Embed presentation
Downloaded 403 times
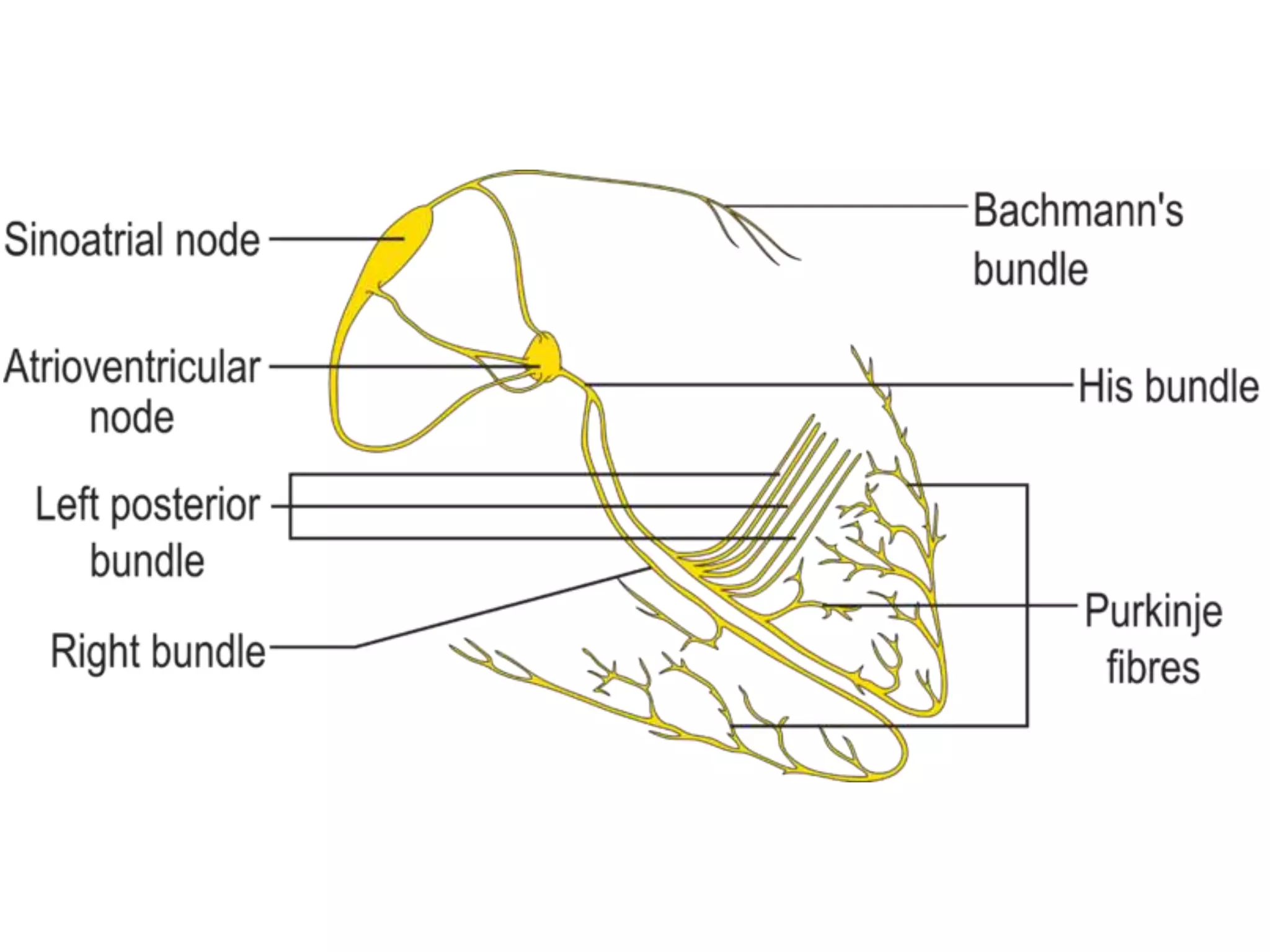
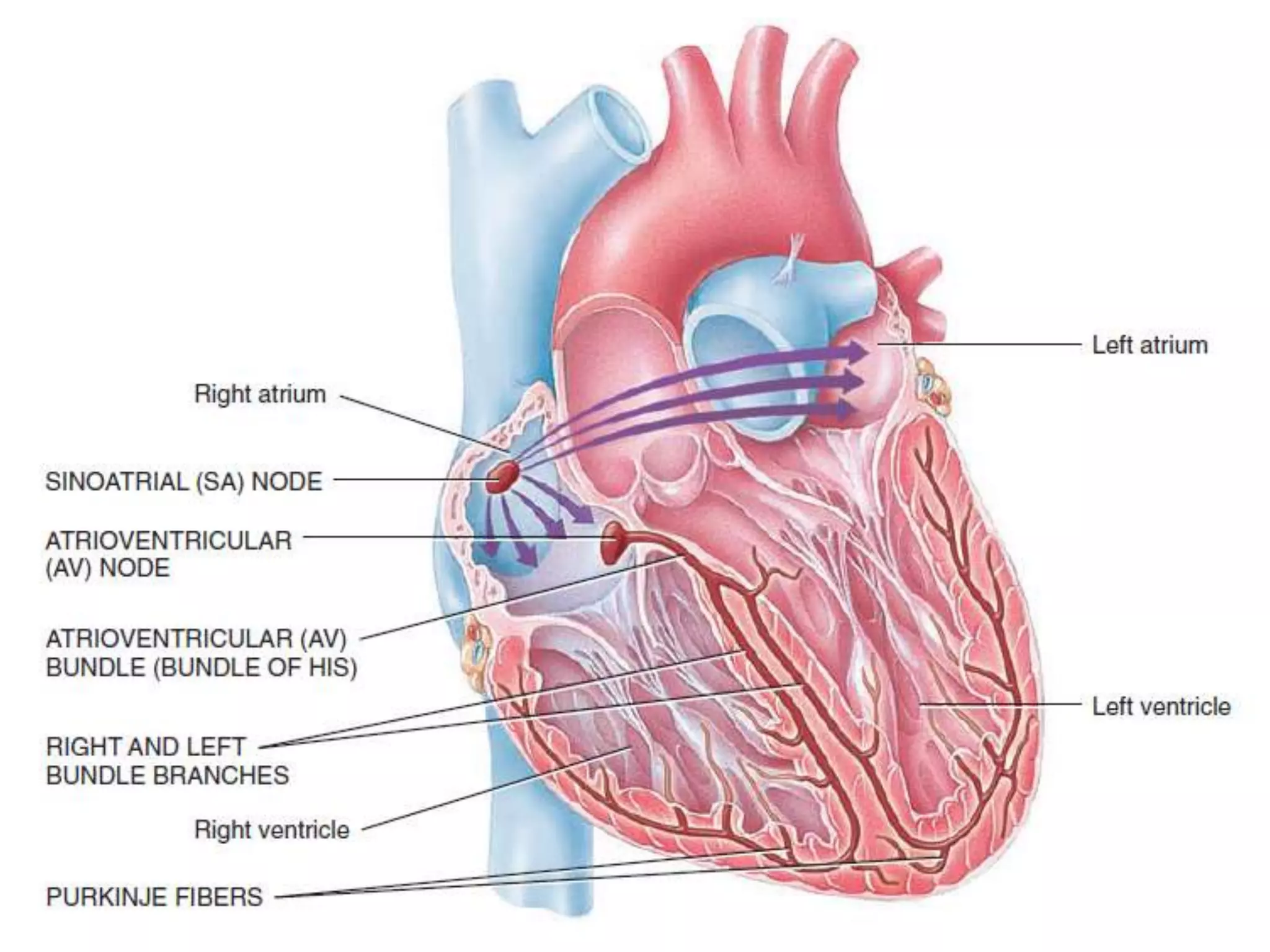
