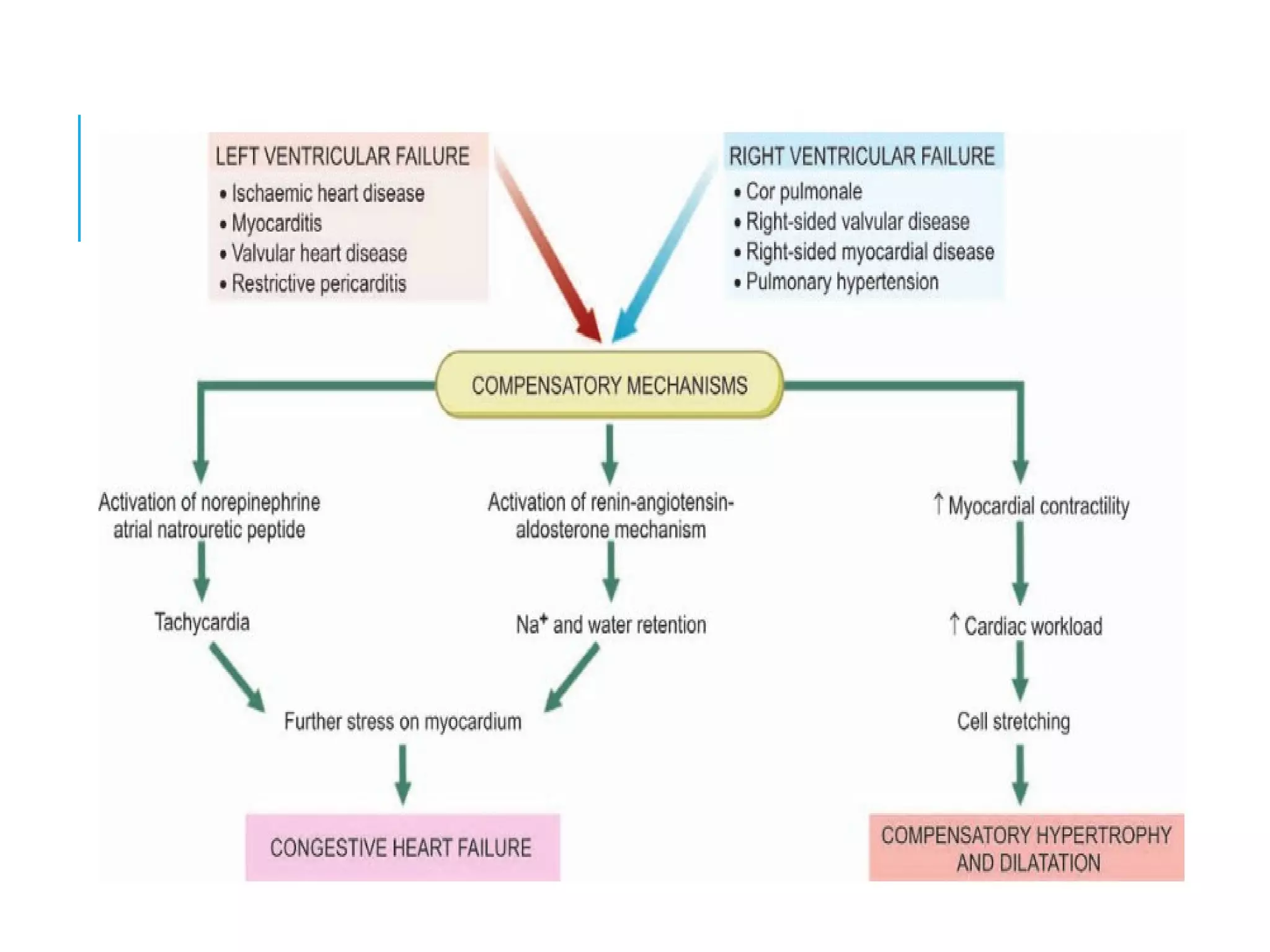
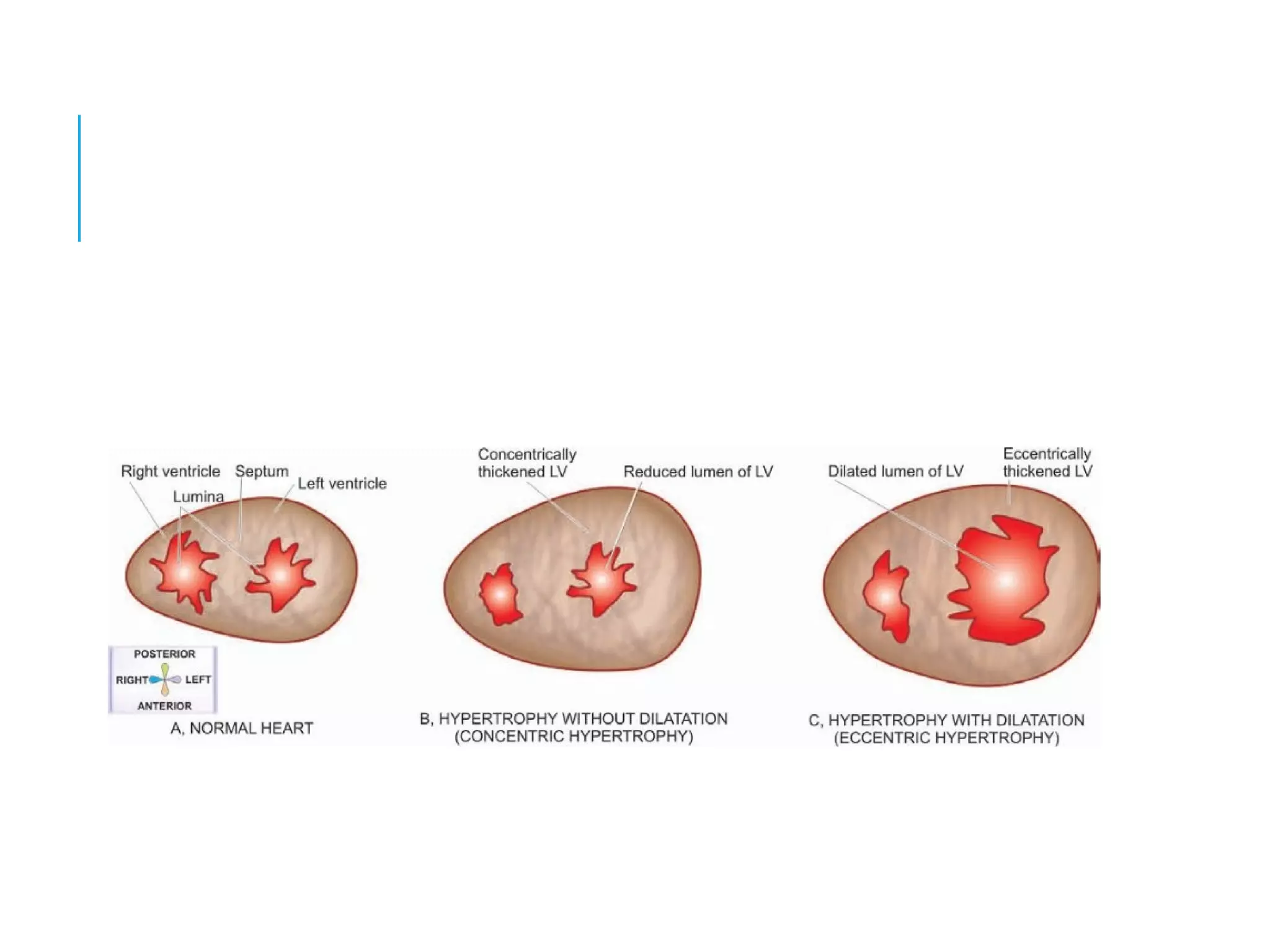
This document discusses heart failure, including its definition, causes, types, and compensatory mechanisms. Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. It can be caused by intrinsic pump failure, an increased workload on the heart, or impaired filling of the cardiac chambers. The types of heart failure include acute or chronic, right-sided or left-sided, and forward or backward failure. When the heart begins to fail, compensatory mechanisms such as cardiac hypertrophy, dilation, and increased heart rate attempt to maintain adequate blood circulation.