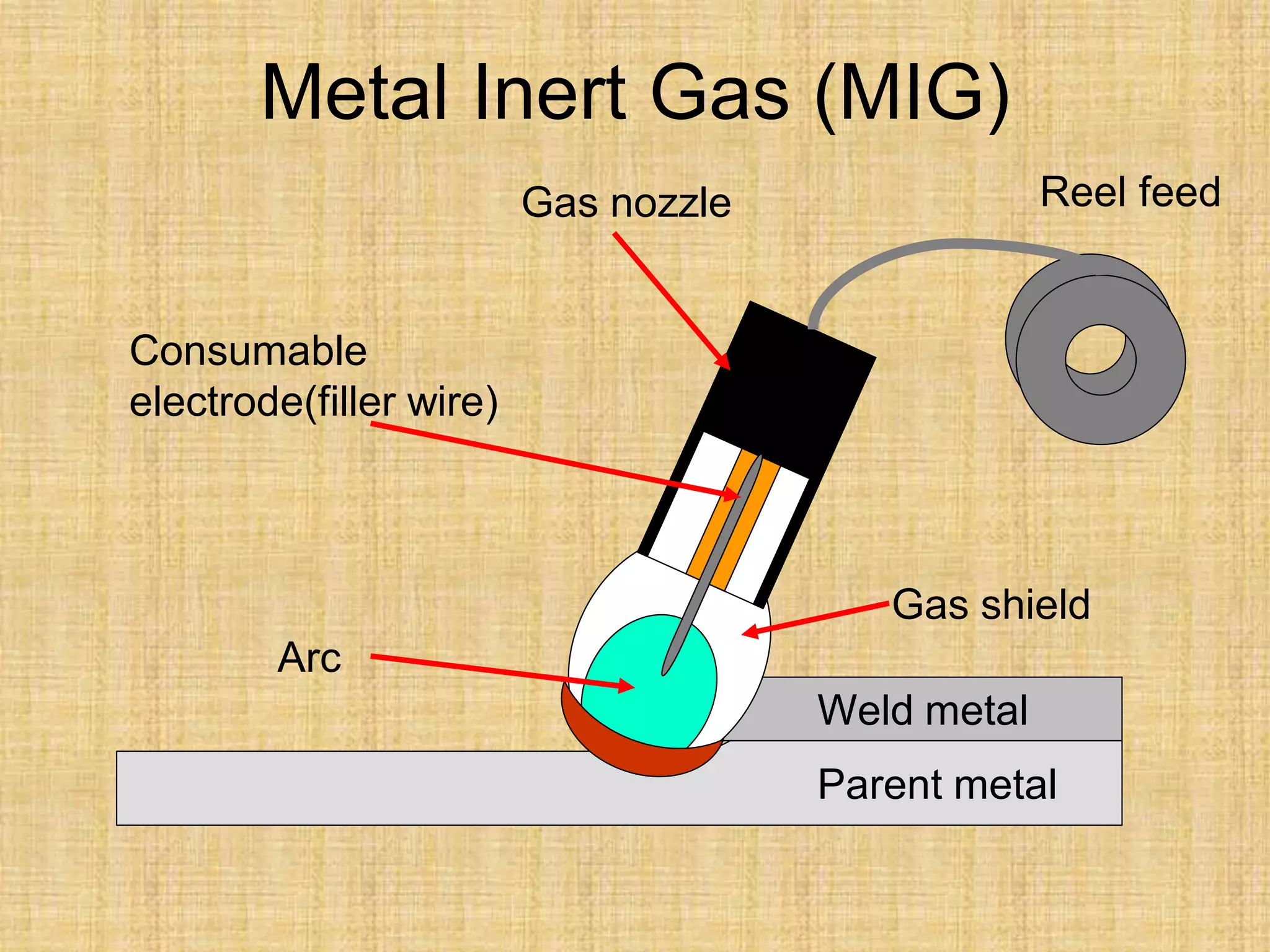
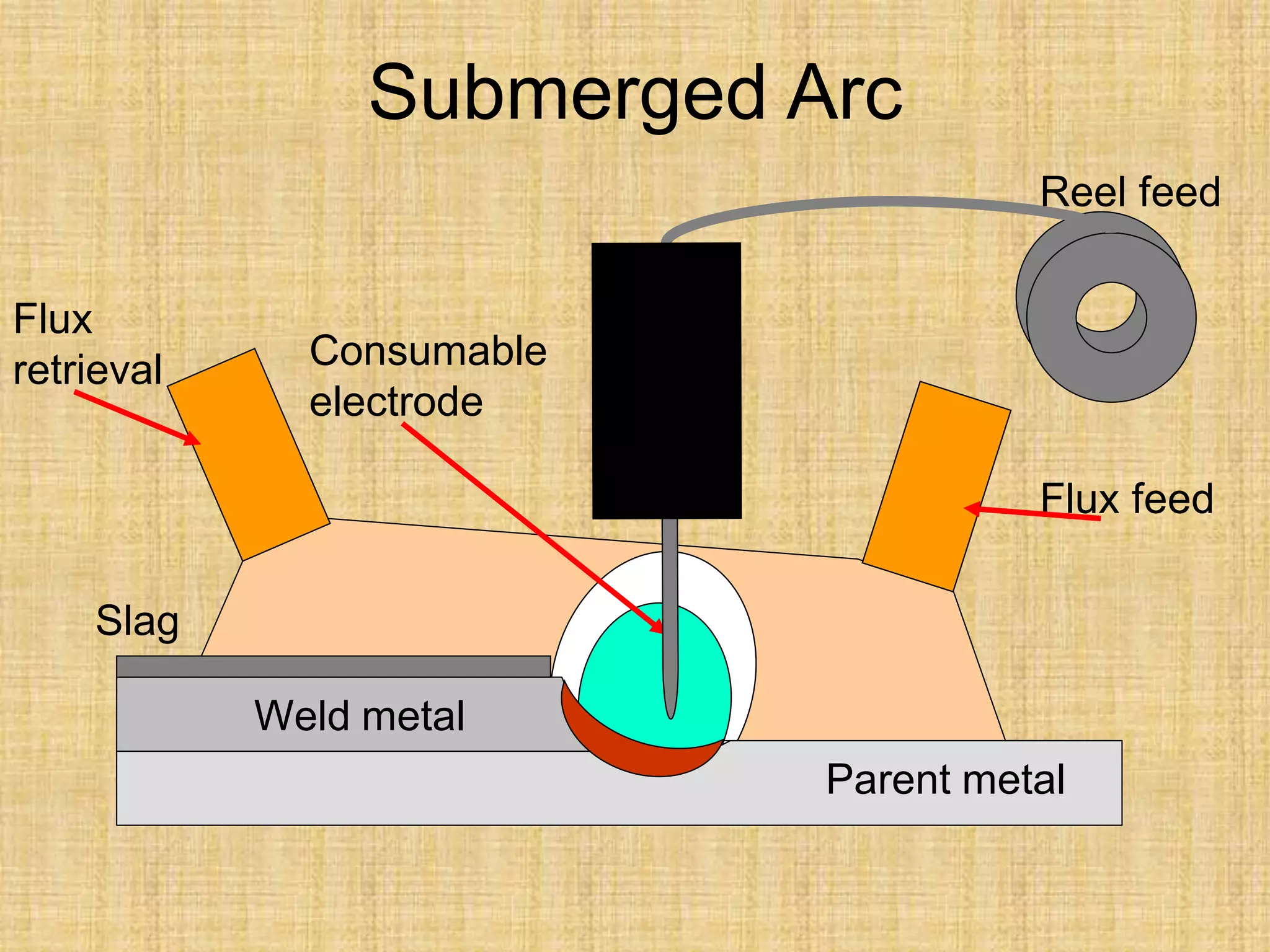
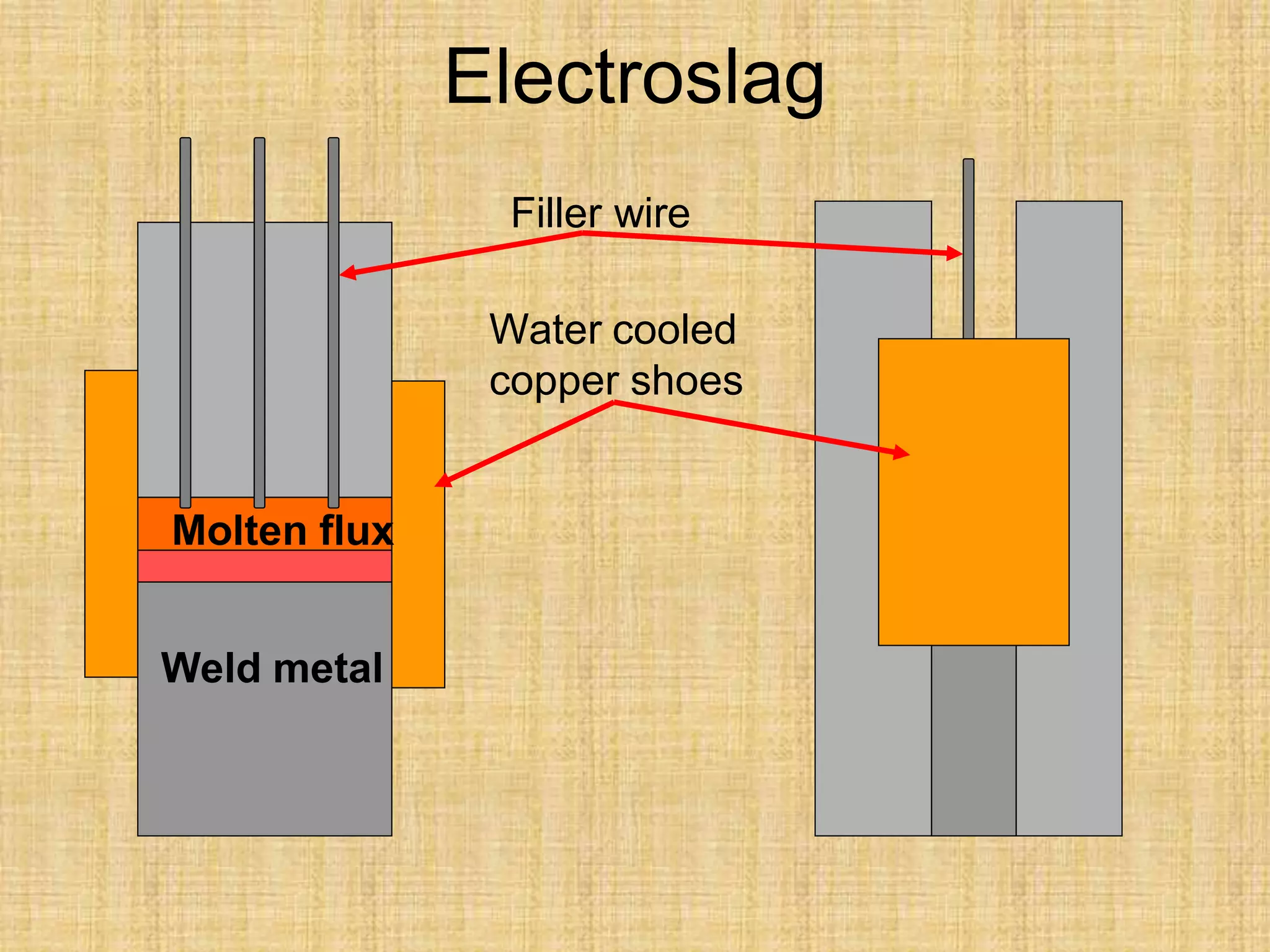