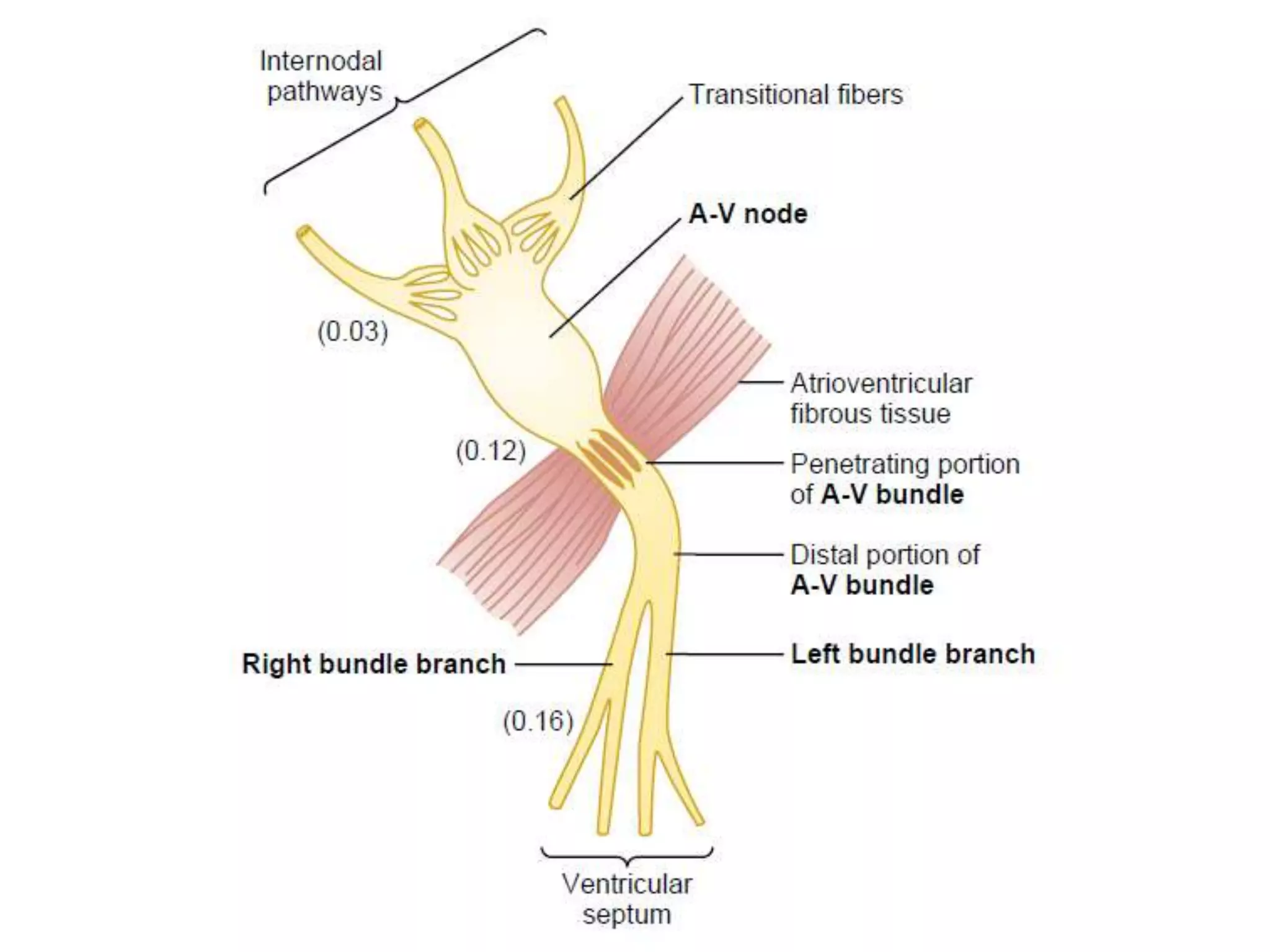
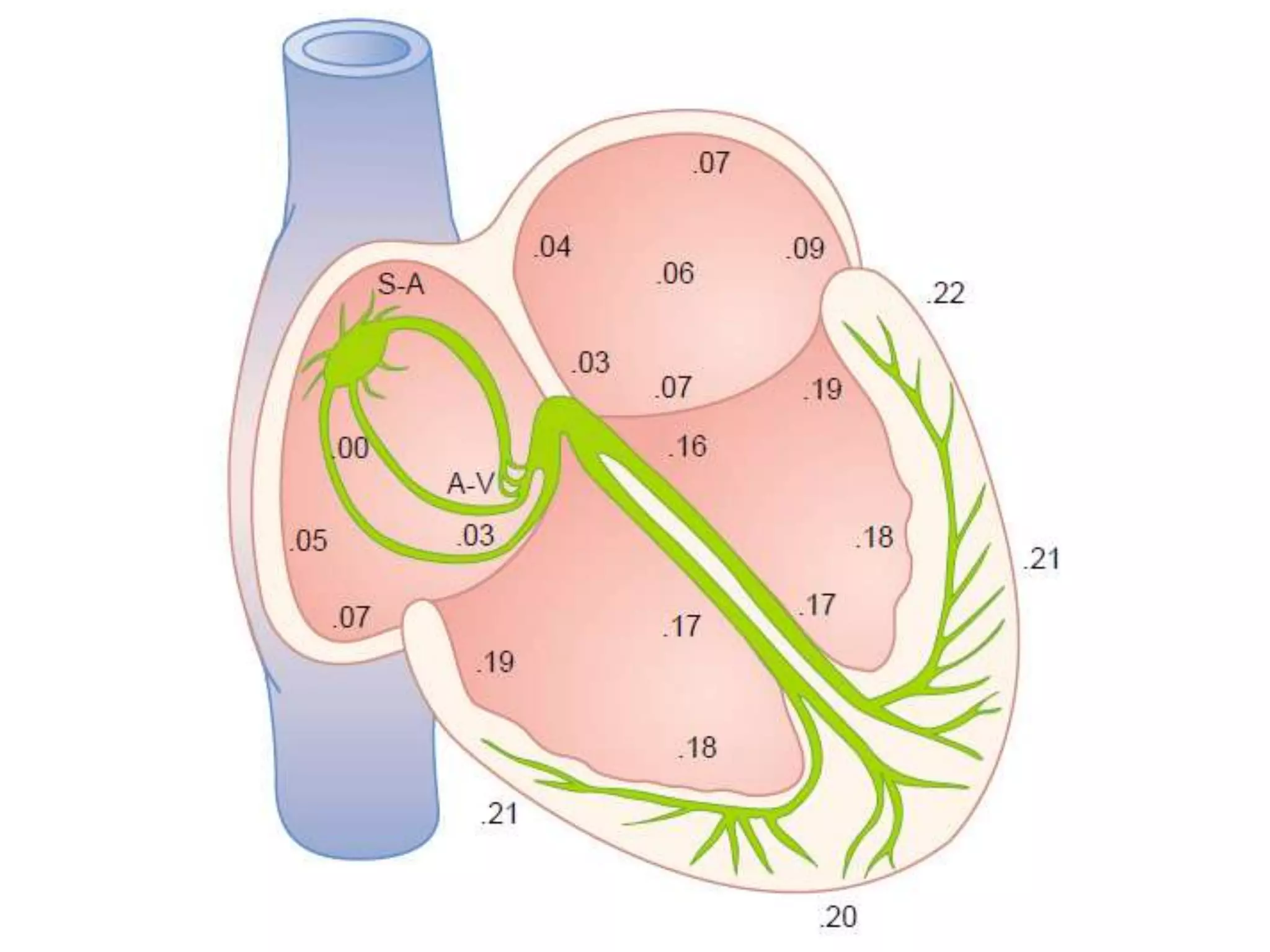
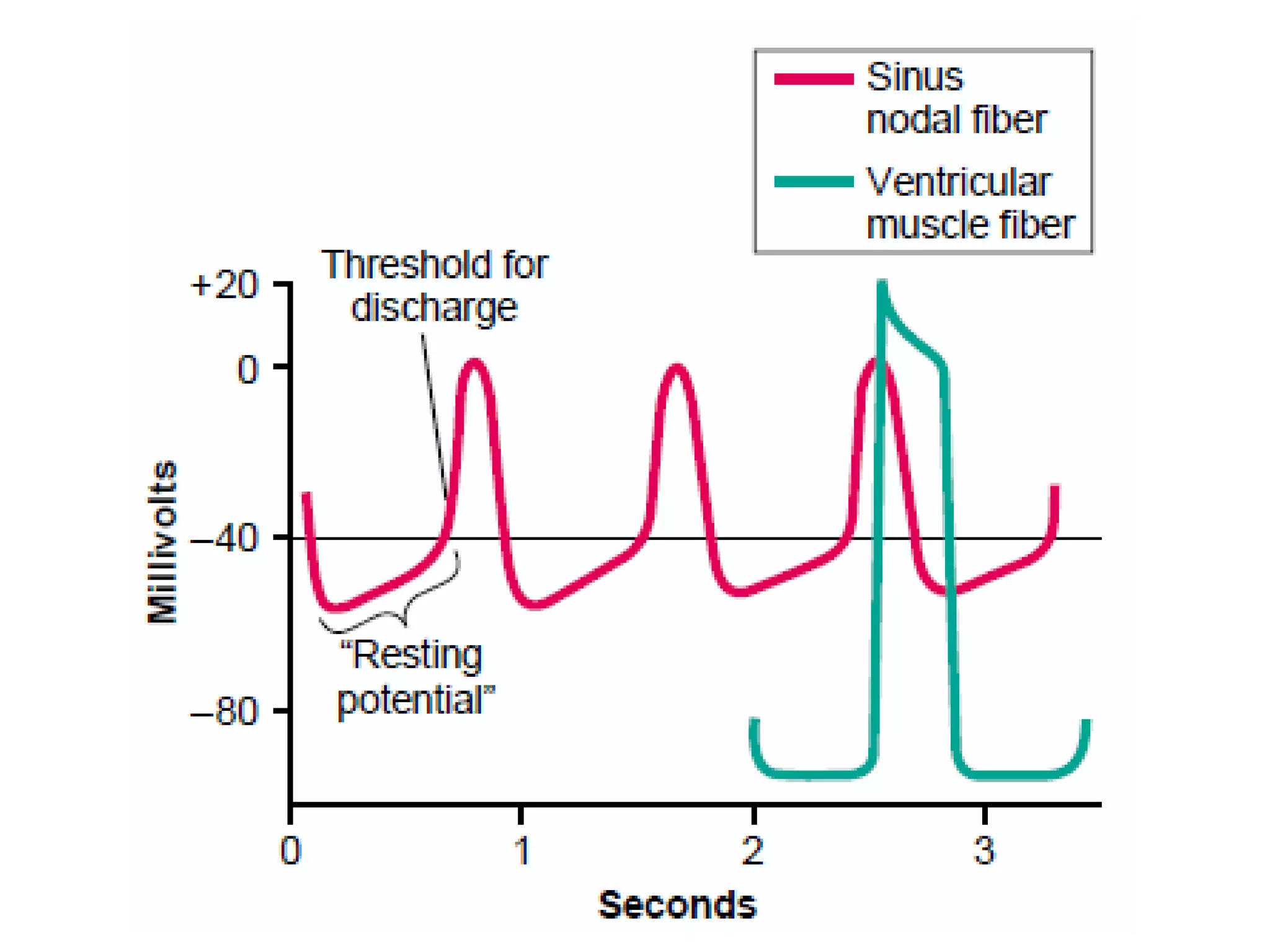
