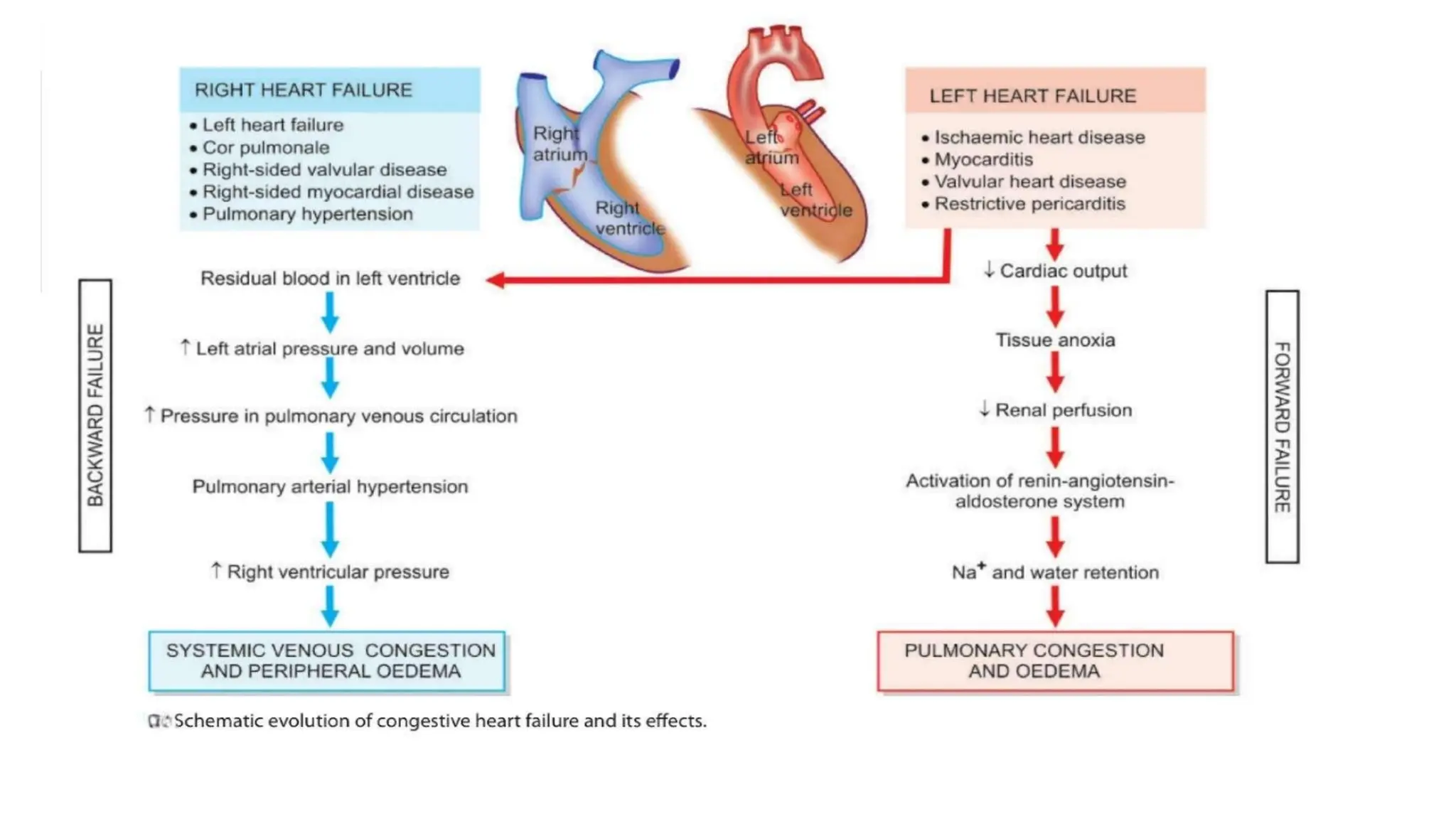
Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. It can develop suddenly (acute) or gradually (chronic). Common causes include intrinsic pump failure from conditions like ischemic heart disease or myocarditis, increased workload from issues like hypertension or valvular disease, and impaired filling of the heart. Heart failure can affect the left side, right side, or both. Left-sided failure causes pulmonary congestion and edema while right-sided failure leads to systemic venous congestion and edema. Chronic heart failure results from gradual progression of diseases like coronary artery disease or hypertension and presents with compensatory mechanisms trying to maintain cardiac output along with fluid accumulation.