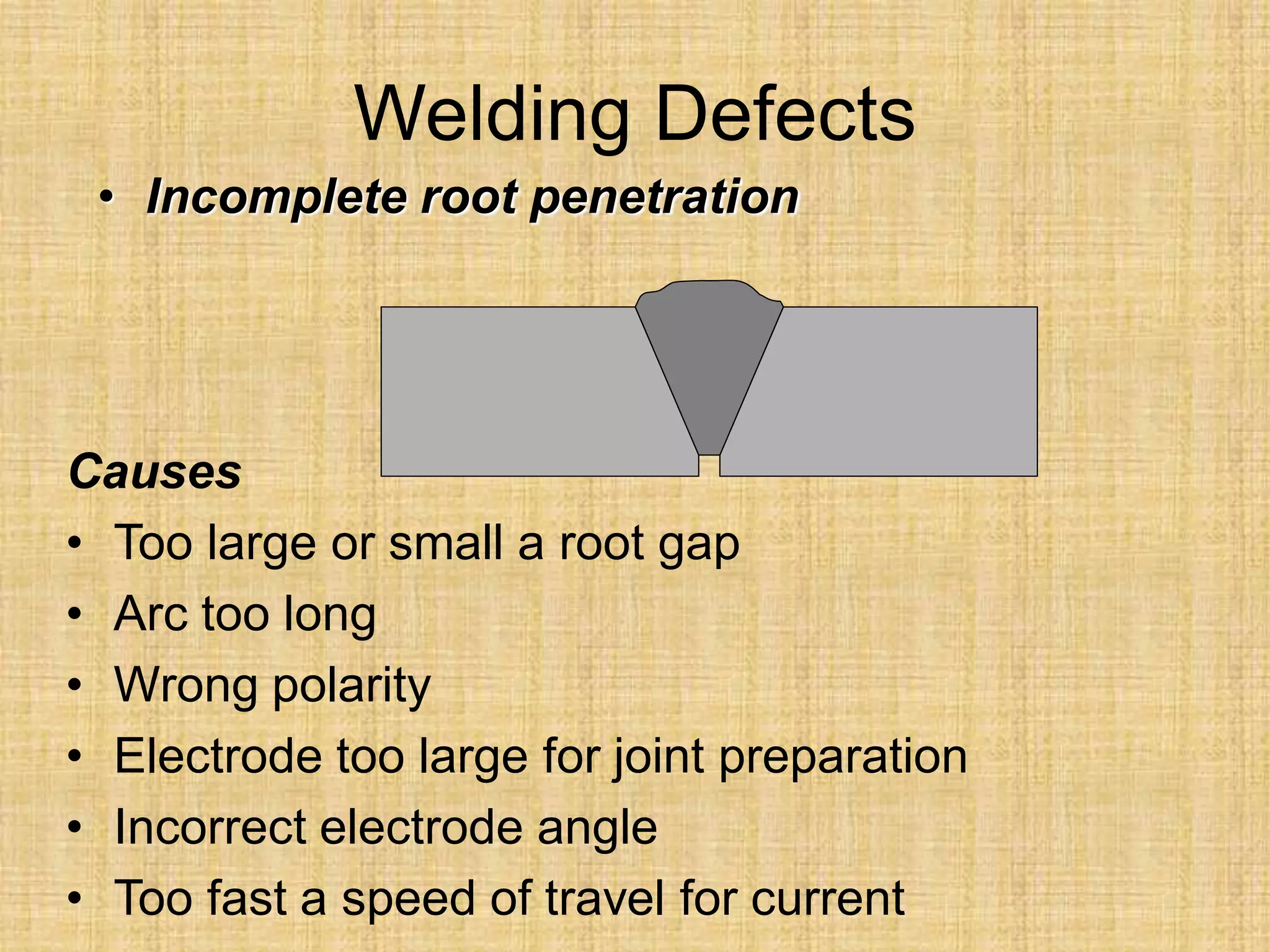
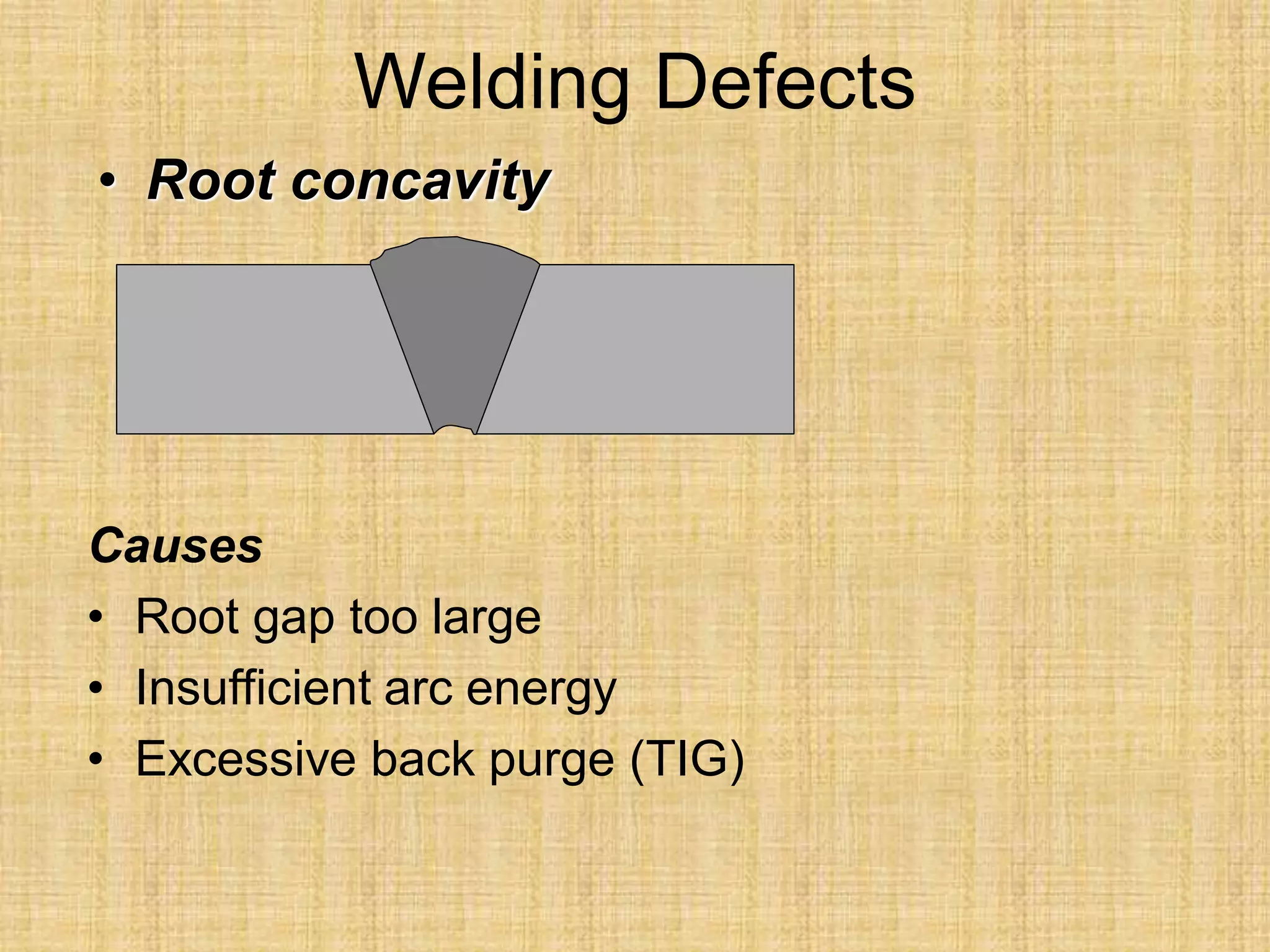
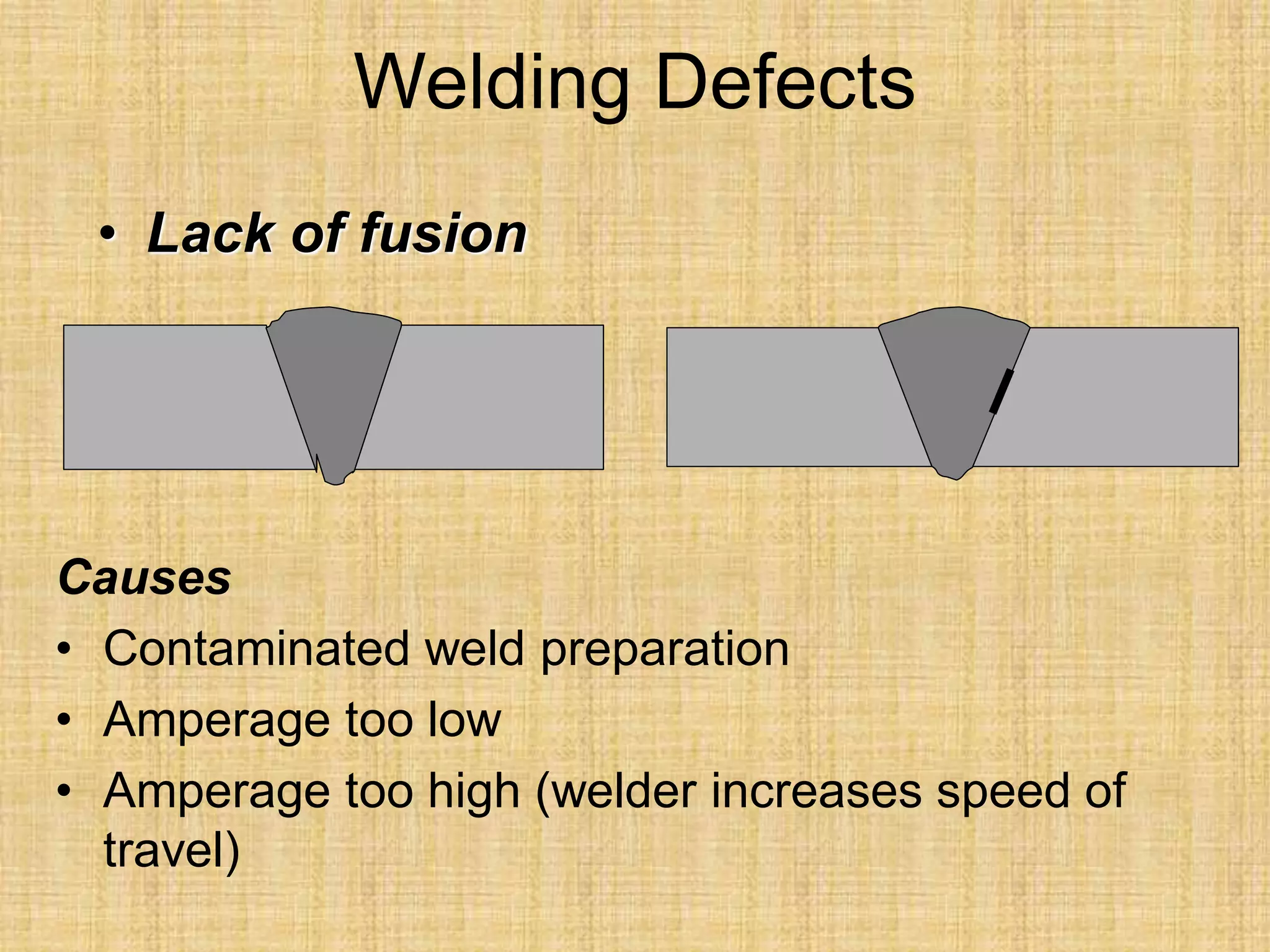
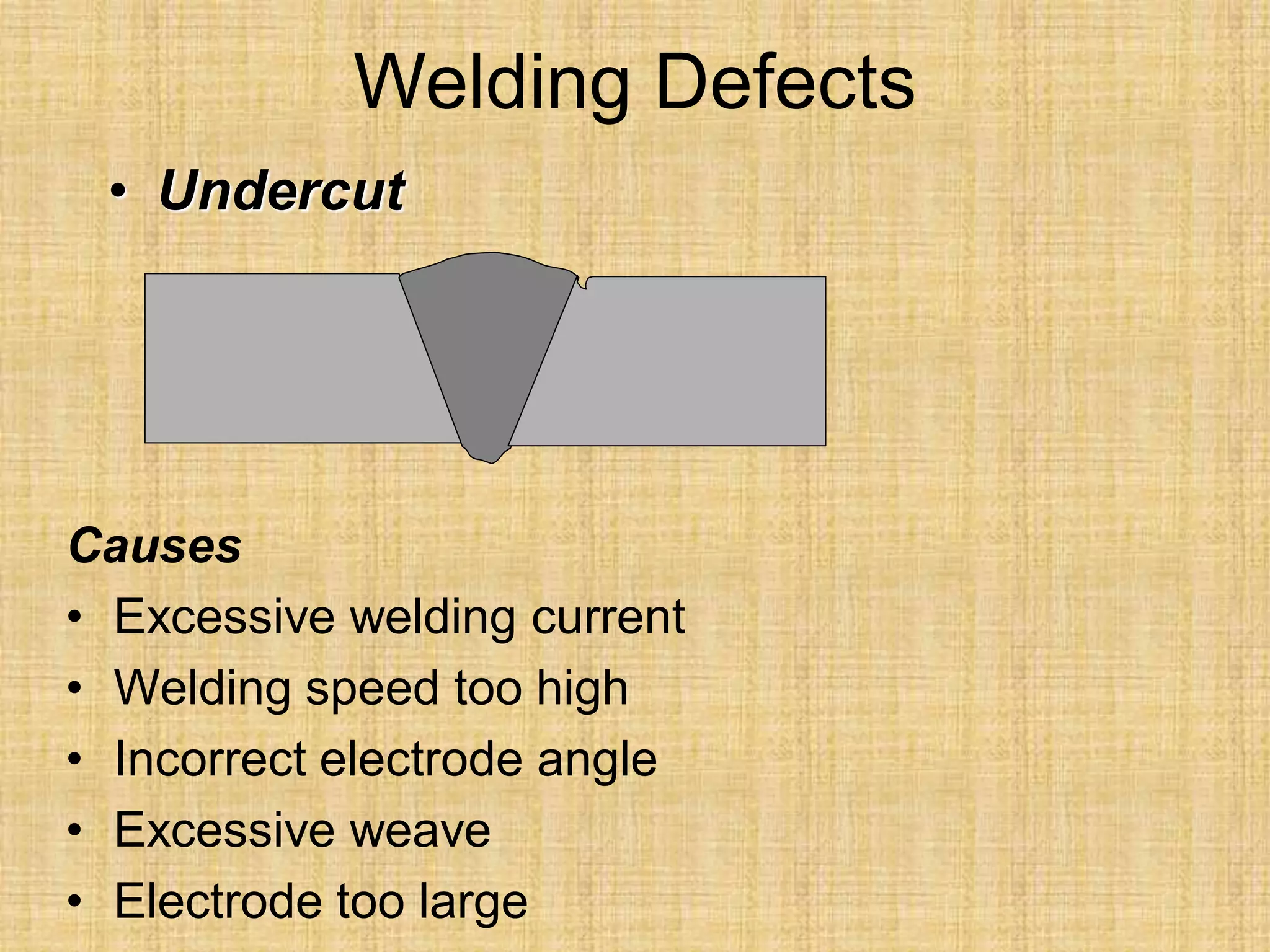
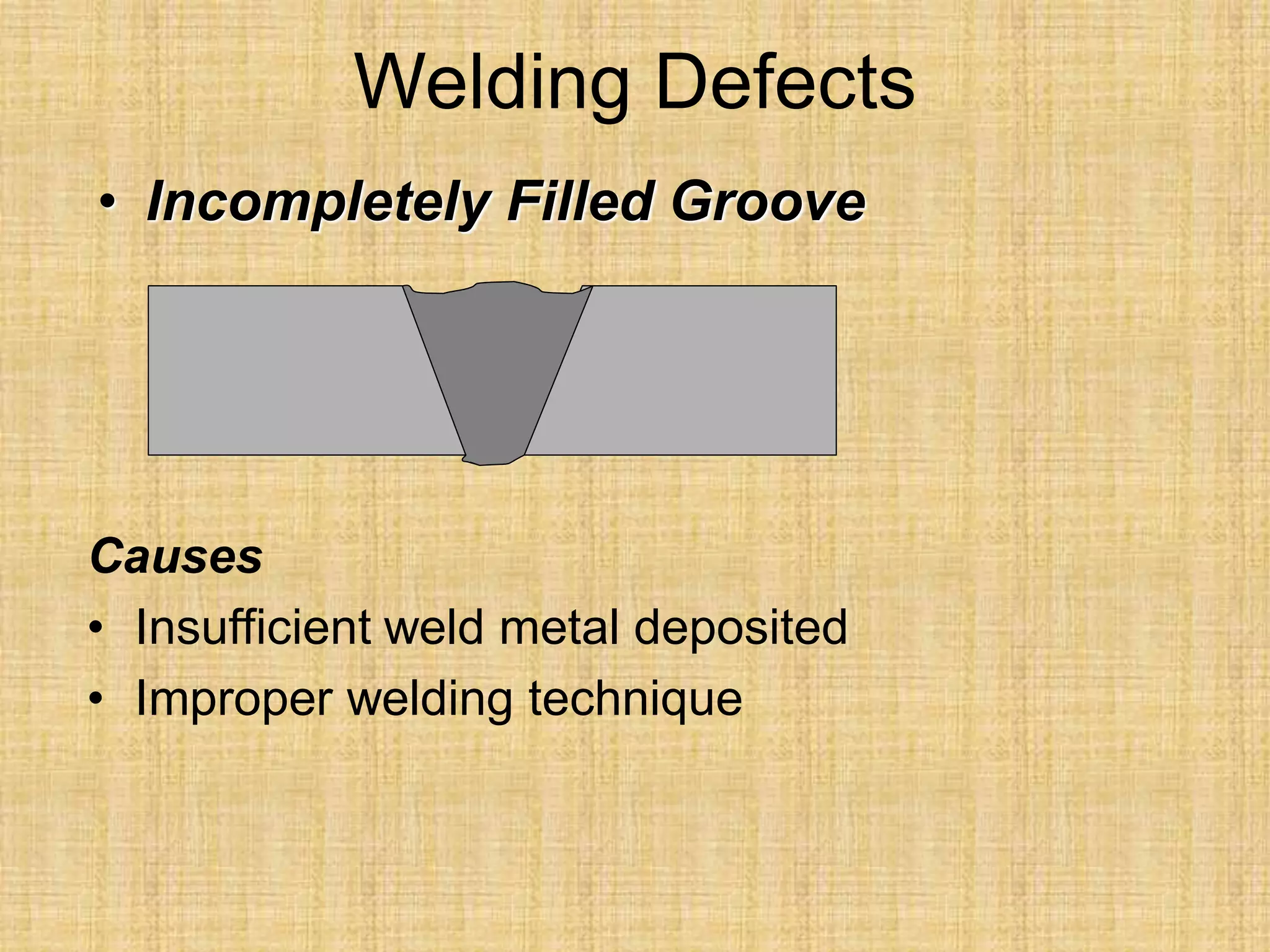