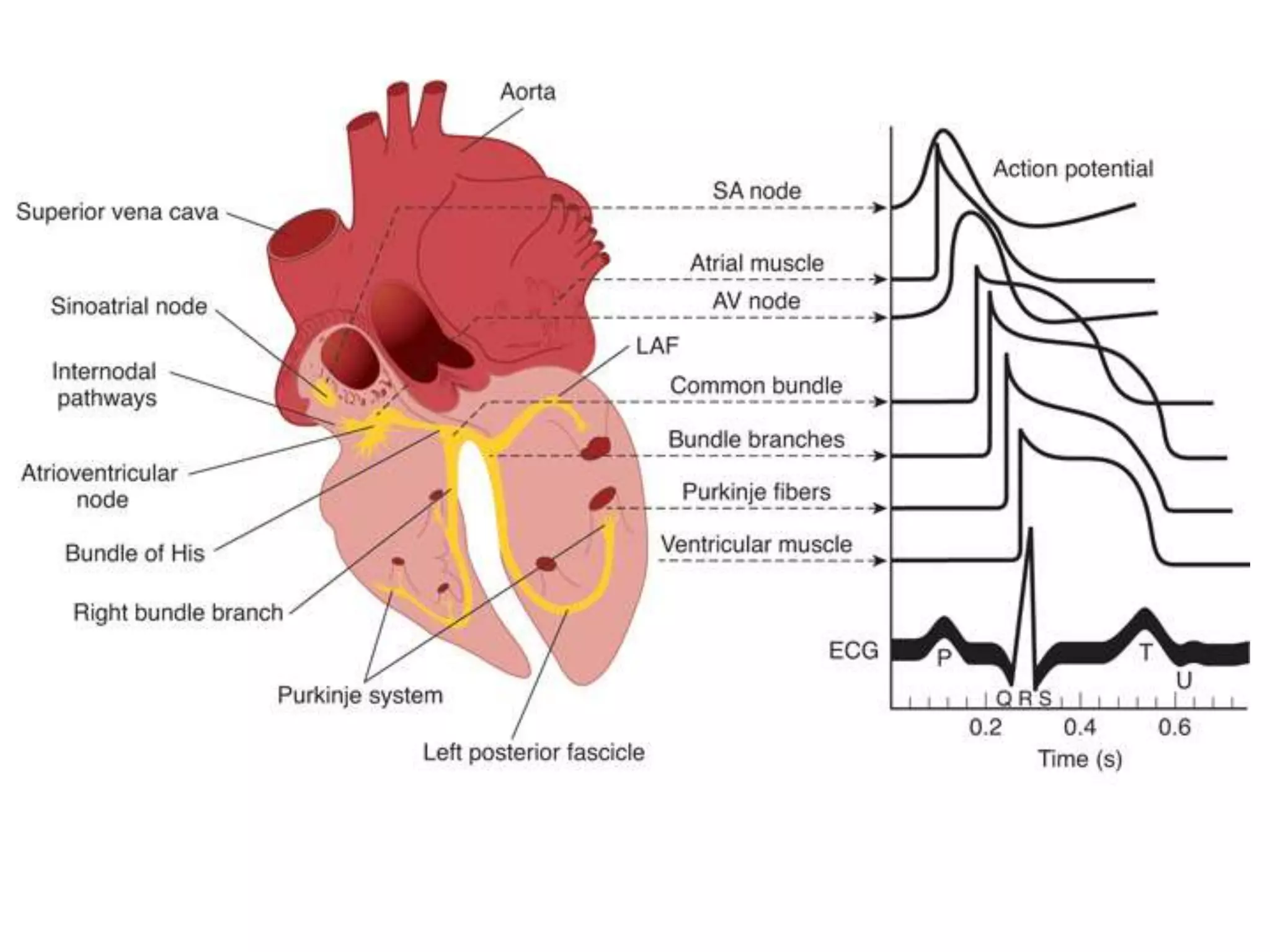
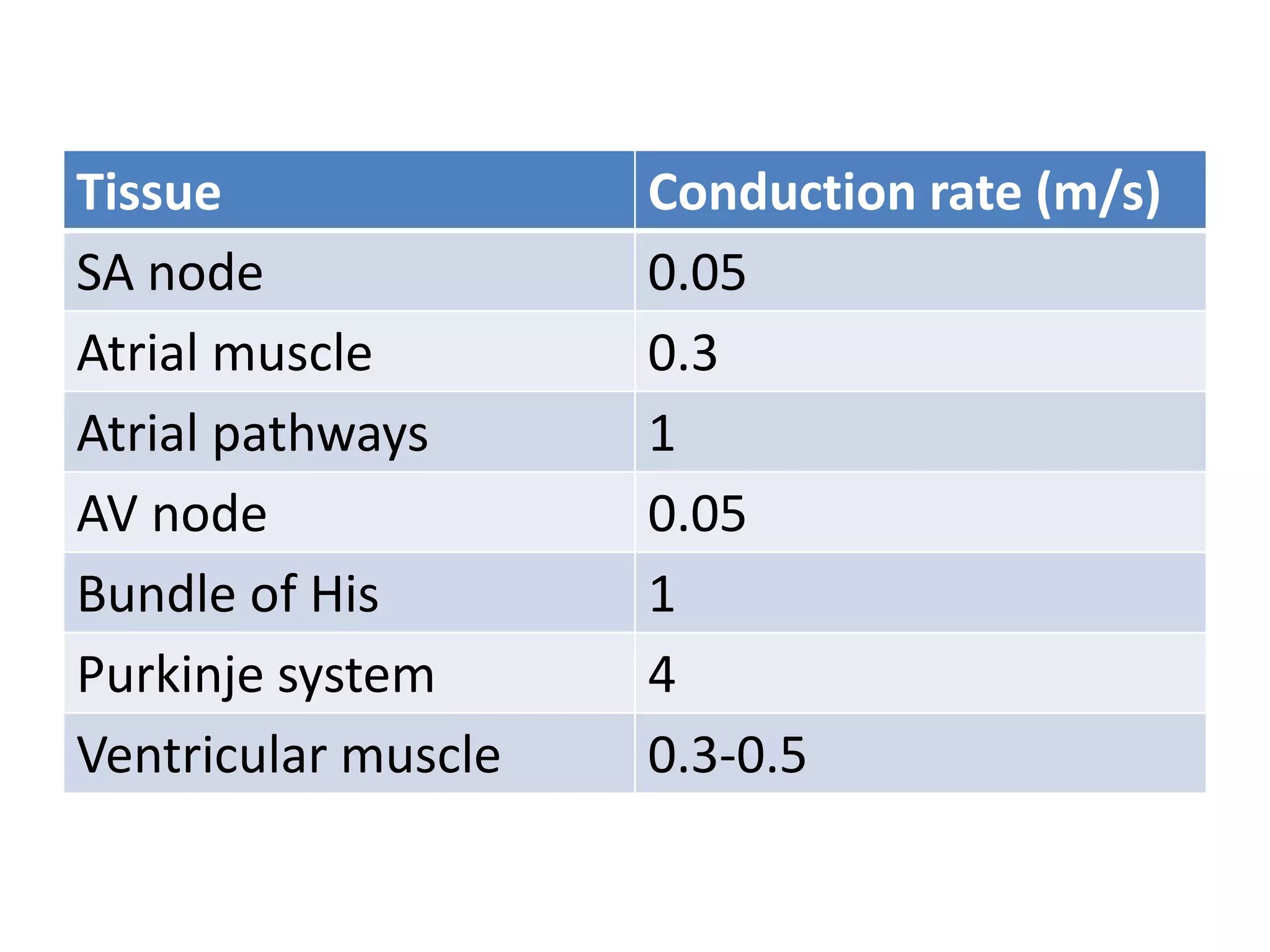
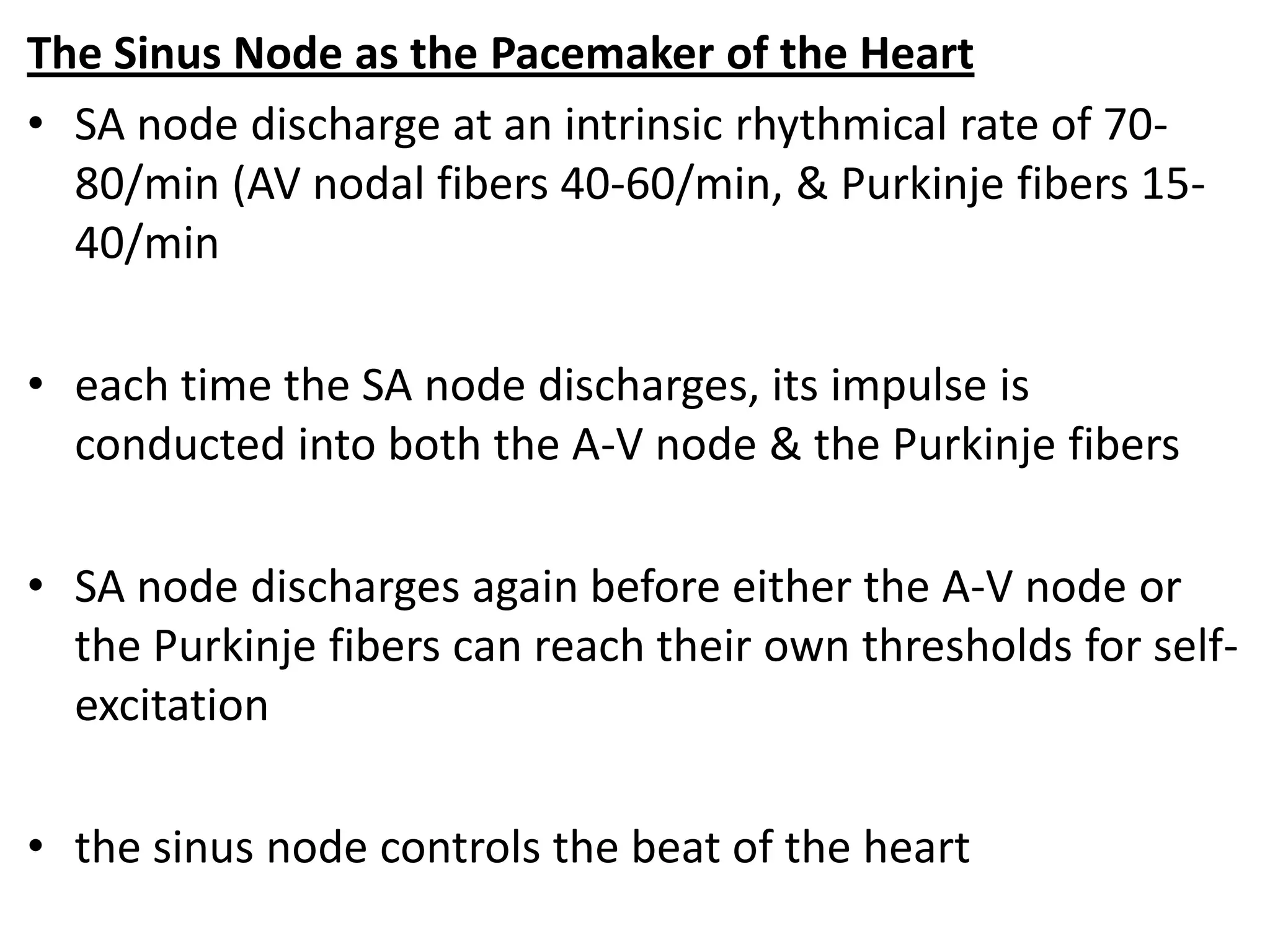
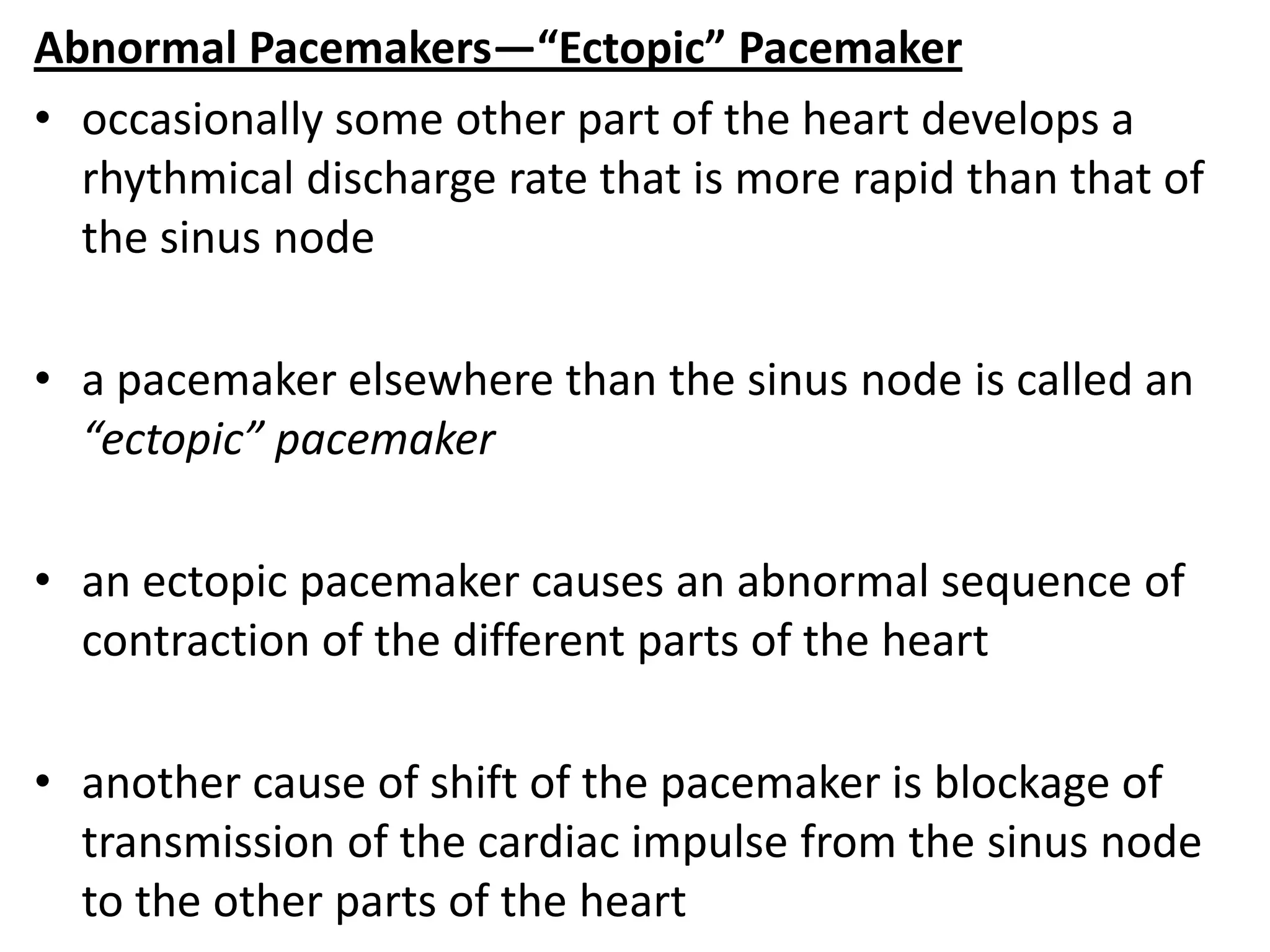



The document discusses the cardiac impulse and conduction system of the heart. It notes that the heartbeat originates from the sinus node, which acts as the natural pacemaker at a rate of 70-80 beats per minute. The impulse then spreads through the atrioventricular node and Purkinje fibers to contract the atria and ventricles in sequence. The conduction rates vary in different cardiac tissues. The sinus node controls the heartbeat under normal conditions, but abnormal pacemakers can develop elsewhere in rare cases. The conduction system ensures coordinated contraction of the heart chambers to effectively pump blood.













