The document discusses muscle physiology concepts including:
1) The all-or-none law which states that a muscle fiber generates full force when stimulated or none at all.
2) Muscle fatigue and oxygen debt which occur when more oxygen is used than taken in, leading to a build up of lactic acid and lower pH levels.
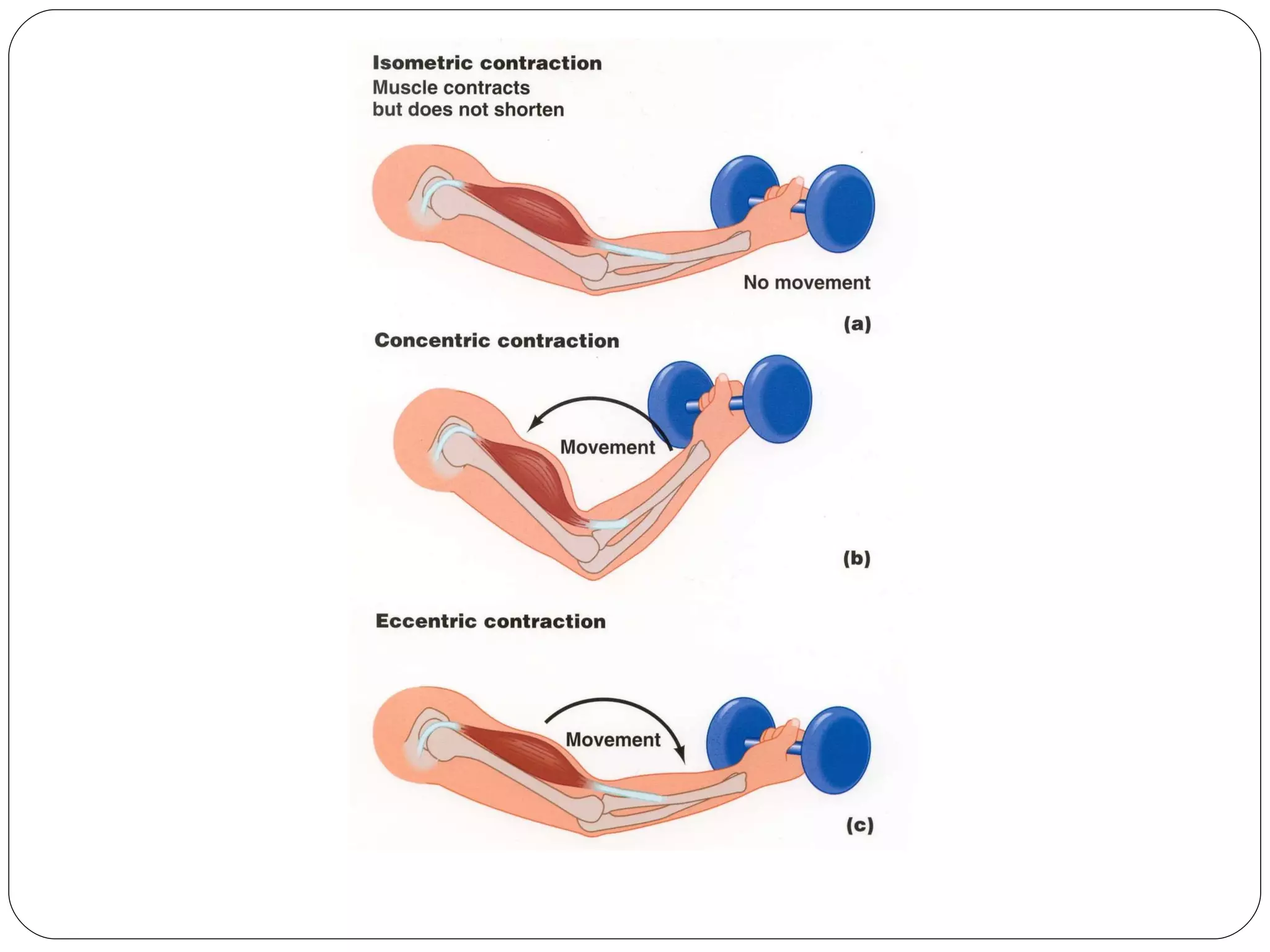
3) The three types of muscle contraction - isometric, concentric, and eccentric - and examples of activities for each type.
