This document summarizes muscle physiology, including:
1. The functions of muscle tissue such as movement, stability, and respiration.
2. The properties of muscle tissue including excitability, conductivity, contractility, extensibility, and elasticity.
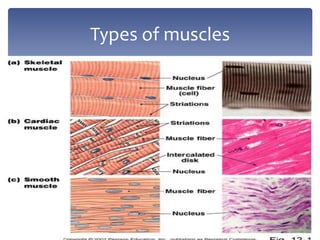
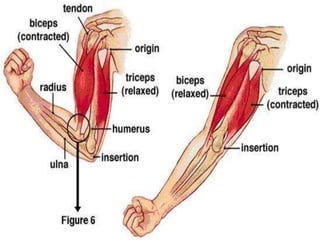
3. The types and classifications of muscles as well as the roles of agonist and antagonist muscles.
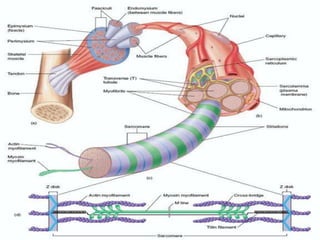
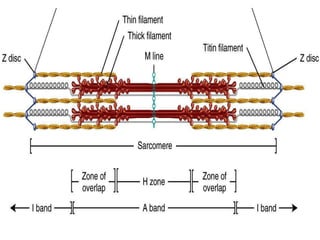
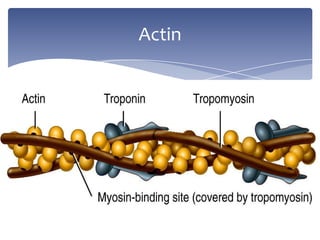
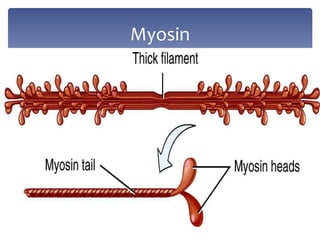
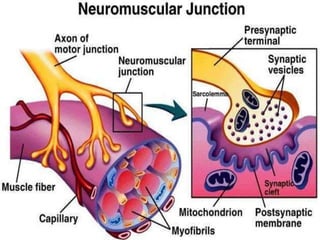
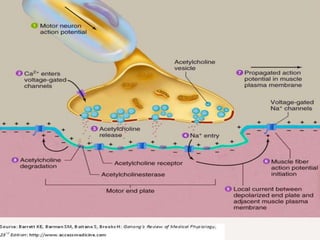
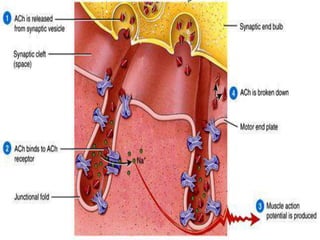
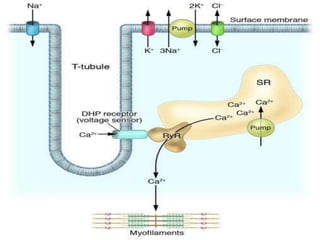
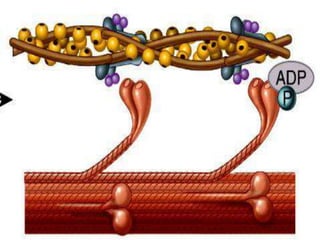
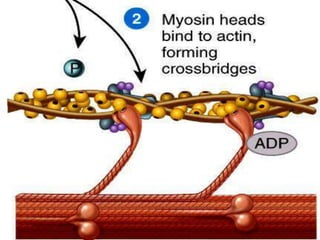
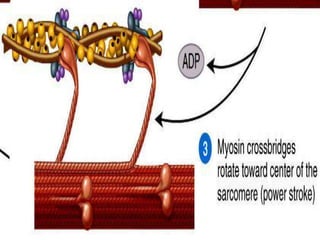
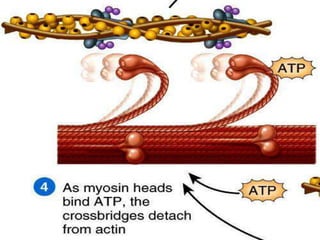
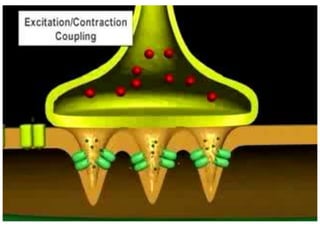
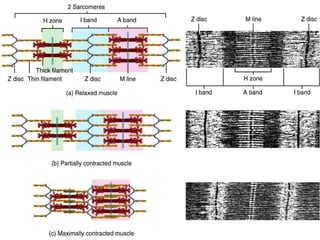
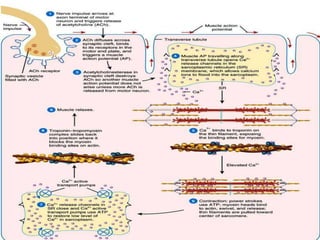
4. Key aspects of muscle anatomy and the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction.