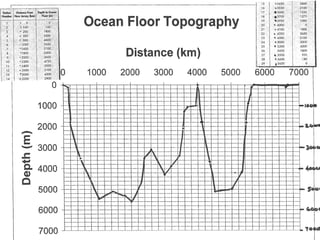
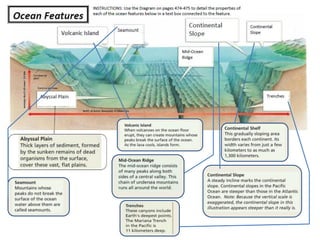
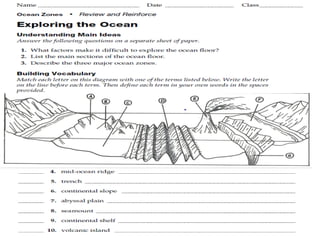
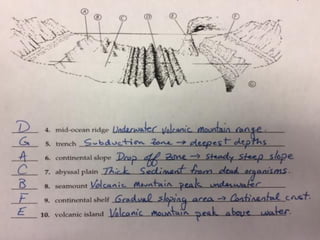
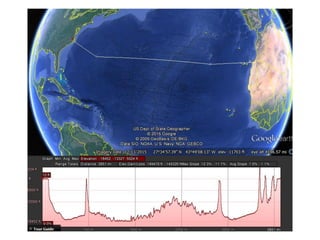
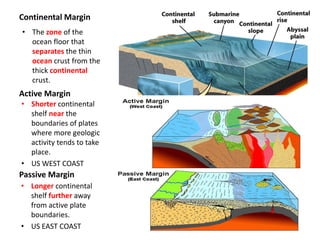
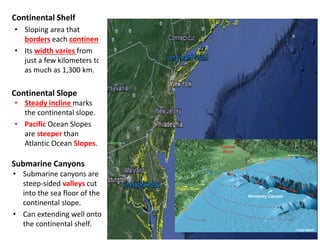
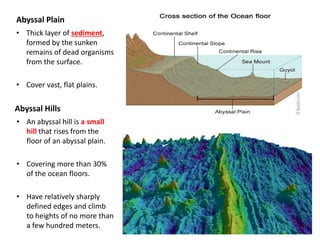
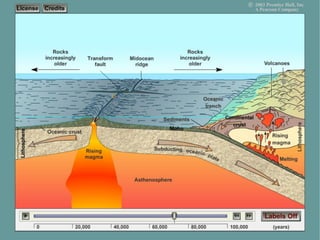
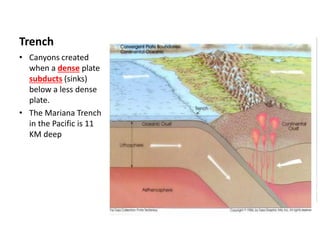
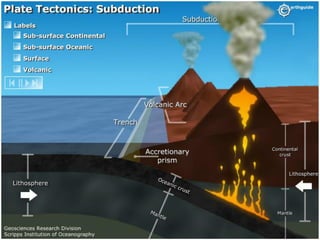
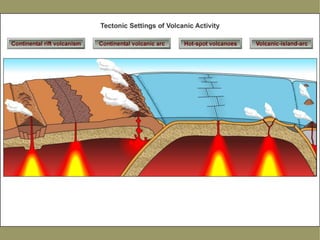
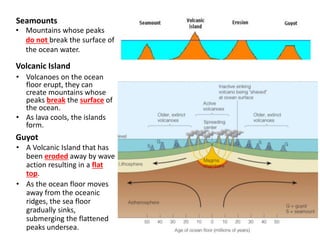
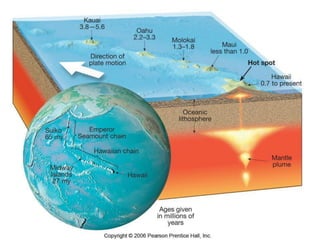
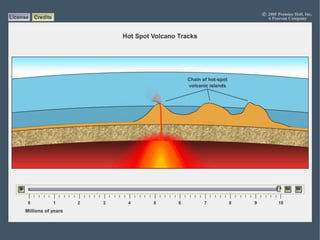
This document describes key features of the ocean floor topography, including continental shelves, slopes, and margins. It also discusses mid-ocean ridges, trenches, seamounts, and underwater volcanic features such as hydrothermal vents. The speed of sound in water and equations for calculating depth from sonar return times are provided.