Embed presentation
Downloaded 2,179 times







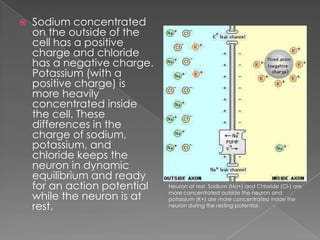



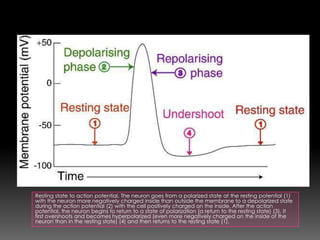


An action potential occurs when a neuron is stimulated enough to reach its threshold of excitation. This causes sodium channels to open, allowing sodium to rush into the neuron and depolarize it. The neuron then repolarizes as potassium leaves and the sodium-potassium pump restores the ion gradients. After an action potential, the neuron enters an absolute refractory period where it cannot fire again, followed by a relative refractory period where a stronger stimulus is needed to trigger another action potential. This process allows neurons to rapidly transmit signals down axons to synapse with other neurons.













