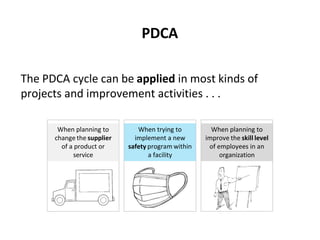
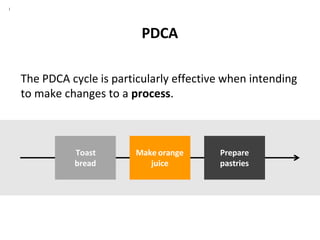
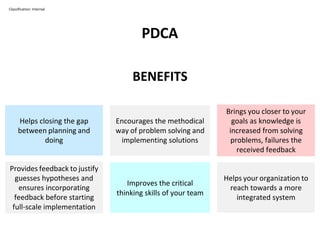
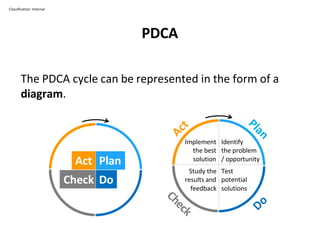
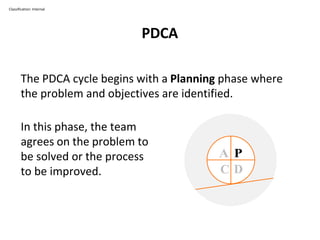
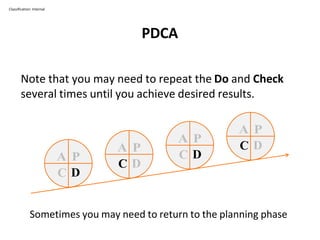
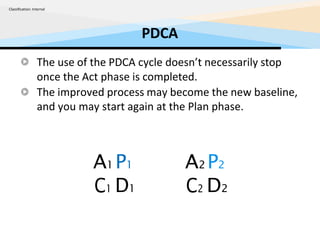
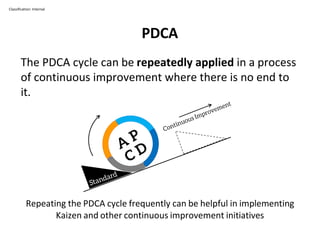
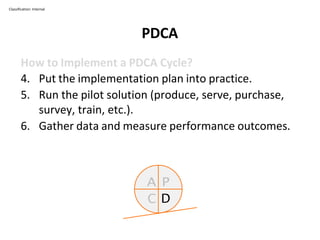
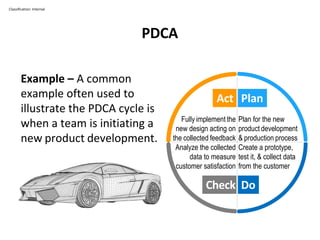
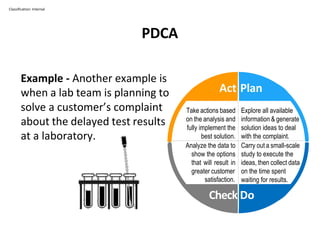
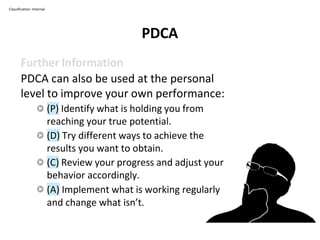
The PDCA cycle is a structured four-step model (Plan, Do, Check, Act) used for problem solving and continuous improvement in various projects. It encourages iterative cycles aimed at enhancing processes, products, and services, and can be applied to multiple scenarios such as supplier changes and employee training. By emphasizing analysis and feedback, the PDCA cycle fosters methodical problem-solving and helps organizations reach their goals through continuous learning and adaptation.