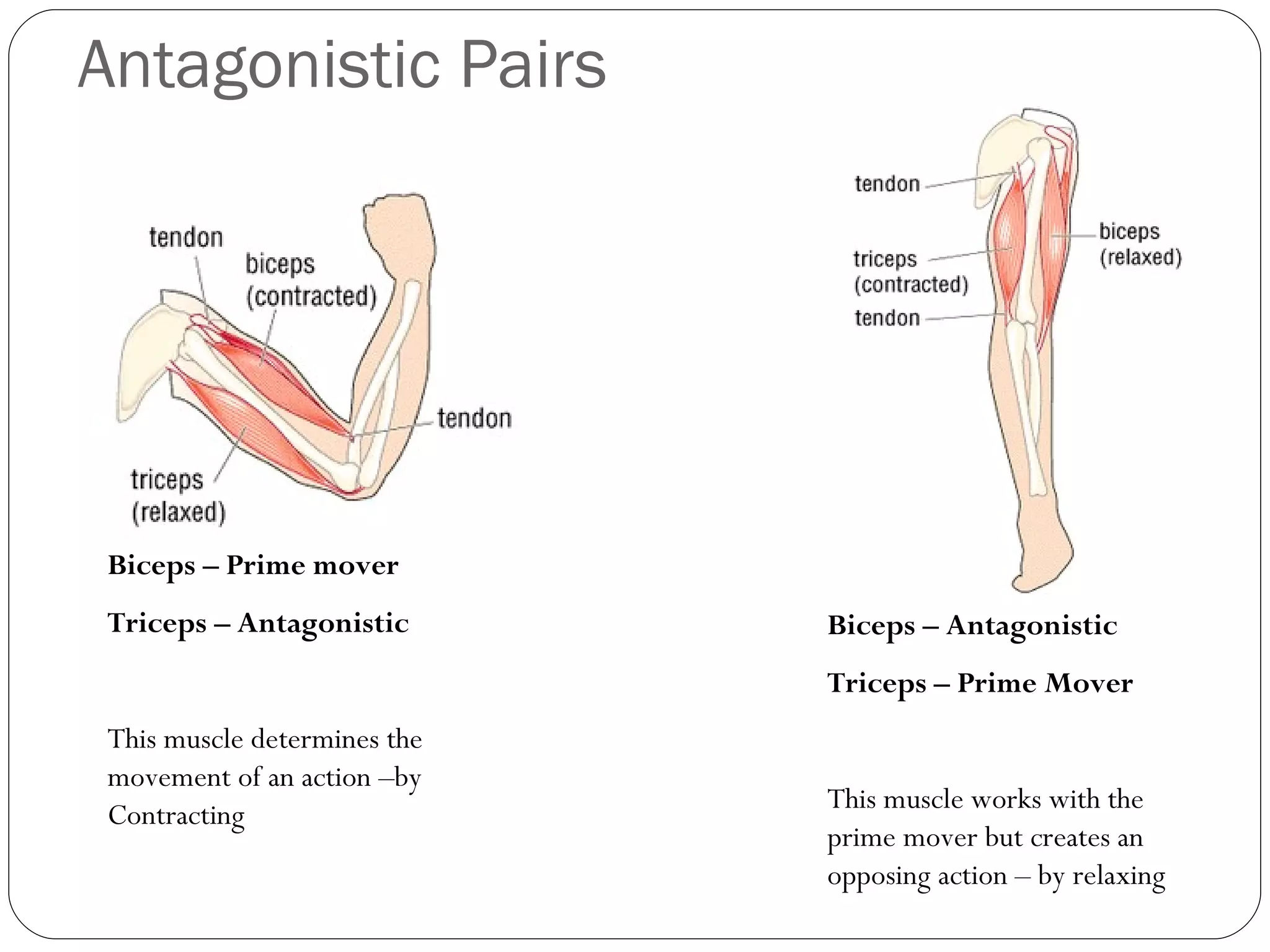
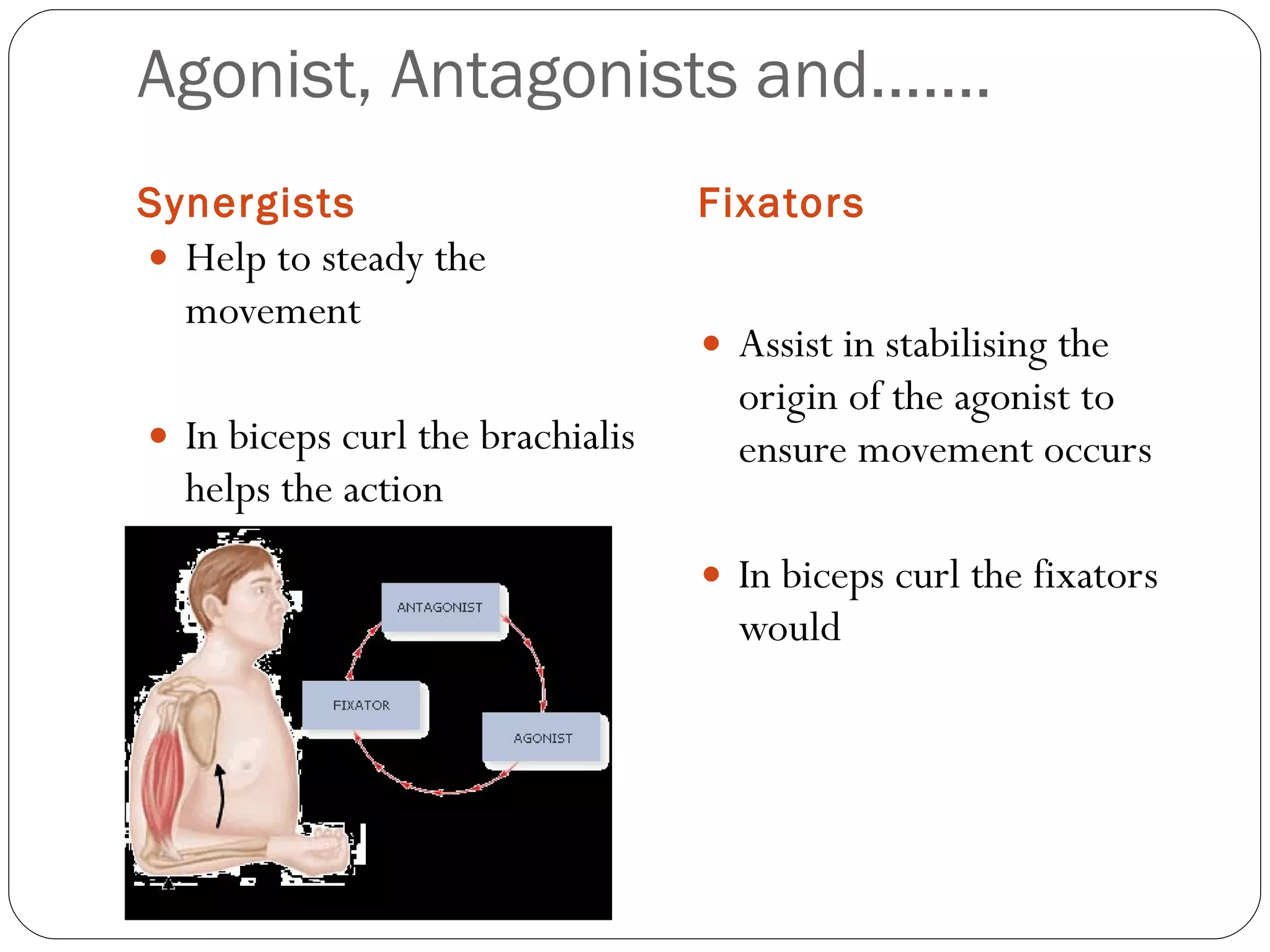
4) The roles of agonists, antagonists, synergists, and fixators in muscle movements and how they work to create or oppose actions.