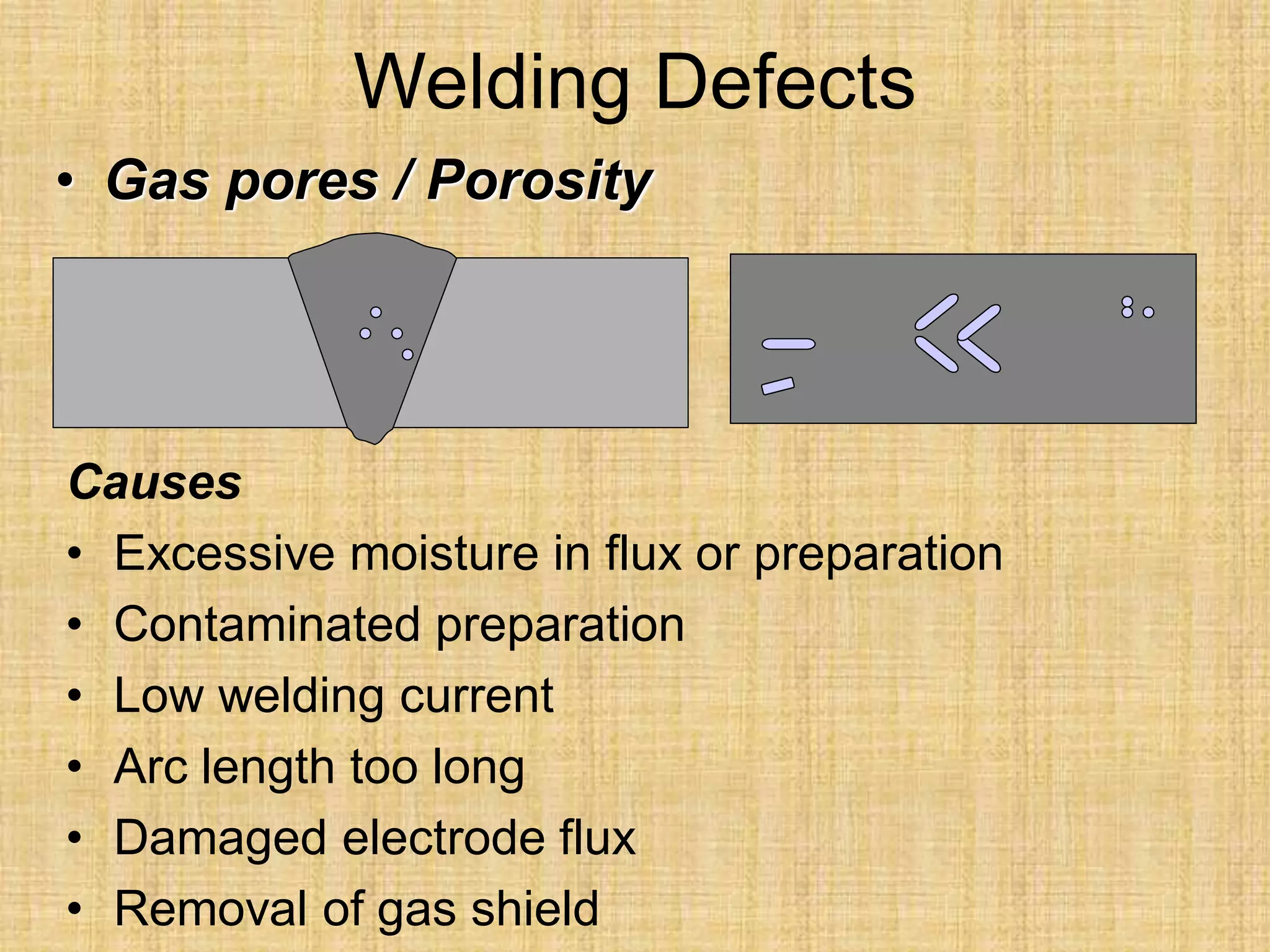
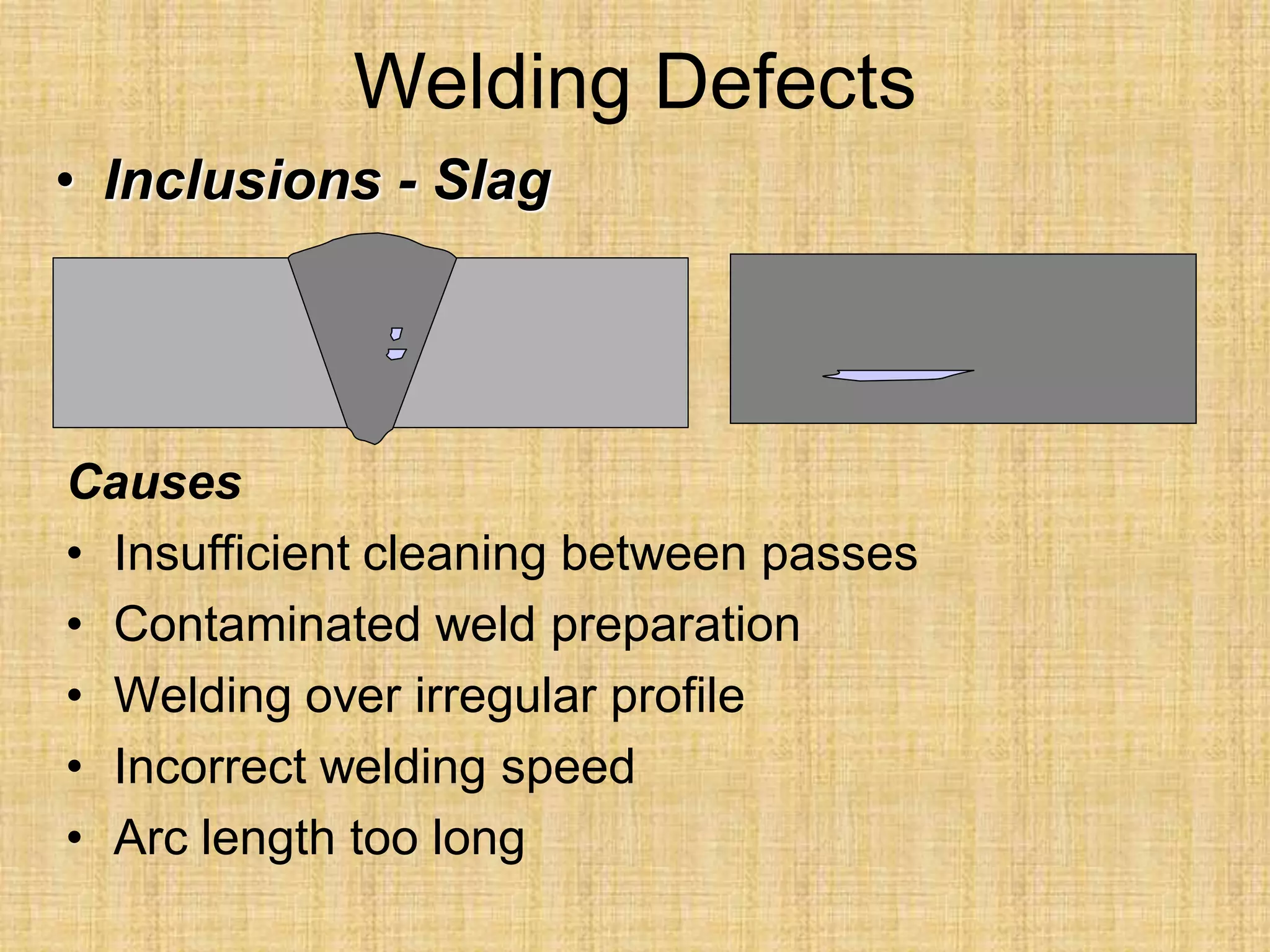
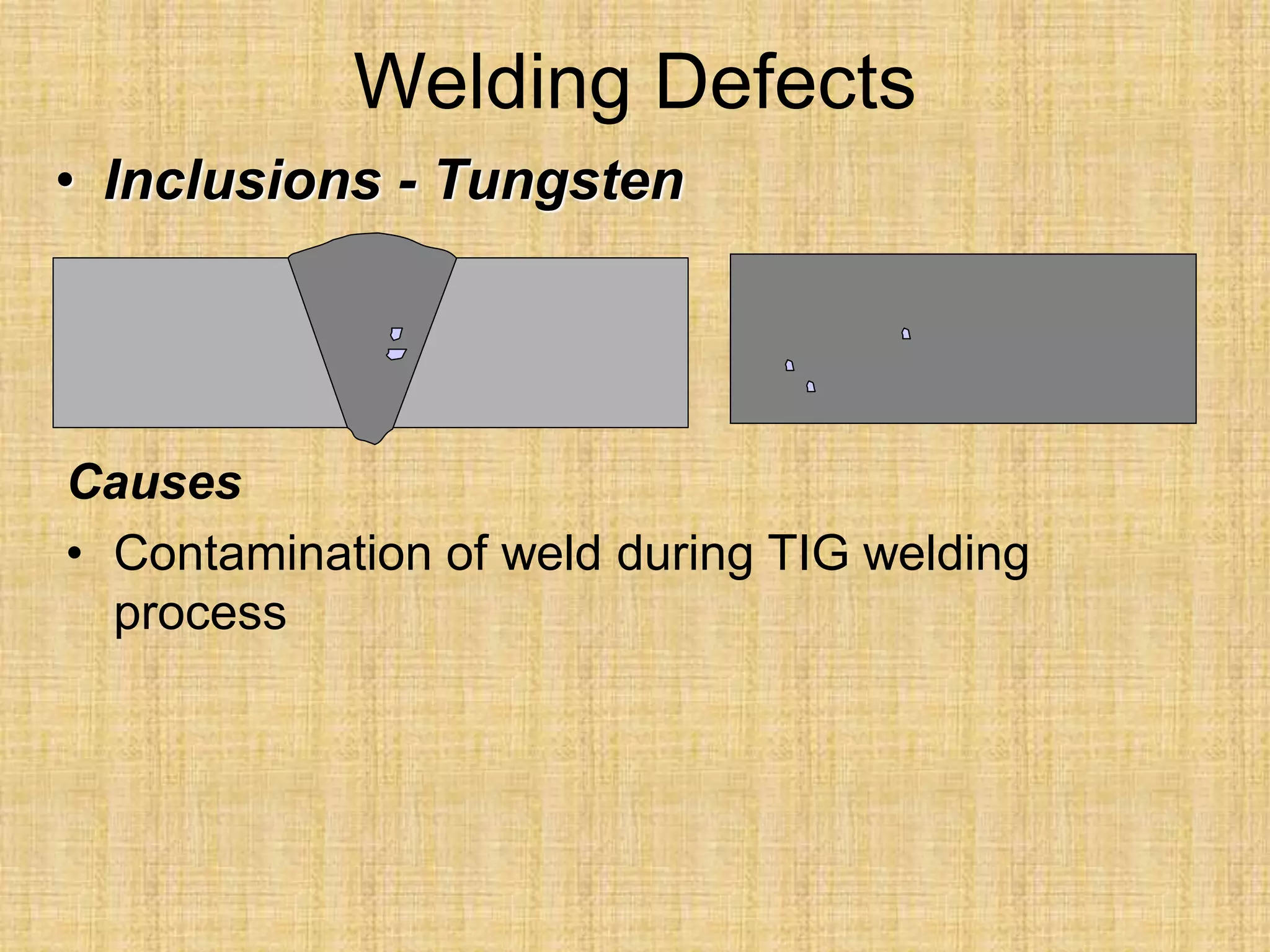
