1. Muscle contraction occurs through the interaction of actin and myosin fibers, generating tension while the muscle may shorten, lengthen, or remain the same length.
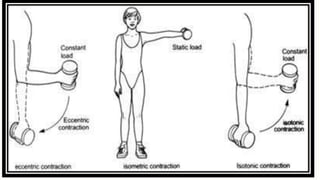
2. There are three main types of muscular contractions: concentric contractions which shorten the muscle, eccentric contractions which lengthen the muscle, and isometric contractions which maintain the same muscle length.
3. Additional contraction types include isotonic where tension remains constant during length changes, isokinetic where speed remains constant, and auxotonic which is a near isotonic contraction. Each contraction type serves a distinct functional role in movement.





![Eccentric Contraction
– During an eccentric contraction, the muscle elongates while under tension due to an
opposing force being greater than the force generated by the muscle.[3] Rather than
working to pull a joint in the direction of the muscle contraction, the muscle acts
to decelerate the joint at the end of a movement or otherwise control the repositioning
of a load.
– During an eccentric contraction of the biceps muscle, the elbow starts the movement
while bent and then straightens as the hand moves away from the shoulder. During an
eccentric contraction of the triceps muscle, the elbow starts the movement straight
and then bends as the hand moves towards the shoulder](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musclecontraction-200518085354/85/Muscle-Contraction-6-320.jpg)