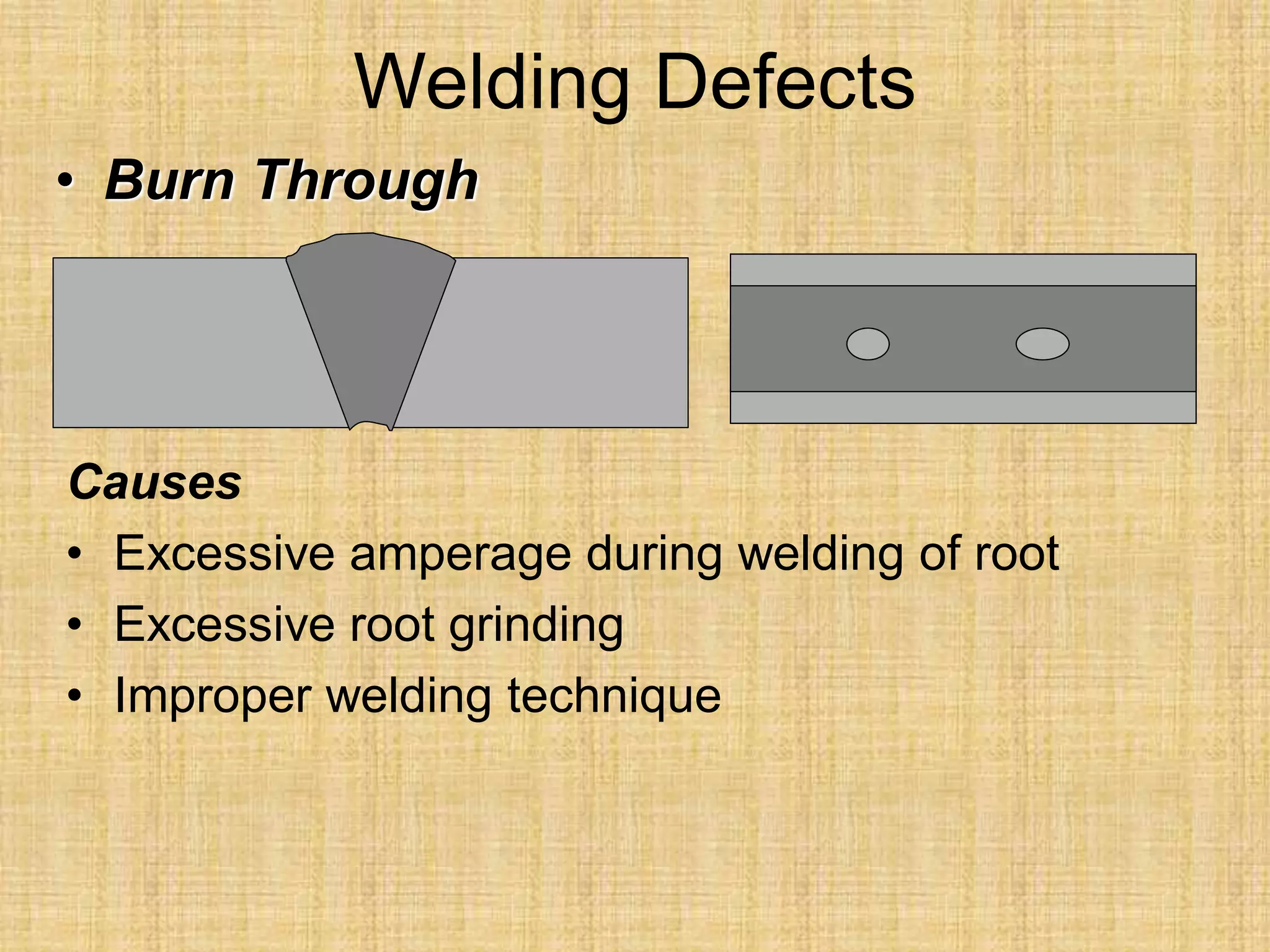
The document discusses visual inspection of welds, including terminology for different types of welds and weld features. It provides checklists for welding procedures before, during, and after welding. Common welding defects such as lack of fusion, undercut, and porosity are described along with their potential causes. Visual inspection procedures and features to examine in butt and fillet welds are also outlined.